Python 简易图形界面库easygui 对话框大全(续)

目录
EasyGUI库
随着Python在数据科学、机器学习和Web开发等多个领域的广泛应用,图形用户界面(GUI)开发也变得越来越重要。对于初学者和快速原型设计来说,使用复杂的GUI库可能会让人感到望而生畏。幸运的是,Python的EasyGUI库提供了一个简单而直观的方式来创建基本的图形用户界面,无需深入了解复杂的GUI编程概念。
EasyGUI是一个用于非常简单的Python GUI编程的库。与Tkinter等更高级的库相比,EasyGUI通过提供一系列预构建的对话框和简单的函数调用来简化GUI开发过程。这使得开发者可以专注于应用程序的逻辑,而不是花费大量时间在界面设计上。
主要特点
- 简单易用:EasyGUI提供了直观的API,通常只需要一行代码就可以调用各种对话框,如消息框、选择框、文件选择框等。
- 跨平台兼容性:EasyGUI可以在Windows、macOS和Linux等多个操作系统上运行,确保您的应用程序具有广泛的可达性。
- 自定义选项:尽管EasyGUI强调的是简单性,但它仍然提供了一定程度的自定义能力,如更改对话框的标题、添加自定义按钮等。
- 集成Python标准库:EasyGUI基于Python的标准Tkinter库构建,这意味着您可以在需要时轻松集成更复杂的Tkinter功能。
使用场景
- 快速原型设计:当您需要快速测试一个想法或展示一个概念验证时,EasyGUI可以帮助您快速构建一个简单的界面。
- 小型项目和教育目的:对于不需要复杂界面的小型项目,或者在教学环境中向学生介绍GUI编程的概念,EasyGUI是一个理想的选择。
- 脚本和工具:对于需要简单用户输入的脚本或工具,使用EasyGUI可以提供一个比命令行更友好的交互方式。
对话框样式
10. 文件打开框 fileopenbox
fileopenbox(msg=None, title=None, default='*', filetypes=None, multiple=False)
? ? Displays an "open file" dialog box and returns the selected file as a string.
? ? The "default" argument specifies a filepath that (normally)?contains one or more wildcards.
? ? fileopenbox() will display only files that match the default filepath.
? ? If omitted, defaults to "\*" (all files in the current directory).
? ? :param str msg: the msg to be displayed.
? ? :param str title: the window title
? ? :param str default: filepath with wildcards
? ? :param object filetypes: filemasks that a user can choose, e.g. "\*.txt"
? ? :param bool multiple: If true, more than one file can be selected
? ? :return: the name of a file, or None if user chose to cancel
显示“打开文件”对话框,并将所选文件作为字符串返回。“default”参数指定(通常)包含一个或多个通配符的文件路径。例如,默认打开Excel文件如下:
import easygui as eg
eg.fileopenbox(msg=None, title=None, default='*.xls', filetypes=None, multiple=False)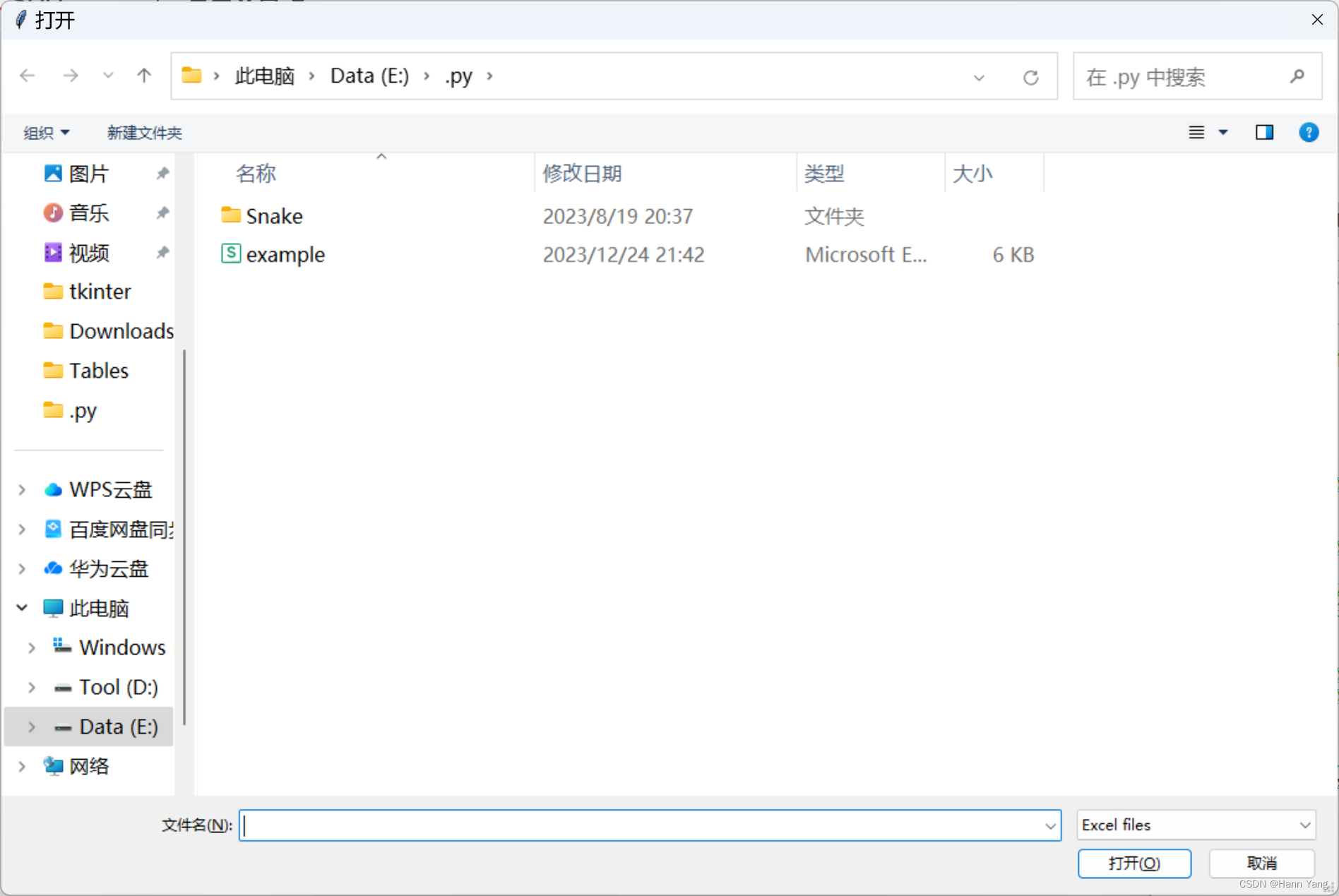
