Yolov8中conv和block添加模块代码
将其复制粘贴到YOLOv8的"ultralytics/nn/modules/conv.py"或者"ultralytics/nn/modules/block.py"目录下面。但是,最好新建一个文件在conv.py的同级目录下,通过建立文件导入其中类的形式。
一、创建新文件导入新模块
任何一个模块都可以像下面的图片一样直接建立一个文件粘贴复制进去。
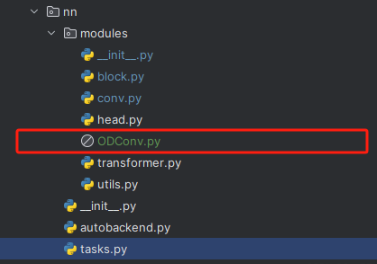
建立上面的文件之后,存在两种情况,一种是官方代码可以直接使用;另外一种需要进行一定的处理。下面分别讲解两种情况。
情况一:官方代码可以直接使用
直接修改"ultralytics/nn/modules/__init__.py"文件就可以了

情况二:官方代码不可以直接使用
官方代码的并不能直接使用,需要经过处理,文件"ultralytics/nn/modules/conv.py"修改
修改一:导入模块

修改二:将额外处理代码添置conv模块,将所需代码添加到conv.py的末尾处
class ODConv2d_yolo(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, groups=1, dilation=1):
super().__init__()
self.conv = Conv(in_channels, out_channels, k=1)
self.dcnv3 = ODConv2d(out_channels,out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, groups=groups,
dilation=dilation)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.gelu = nn.GELU()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.dcnv3(x)
x = self.gelu(self.bn(x))
return x修改三:配置头文件

修改四:重复情况一的步骤
修改"ultralytics/nn/modules/__init__.py"文件如下

二、Conv模块
已经把定义的模块放入Conv模块中了,还需要其他配置。当然不同的模块导入方式略有不同。
修改一:如下的文件"ultralytics/nn/tasks.py"
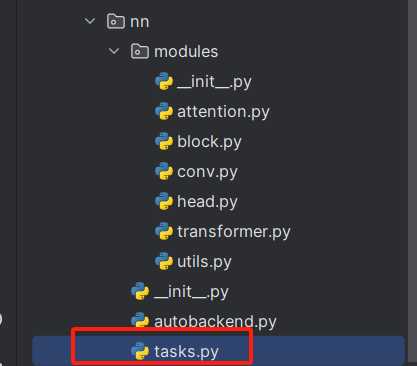
先把在上面"ultralytics/nn/modules/__init__.py"文件的函数头中导入的类,在下面的地方导入进"ultralytics/nn/tasks.py"文件中。
修改二:找到"parse_model"?然后进行翻滚很容易就找到了下面的部分,同时进行红框内部的修改。

修改三:到此定义的模块已经加入到模型中,已经可以修改yaml文件了。
三、C2f、Bottleneck模块
下面拿修改后的C2f、Bottleneck举例,这两个模块定义在该文件中"ultralytics/nn/modules/block.py",所以如果想添加修改后的C2f和Bottleneck(这俩一般配套使用),就需要在该文件中进行修改,修改步骤如下:
修改一:文件"ultralytics/nn/modules/block.py"

修改二:添加修改后的C2f和Bottleneck模块,这里起名为C2f_ODConv和Bottleneck_ODConv,将下面代码复制到文件"ultralytics/nn/modules/block.py"的末尾,?
class Bottleneck_ODConv(nn.Module):
"""Standard bottleneck."""
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, k=(3, 3), e=0.5):
"""Initializes a bottleneck module with given input/output channels, shortcut option, group, kernels, and
expansion.
"""
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, k[0], 1)
self.cv2 = ODConv2d_yolo(c_, c2, k[1], 1, groups=g)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
def forward(self, x):
"""'forward()' applies the YOLO FPN to input data."""
return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
class C2f_ODConv(nn.Module):
"""Faster Implementation of CSP Bottleneck with 2 convolutions."""
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5):
"""Initialize CSP bottleneck layer with two convolutions with arguments ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups,
expansion.
"""
super().__init__()
self.c = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, 2 * self.c, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv((2 + n) * self.c, c2, 1) # optional act=FReLU(c2)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(Bottleneck_ODConv(self.c, self.c, shortcut, g, k=((3, 3), (3, 3)), e=1.0) for _ in range(n))
def forward(self, x):
"""Forward pass through C2f layer."""
y = list(self.cv1(x).chunk(2, 1))
y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)
return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))
def forward_split(self, x):
"""Forward pass using split() instead of chunk()."""
y = list(self.cv1(x).split((self.c, self.c), 1))
y.extend(m(y[-1]) for m in self.m)
return self.cv2(torch.cat(y, 1))修改三:修改头文件

修改四:"ultralytics/nn/modules/__init__.py"

