Umi3 创建,配置环境,路由传参(代码示例)
目录
创建项目
配置环境
首先得有 node,并确保 node 版本是 10.13 或以上。(18版本可能会不适配)
$ node -v //查看版本
v16.20.2如果出现版本错误,可以使用nvm进行node版本管理https://blog.csdn.net/kkkys_kkk/article/details/135071784?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
推荐使用 yarn 管理 npm 依赖,并使用国内源(阿里用户使用内网源)。
# 国内源
$ npm i yarn tyarn -g
# 后面文档里的 yarn 换成 tyarn
$ tyarn -v
# 阿里内网源
$ tnpm i yarn @ali/yarn -g
# 后面文档里的 yarn 换成 ayarn
$ ayarn -v创建脚手架
?创建项目文件夹
$ mkdir myapp && cd myapp通过官方工具创建项目,
$ yarn create @umijs/umi-app
# 或 npx @umijs/create-umi-app
Copy: .editorconfig
Write: .gitignore
Copy: .prettierignore
Copy: .prettierrc
Write: .umirc.ts
Copy: mock/.gitkeep
Write: package.json
Copy: README.md
Copy: src/pages/index.less
Copy: src/pages/index.tsx
Copy: tsconfig.json
Copy: typings.d.ts安装依赖
$ yarn
或者
$ npm i启动项目
$ yarn start
或者
$ npm start在浏览器里打开 http://localhost:8000/,能看到以下界面
项目结构及其目录、
├── package.json 项目基本信息 、依赖信息
├── tsconfig.json ts的配置文件
├── typings.d.ts ts的类型声明文件(凡是以xxx.d.ts结尾的文件都是咱们的ts类型声明文件)
├── .umirc.ts 核心配置文件
├── .env 环境参数文件
├── mock mock数据
├── src
├── .umi 编译后自动生成的文件,不需要动
├── pages 业务组件文件夹(页面)
├── index.less
└── index.tsx 业务组件路由
umi的路由分为配置路由与约定路由
配置路由
在`pages`中新建一个页面
export default function Home() {
return (
<div>Home</div>
)
}在.umirc.ts中的routes配置项中新增路由配置
import { defineConfig } from 'umi';
export default defineConfig({
nodeModulesTransform: {
type: 'none',
},
routes: [
{
path: '/home',
component: '@/pages/Home'
},
{
path: '/course',
component: '@/pages/Course'
}
],
fastRefresh: {},
});umi官方推荐我们使用config方法
在项目文件下创建config文件夹,复制umirc.ts内容,同时删除umirc.ts文件,因为umirc.ts的权重高
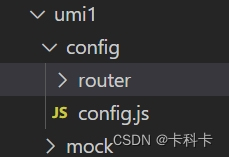
创建config文件,粘贴umirc.ts,将routes作为文件导入引入
import { defineConfig } from 'umi';
import routes from './router/index';
export default defineConfig({
nodeModulesTransform: {
type: 'none',
},
fastRefresh: {},
routes
});创建路由文件,声明路由,导出
const routes=[
{
path: '/home',
component: '@/pages/Home'
},
{
path: '/course',
component: '@/pages/Course'
}
],
export default routes嵌套路由
嵌套路由是通过`routes`属性来实现的
const routes=[
{
path:'/index',
component:'@/pages/Base/Base',
routes:[
{
path:'one',
component:'@/pages/One/One'
},
{path:'two',component:'@/pages/Two/Two'},
{path:'three',component:'@/pages/Three/Three'},
]
},
]然后在组件中通过props.children来渲染子路由
import React from 'react';
import styles from './index.less';
export default (props:any) => {
return (
<div className={ styles['container'] }>
{ props.children }
</div>
)
}编程式导航和声明式导航
声明式导航
import React from 'react';
import styles from './index.less';
import { NavLink } from 'umi';
// 通过接口定义props类型
interface Props {
children: React.ReactNode
}
// 在umijs中,Props类型的定义一般会用到React.FC类型,FunctionComponent类型
// 在React.FC类型中,Props类型是一个泛型,用来定义组件所接收的Props类型
const Course:React.FC<Props> = (props) => {
return (
<div className={ styles['container'] }>
{/* v5版本的路由是一样的 */}
<NavLink to="/course" activeClassName="active">去课程</NavLink>
Course <br />
{ props.children }
</div>
)
}
export default Course;编程式导航
编程式导航是通过: history.push 方法来实现的
import styles from './index.less';
import { NavLink, history } from 'umi';
export default function Home() {
return (
<div className={ styles['container'] }>
Pages Home
{/* 声明式导航 */}
<NavLink to="/course" activeClassName="active">去课程</NavLink>
{/* 编程式导航 */}
<button onClick={ () => history.push('/course') }>去课程</button>
</div>
)
}约定式路由
如果没有routes 配置 , Umi 会进入约定式路由模式, 然后分析src/pages 目录拿到路由配置。 比如以下文件结构:
└── pages
├── index.tsx
└── users.tsx会得到以下路由配置
[
{ exact: true, path: '/', component: '@/pages/index' },
{ exact: true, path: '/users', component: '@/pages/users' }
]路由传参
query传参(问号)
写入路径中
history.push('/list?id=1');
以对象形式
history.push({
pathname: '/list',
query: {
name: 'b',
},
});接收参数
使用history方法
import {history } from 'umi'
生成变量接收参数
const id =history.location.search.split('=')[1]?或者使用useLocation函数,返回表示当前 URL 的对象。您可以将其视为每当 URL 更改时返回新位置。
import { useLocation } from 'umi';
export default () => {
const location = useLocation();
return (
<div>
<ul>
<li>location: {location.pathname}</li>
</ul>
</div>
);
};params传参(动态传参)
路由表配置改为动态
{
path:'/anthor/:id',
component:'@/pages/detail/Id'
},
同样使用history方法
<button onClick={()=>{history.push('/anthor/1')}}>click me</button>将需要传递的参数直接写入路径当中
接收参数
useParams返回 URL 参数的键/值对的对象。使用它来访问当前路由
import { useParams } from 'umi';
export default () => {
const params = useParams();
return (
<div>
<ul>
<li>params: {JSON.stringify(params)}</li>
</ul>
</div>
);
};返回的是包含数据信息的对象
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!