11. 文件保存框 filesavebox
filesavebox(msg=None, title=None, default='', filetypes=None)
? ? A file to get the name of a file to save.
? ? Returns the name of a file, or None if user chose to cancel.
? ? **About the "default" argument**
? ? The ``default`` argument specifies the path and "glob pattern" for file names. The "\*" value, for example, sets the open file dialog to the current working directory and showing all files.
? ? For another example, setting the ``default`` argument to ``"C:/myjunk/*.py"`` sets the open file dialog to the C:\myjunk folder and showing only files that have the .py file extension. This glob pattern at the end of the ``default`` argument is required: passing ``"C:/myjunk"`` would not set the open file dialog to the C:\myjunk folder, but rather to the C:\ folder and "myjunk" as the initial filename.
? ? Note that on Windows, ``fileopenbox()`` automatically changes the path separator to the Windows path separator (backslash).
? ? The "filetypes" argument works like the "filetypes" argument to fileopenbox.
? ? :param str msg: the msg to be displayed.
? ? :param str title: the window title
? ? :param str default: default filename to return
? ? :param object filetypes: filemasks that a user can choose, e.g. " \*.txt"
? ? :return: the name of a file, or None if user chose to cancel
用于获取要保存的文件的名称的文件。返回文件名,如果用户选择取消,则返回“无”。
import easygui as eg
eg.filesavebox(msg=None, title=None, default='*.xls', filetypes=None)
12. 目录打开框 diropenbox
diropenbox(msg=None, title=None, default=None)
? ? A dialog to get a directory name.
? ? Returns the name of a directory, or None if user chose to cancel.
? ? If the "default" argument specifies a directory name, and that?directory exists, then the dialog box will start with that directory.
