2.常见的点云数据滤波的方法总结(C++)
? ? ? ?常见的点云数据处理有体素网格滤波、半径滤波、直通滤波、双边滤波器,统计滤波器,卷积滤波,条件滤波,高斯滤波等等。每种方法的原理和代码如下:
1.体素网格滤波
? ? ? ?体素网格滤波是对密度大的三维的点在保持原来形状的条件下进行稀疏,目的是为了减小后期点云数据处理的计算量。
? ? ? ?体素是三维的一个个小空间。在输入的点云数据上创建一个个3D体素网格(将体素网格视为一组空间中的微小3D小空间,类似处理二维图片的卷积核)。 然后,在每个体素中,所有存在的点将用它们的质心近似(质心一般用体素内所有坐标的均值表示)。 这种方法比用体素的中心值(坐标的中位数)接代替它们要慢一些,但它可以更准确地保持宏观的几何外形。
PCL代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
pcl::PCLPointCloud2::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PCLPointCloud2 ());
pcl::PCLPointCloud2::Ptr cloud_filtered (new pcl::PCLPointCloud2 ());
// 1.读取pcd文件(点云文件)
pcl::PCDReader reader;
reader.read ("table_scene_lms400.pcd", *cloud);
std::cerr << "PointCloud before filtering: " << cloud->width * cloud->height
<< " data points (" << pcl::getFieldsList (*cloud) << ").";
// 2.体素网格滤波的处理
pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PCLPointCloud2> sor;//创建体素滤波器对象
sor.setInputCloud (cloud);//设置输入的点云
sor.setLeafSize (0.01f, 0.01f, 0.01f);//设置体素大小为5cm*5cm*5cm
sor.filter (*cloud_filtered);//执行滤波
// 以下是打印输出
std::cerr << "PointCloud after filtering: " << cloud_filtered->width * cloud_filtered->height
<< " data points (" << pcl::getFieldsList (*cloud_filtered) << ").";
// 3.保存处理后的点云数据,保存为pcd文件
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
writer.write ("table_scene_lms400_downsampled.pcd", *cloud_filtered,
Eigen::Vector4f::Zero (), Eigen::Quaternionf::Identity (), false);
return (0);
}
2.半径滤波
? ? ? ?半径滤波通过计算每个点在设置半径范围内是否有足够的点云数量来进行滤波处理,可以去除稀疏的离群点,实际上,离群点对后续的点云拟合等处理只是起到噪点的作用,去除掉对后续处理有好处。
PCL代码如下:
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> //文件输入输出
#include <pcl/point_types.h> //点类型相关定义
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h> //点云可视化相关定义
#include <pcl/filters/radius_outlier_removal.h> //滤波相关
#include <pcl/common/common.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//1.读取点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PCDReader r;
r.read<pcl::PointXYZ>("data\\table_scene_lms400.pcd", *cloud);
cout << "there are " << cloud->points.size() << " points before filtering." << endl;
//2.半径滤波
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filter(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::RadiusOutlierRemoval<pcl::PointXYZ> sor; // 创建滤波器
sor.setInputCloud(cloud); //设置输入点云
sor.setRadiusSearch(0.02); //设置在radius半径的范围内找邻近点
sor.setMinNeighborsInRadius(15); //设置查询点的邻近点集数小于15的删除
sor.setNegative(false);
sor.filter(*cloud_filter); //执行条件滤波,存储结果到cloud_filte
//3.滤波结果保存
pcl::PCDWriter w;
w.writeASCII<pcl::PointXYZ>("data\\table_scene_lms400_Radius_filter.pcd", *cloud_filter);