修改五:"ultralytics/nn/tasks.py"进行修改(其实和卷积模块的一模一样),

修改六:找到"parse_model"?然后进行翻滚很容易就找到了下面的部分,同时进行红框内部的修改。

修改七:到此模块已经添加到模型中了,可以修改yaml文件了。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.autograd
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, groups=1, reduction=0.0625, kernel_num=4, min_channel=16):
super(Attention, self).__init__()
attention_channel = max(int(in_planes * reduction), min_channel)
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.kernel_num = kernel_num
self.temperature = 1.0
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, attention_channel, 1, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(attention_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.channel_fc = nn.Conv2d(attention_channel, in_planes, 1, bias=True)
self.func_channel = self.get_channel_attention
if in_planes == groups and in_planes == out_planes: # depth-wise convolution
self.func_filter = self.skip
else:
self.filter_fc = nn.Conv2d(attention_channel, out_planes, 1, bias=True)
self.func_filter = self.get_filter_attention
if kernel_size == 1: # point-wise convolution
self.func_spatial = self.skip
else:
self.spatial_fc = nn.Conv2d(attention_channel, kernel_size * kernel_size, 1, bias=True)
self.func_spatial = self.get_spatial_attention
if kernel_num == 1:
self.func_kernel = self.skip
else:
self.kernel_fc = nn.Conv2d(attention_channel, kernel_num, 1, bias=True)
self.func_kernel = self.get_kernel_attention
self._initialize_weights()
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
if isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def update_temperature(self, temperature):
self.temperature = temperature
@staticmethod
def skip(_):
return 1.0
def get_channel_attention(self, x):
channel_attention = torch.sigmoid(self.channel_fc(x).view(x.size(0), -1, 1, 1) / self.temperature)
return channel_attention
def get_filter_attention(self, x):
filter_attention = torch.sigmoid(self.filter_fc(x).view(x.size(0), -1, 1, 1) / self.temperature)
return filter_attention
def get_spatial_attention(self, x):
spatial_attention = self.spatial_fc(x).view(x.size(0), 1, 1, 1, self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size)
spatial_attention = torch.sigmoid(spatial_attention / self.temperature)
return spatial_attention
def get_kernel_attention(self, x):
kernel_attention = self.kernel_fc(x).view(x.size(0), -1, 1, 1, 1, 1)
kernel_attention = F.softmax(kernel_attention / self.temperature, dim=1)
return kernel_attention
def forward(self, x):
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = self.fc(x)
# x = self.bn(x) # 在外面我提供了一个bn这里会报错
x = self.relu(x)
return self.func_channel(x), self.func_filter(x), self.func_spatial(x), self.func_kernel(x)
class ODConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1, groups=1,
reduction=0.0625, kernel_num=4):
super(ODConv2d, self).__init__()
kernel_size = kernel_size[0]
in_planes = in_planes
self.in_planes = in_planes
self.out_planes = out_planes
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.stride = stride
self.padding = padding
self.dilation = dilation
self.groups = groups
self.kernel_num = kernel_num
self.attention = Attention(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, groups=groups,
reduction=reduction, kernel_num=kernel_num)
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(kernel_num, out_planes, in_planes//groups, kernel_size, kernel_size),
requires_grad=True)
self._initialize_weights()
if self.kernel_size == 1 and self.kernel_num == 1:
self._forward_impl = self._forward_impl_pw1x
else:
self._forward_impl = self._forward_impl_common
def _initialize_weights(self):
for i in range(self.kernel_num):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(self.weight[i], mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
def update_temperature(self, temperature):
self.attention.update_temperature(temperature)
def _forward_impl_common(self, x):
# Multiplying channel attention (or filter attention) to weights and feature maps are equivalent,
# while we observe that when using the latter method the models will run faster with less gpu memory cost.
channel_attention, filter_attention, spatial_attention, kernel_attention = self.attention(x)
batch_size, in_planes, height, width = x.size()
x = x * channel_attention
x = x.reshape(1, -1, height, width)
aggregate_weight = spatial_attention * kernel_attention * self.weight.unsqueeze(dim=0)
aggregate_weight = torch.sum(aggregate_weight, dim=1).view(
[-1, self.in_planes // self.groups, self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size])
output = F.conv2d(x, weight=aggregate_weight, bias=None, stride=self.stride, padding=self.padding,
dilation=self.dilation, groups=self.groups * batch_size)
output = output.view(batch_size, self.out_planes, output.size(-2), output.size(-1))
output = output * filter_attention
return output
def _forward_impl_pw1x(self, x):
channel_attention, filter_attention, spatial_attention, kernel_attention = self.attention(x)
x = x * channel_attention
output = F.conv2d(x, weight=self.weight.squeeze(dim=0), bias=None, stride=self.stride, padding=self.padding,
dilation=self.dilation, groups=self.groups)
output = output * filter_attention
return output
def forward(self, x):
return self._forward_impl(x)最后:
如果你想要进一步了解更多的相关知识,可以关注下面公众号联系~会不定期发布相关设计内容包括但不限于如下内容:信号处理、通信仿真、算法设计、matlab appdesigner,gui设计、simulink仿真......希望能帮到你!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!