? ? :param str msg: used in the window title on some platforms
? ? :param str title: the window title
? ? :param str default: starting directory when dialog opens
? ? :return: Normalized path selected by user
用于获取目录名的对话框。返回目录的名称,如果用户选择取消,则返回“无”。
如果“default”参数指定了一个目录名,并且该目录存在,则对话框将从该目录开始。
import easygui as eg
eg.diropenbox(msg=None, title=None, default=r'E:\Tables')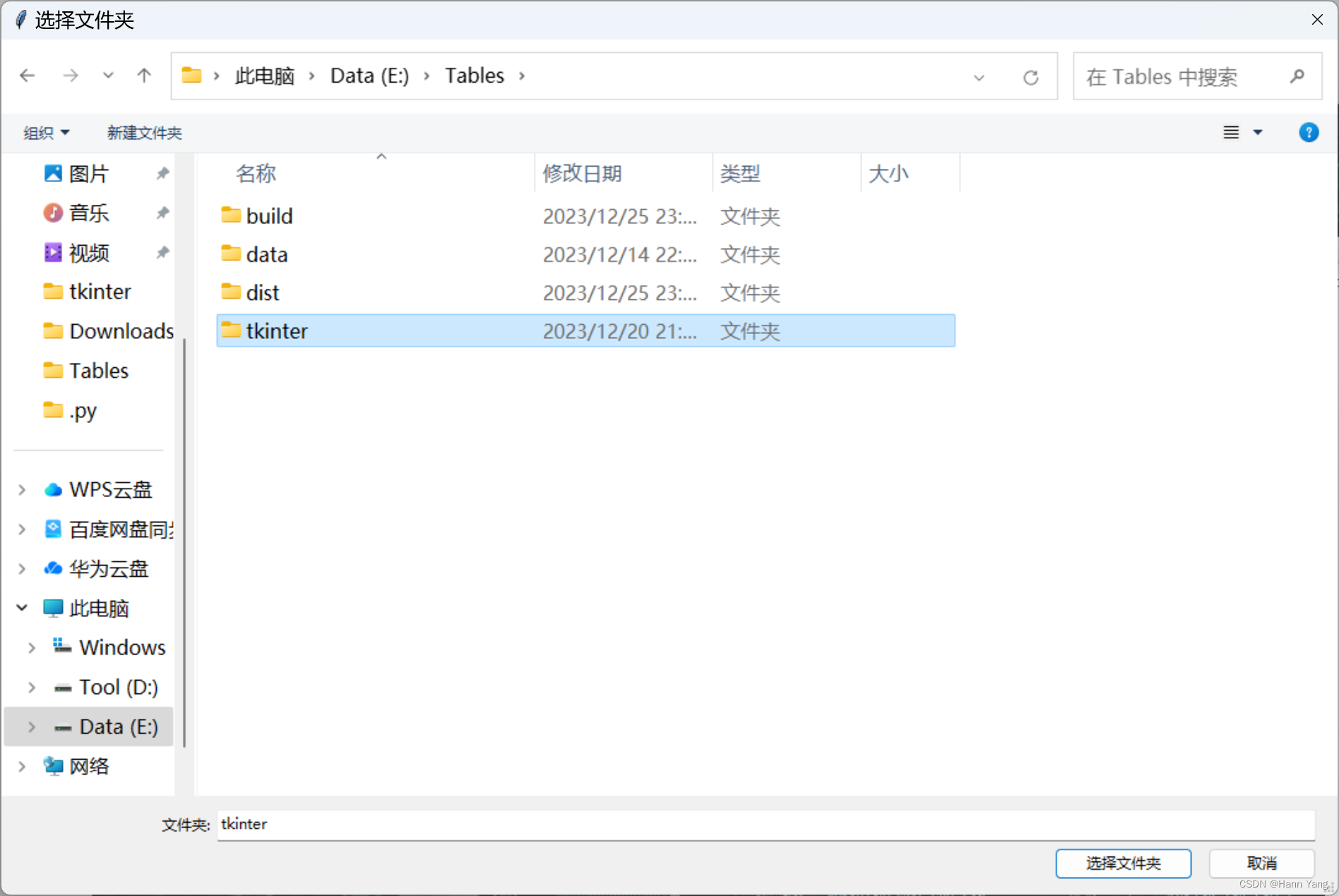
13. 索引对话框?indexbox
indexbox(msg='Shall I continue?', title=' ', choices=('Yes', 'No'), image=None, default_choice='Yes', cancel_choice='No')
? ? The ``indexbox()`` function displays a set of buttons, and returns the index of the selected button. For example, if you invoked index box with three choices (A, B, C), indexbox would return 0 if the user picked A, 1 if he picked B, and 2 if he picked C.
? ? :param str msg: the msg to be displayed
? ? :param str title: the window title
? ? :param list choices: a list or tuple of the choices to be displayed
? ? :param str image: Filename of image to display
? ? :param str default_choice: The choice you want highlighted when the gui appears
? ? :param str cancel_choice: If the user presses the 'X' close,?which button should be pressed
? ? :return: the index of the choice selected, starting from 0
显示一组按钮,并返回所选按钮的索引。例如,如果您使用三个选项(A、B、C)调用索引框,则如果用户选择A,indexbox将返回0,如果用户选择B,则返回1,如果选择C,则返回2。
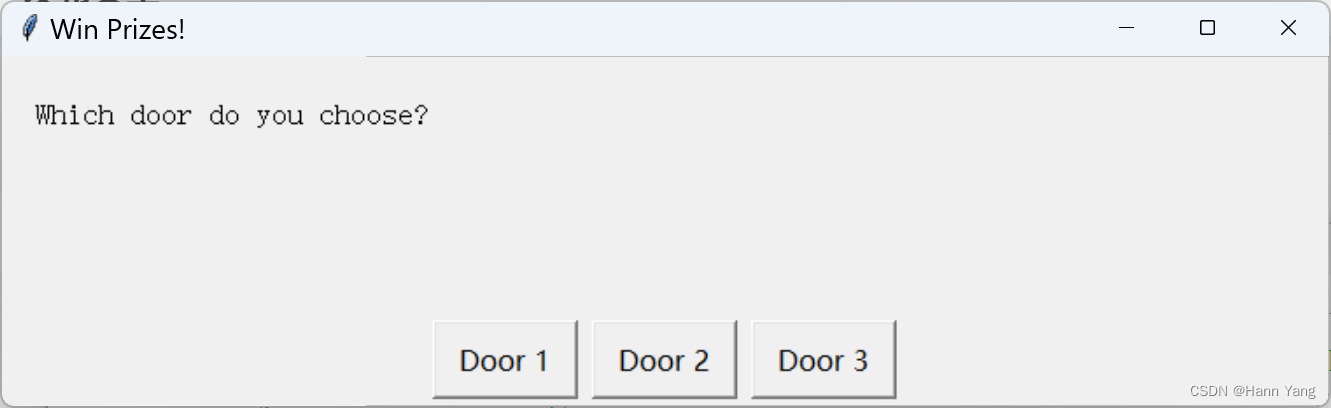
import easygui as eg
result = eg.indexbox('Which door do you choose?', 'Win Prizes!', choices=['Door 1', 'Door 2', 'Door 3'])
if result == 2:
eg.msgbox('You win a new car!')
else:
eg.msgbox('Better luck next time.')14. 例外报告框 exceptionbox
exceptionbox(msg=None, title=None)
? ? Display a box that gives information about an exception that has just been raised.
? ? The caller may optionally pass in a title for the window, or a msg to accompany the error information.
? ? Note that you do not need to (and cannot) pass an exception object as an argument. ?The latest exception will automatically be used.
? ? :param str msg: the msg to be displayed
? ? :param str title: the window title
? ? :return: None
报告错误或例外异常的信息,调用者可以选择性地传入窗口的标题或伴随错误信息的消息。
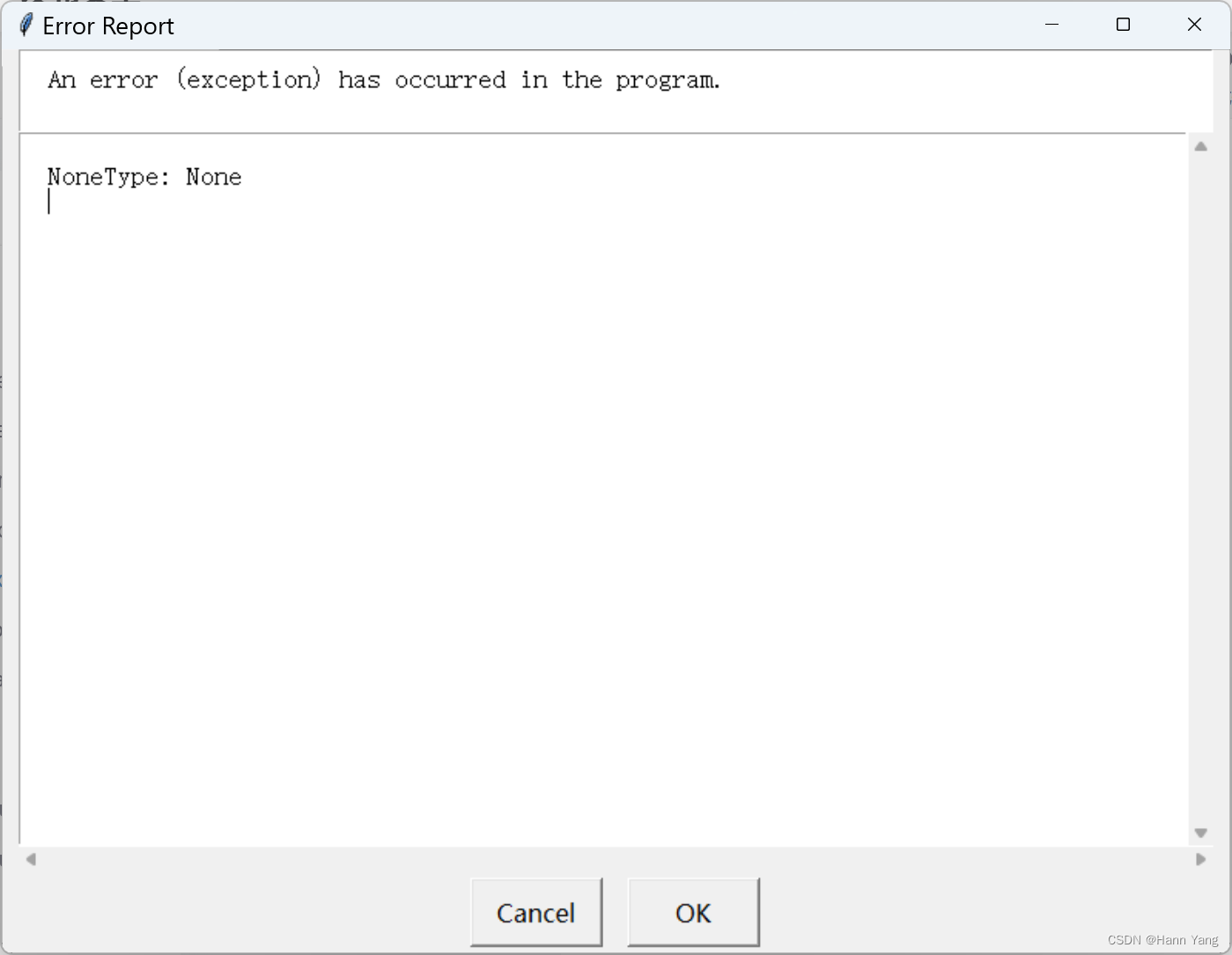
15. 代码文本框 codebox
codebox(msg='', title=' ', text='')
? ? Display some text in a monospaced font, with no line wrapping.
? ? This function is suitable for displaying code and text that is formatted using spaces.
? ? The text parameter should be a string, or a list or tuple of lines to be displayed in the textbox.
? ? :param str msg: the msg to be displayed
? ? :param str title: the window title
? ? :param str text: what to display in the textbox
与多行文本框textbox(msg='', title=' ', text='', codebox=False, callback=None, run=True)很相似,少了后面三个参数:

16. 密码输入框?passwordbox
passwordbox(msg='Enter your password.', title=' ', default='', image=None, root=None)
? ? Show a box in which a user can enter a password.
? ? The text is masked with asterisks, so the password is not displayed.
? ? :param str msg: the msg to be displayed.
? ? :param str title: the window title
? ? :param str default: value returned if user does not change it
? ? :return: the text that the user entered, or None if they cancel
? ? ? the operation.
显示一个框,用户可以在其中输入密码。文本用星号屏蔽,因此不会显示密码。
import easygui as eg
eg.passwordbox(msg='请输入密码:', title='密码输入框', default='456123', image=None, root=None)
17. 多重文本框 multenterbox
multenterbox(msg='Fill in values for the fields.', title=' ', fields=[], values=[], callback=None, run=True)
? ? Show screen with multiple data entry fields.
? ? If there are fewer values than names, the list of values is padded with empty strings until the number of values is the same as the number of names.
? ? If there are more values than names, the list of values is truncated so that there are as many values as names.
? ? Returns a list of the values of the fields,?or None if the user cancels the operation.
? ? :param str msg: the msg to be displayed.
? ? :param str title: the window title
? ? :param list fields: a list of fieldnames.
? ? :param list values: a list of field values
? ? :return: String
显示包含多个数据输入字段,即同一个对话框中有多个单行文本框。例如:
import easygui as eg
msg = "Enter your personal information"
title = "Credit Card Application"
fieldNames = ["Name","Address","City","State","ZipCode"]
fieldValues = [] # we start with blanks for the values
fieldValues = eg.multenterbox(msg,title, fieldNames)
# make sure that none of the fields was left blank
while 1:
if fieldValues is None: break
errmsg = ""
for i in range(len(fieldNames)):
if fieldValues[i].strip() == "":
errmsg += ('"%s" is a required field.\n\n' % fieldNames[i])
if errmsg == "":
break # no problems found
fieldValues = eg.multenterbox(errmsg, title, fieldNames, fieldValues)
print("Reply was: %s" % str(fieldValues))
18. 组合密码框 multpasswordbox
multpasswordbox(msg='Fill in values for the fields.', title=' ', fields=(), values=(), callback=None, run=True)
? ? Same interface as multenterbox. ?But in multpassword box,?the last of the fields is assumed to be a password, and?is masked with asterisks.
? ? :param str msg: the msg to be displayed.
? ? :param str title: the window title
? ? :param list fields: a list of fieldnames.
? ? :param list values: a list of field values
? ? :return: String
与多重文本框相似,但最后一个是密码框,输入会补星号代替,例如:
import easygui as eg
msg = "输入你的登录信息:"
title = "组合密码框"
fieldNames = ["账号:", "密码:"]
fieldValues = eg.multpasswordbox(msg,title, fieldNames)
# make sure that none of the fields was left blank
while 1:
if fieldValues[0].strip() == "":
errmsg = '账号不可为空!'
fieldValues = eg.multpasswordbox(errmsg, title, fieldNames, fieldValues)
elif fieldValues[1].strip() == "":
errmsg = '密码不可为空!'
fieldValues = eg.multpasswordbox(errmsg, title, fieldNames, fieldValues)
else:
break
print("账号、密码分别为: %s" % fieldValues)
19. 多项选择框 multchoicebox
multchoicebox(msg='Pick an item', title='', choices=None, preselect=0, callback=None, run=True)
? ? The ``multchoicebox()`` function provides a way for a user to select from a list of choices. The interface looks just like the ``choicebox()`` function's dialog box, but the user may select zero, one, or multiple choices.
? ? The choices are specified in a sequence (a tuple or a list).
? ? :param str msg: the msg to be displayed
? ? :param str title: the window title
? ? :param list choices: a list or tuple of the choices to be displayed
? ? :param preselect: Which item, if any are preselected when dialog appears
? ? :return: A list of strings of the selected choices or None if cancelled.
与单项选择框 choicebox() 相似,只有单项选择和多项选择的区别:
import easygui as eg
msg ="What is your favorite flavor?"
title = "Ice Cream Survey"
choices = ["Vanilla", "Chocolate", "Strawberry", "Rocky Road"]
choice = eg.multchoicebox(msg, title, choices)
总结
EasyGUI为Python开发者提供了一个快速创建基本图形用户界面的途径。它降低了GUI开发的门槛,使得即使是没有经验的开发者也能轻松构建出功能完善的界面。尽管它可能不适合复杂的应用程序或专业的软件开发项目,但对于快速原型设计、小型项目和教学目的来说,它是一个强大而高效的工具。通过利用EasyGUI的简单性和灵活性,开发者可以专注于解决问题,而不是纠结于复杂的界面细节。
完
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 发掘企业知识宝藏,开启专属知识付费新时代
- django邮件通知功能-
- 软考考试多少分通过?
- 2023年12月 Python(一级)真题解析#中国电子学会#全国青少年软件编程等级考试
- 数据库-期末考前复习-第6章-关系数据库理论
- 关于“Python”的核心知识点整理大全37
- 线性代数 --- 为什么LU分解中的下三角矩阵L的主对角线上都是1?
- 观测脚本 网关【1】
- 编程笔记 html5&css&js 044 CSS显示
- webstorm中直接运行ts(TypeScript)