cout << "there are " << cloud_filter->points.size() << " points after filtering." << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.直通滤波
? ? ? ?直通滤波的作用是过滤掉在指定维度方向上取值不在给定值域内的点,即通过限定点云三轴坐标的范围快速剔除掉不在需求范围内的点,适用于消除背景等操作。实现原理是:首先,指定一个维度以及该维度下的值域,其次,遍历点云中的每个点,判断该点在指定维度上的取值是否在值域内,删除取值不在值域内的点,最后,遍历结束,留下的点即构成滤波后的点云。
PCL代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h>
int
main (int argc, char** argv)
{ srand(time(0));
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filtered (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
//填入点云数据
cloud->width = 5;
cloud->height = 1;
cloud->points.resize (cloud->width * cloud->height);
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud->points.size (); ++i)
{
cloud->points[i].x = rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f)-0.5;
cloud->points[i].y = rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f)-0.5;
cloud->points[i].z = rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f)-0.5;
}
std::cerr << "Cloud before filtering: " << std::endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud->points.size (); ++i)
std::cerr << " " << cloud->points[i].x << " "
<< cloud->points[i].y << " "
<< cloud->points[i].z << std::endl;
// 创建滤波器对象
pcl::PassThrough<pcl::PointXYZ> pass;//创建滤波器对象
pass.setInputCloud (cloud); //设置待滤波的点云
pass.setFilterFieldName ("z"); //设置在Z轴方向上进行滤波
pass.setFilterLimits (0.0, 1.0); //设置滤波范围为0~1,在范围之外的点会被剪除
//pass.setFilterLimitsNegative (true);//是否反向过滤,默认为false
pass.filter (*cloud_filtered); //开始过滤
std::cerr << "Cloud after filtering: " << std::endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_filtered->points.size (); ++i)
std::cerr << " " << cloud_filtered->points[i].x << " "
<< cloud_filtered->points[i].y << " "
<< cloud_filtered->points[i].z << std::endl;
return (0);
}4.双边滤波
? ? ? ?双边滤波是一种非线性滤波器,它可以达到保持边缘、降噪平滑的效果。一定程度上拟补了高斯滤波的缺点。双边滤波对高斯噪声效果比较好。双边滤波从单纯的考虑空间域点的位置的高斯滤波上,又加上一个维度上的权重。在点云处理上,可以叫做为特征域,即当前点的法向量与临近点的法向量。
PCL代码如下:
#include <pcl/filters/fast_bilateral.h>
void Bilateral_Filter(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr cloud_input,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr &result,
float sigma_s, float sigma_R )
{
pcl::FastBilateralFilter<pcl::PointXYZI> filter;
filter.setInputCloud(cloud_input);
filter.setSigmaS(sigma_s); //0.5 空间邻域/窗口设置双边滤波器使用的高斯标准差
filter.setSigmaR(sigma_R); //0.0004 设置高斯的标准偏差,用于控制由于强度差,而使相邻像素的权重降低的程度
filter.applyFilter(*result);
}5.统计滤波
? ? ?理论看了以下博主点云统计滤波理解-CSDN博客的,觉得他写的详细明了,其实就是运用统计,通过所有的点云计算一个均值和方差,再通过均值和方差得到一个距离,然后通过这个距离剔除掉一些点。
? ? ? 统计滤波算法(Statistical Outlier Removal),基于点云数据中点到其邻域点距离的分布(有点类似最近邻算法)进行滤波,自我理解其实现步骤如下:
1、分别计算点云中各点k邻域距离的平均值,如假设一点云中有50个点,我设定条件为计算各点k邻域距离的平均值,则有50个平均值,各点k领域(以8领域为例)平均值计算方式如下图所示: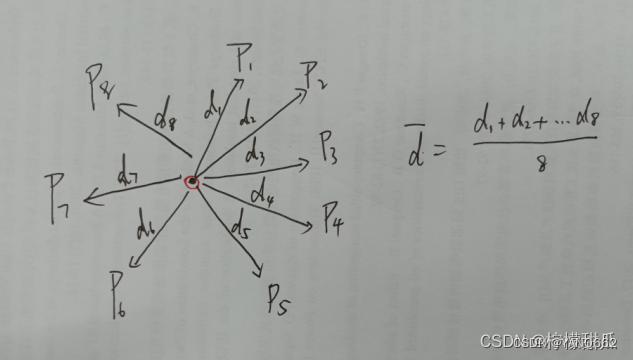
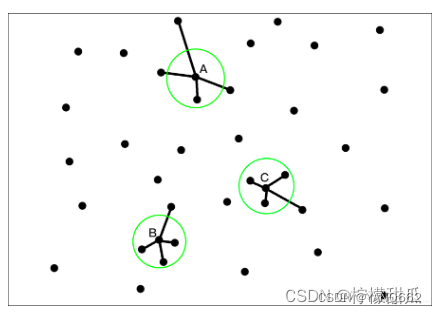
? ? ? ?作者认为,整个点云得到的50个平均值在分布上应该是呈高斯分布的,就可以得到均值μ和标准差σ,以μ+std_mul*σ为距离阈值,距离在区间之外的点便视为离群点,并可以在点云数据中去除,其中std_mul是用户指定的标准差倍数的阈值。如图2所示,圆形的半径为统计后根据设置所得距离阈值,则A点邻域有3个点被视为离群点,B、C点邻域各有1个点被视为离群点在滤波过程中被删除。
PCL代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/statistical_outlier_removal.h> //统计滤波器头文件
//统计滤波器
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
// 1.定义读取对象
pcl::PCDReader reader;
// 读取点云文件
reader.read<pcl::PointXYZ>(argv[1], *cloud);
std::cerr << "Cloud before filtering: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << *cloud << std::endl;
// 2.创建滤波器,对每个点分析的临近点的个数设置为50 ,并将标准差的倍数设置为1 这意味着如果一
//个点的距离超出了平均距离一个标准差以上,则该点被标记为离群点,并将它移除,存储起来
pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval<pcl::PointXYZ> sor; //创建滤波器对象
sor.setInputCloud(cloud); //设置待滤波的点云
sor.setMeanK(50); //设置在进行统计时考虑查询点临近点数
sor.setStddevMulThresh(1.0); //设置判断是否为离群点的阀值
sor.filter(*cloud_filtered); //存储
std::cerr << "Cloud after filtering: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << *cloud_filtered << std::endl;
//3.保存滤波后的点云
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
writer.write<pcl::PointXYZ>("after_filter.pcd", *cloud_filtered, false);
//sor.setNegative(true);
//sor.filter(*cloud_filtered);
//writer.write<pcl::PointXYZ>("1_outliers.pcd", *cloud_filtered, false);
return (0);
}
6.条件滤波
? ? ? ?条件滤波器通过设定滤波条件进行滤波,有点分段函数的味道,当点云在一定范围则留下,不在则舍弃,滤除离群点的一种滤波方法。
PCL代码如下:
//创建条件对象
pcl::ConditionAnd<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr range_cond (new pcl::ConditionAnd<pcl::PointXYZ> ());
/*
//比较条件符号说明:
//GT greater than
//EQ equal
//LT less than
//GE greater than or equal
//LE less than or equal
*/
//添加比较条件1:z>0.0
range_cond->addComparison (pcl::FieldComparison<pcl::PointXYZ>::ConstPtr (new pcl::FieldComparison<pcl::PointXYZ> ("z", pcl::ComparisonOps::GT, 0.0)));
//添加比较条件2:z<0.8
range_cond->addComparison (pcl::FieldComparison<pcl::PointXYZ>::ConstPtr (new pcl::FieldComparison<pcl::PointXYZ> ("z", pcl::ComparisonOps::LT, 0.8)));
pcl::ConditionalRemoval<pcl::PointXYZ> condrem; //创建条件滤波器对象
condrem.setCondition (range_cond); //设置条件
condrem.setInputCloud (cloud); //设置输入点云
condrem.setKeepOrganized(true); //设置保持点云的结构
condrem.filter (*cloud_filtered); //执行滤波
condrem.setKeepOrganized( )详解:
设置受保持点云的结构。
有序点云执行滤波之后,希望仍然能够保持有序性
若设置为true,再通过setuserFilterValue设置一个指定的值,被滤除的点将会被用户指定的值代替。
若设置为true,没有通过setuserFilterValue设置一个指定的值,则用nan填充被滤除的点
若设置为false,则直接将滤除的点删除,从而可能改变点云的组织结构
?
? ? ? ?通过以上滤波方法,我大概可以总结为:滤波的目的就是去除掉点云的噪点。其实就是以体素网格为主的降维或者以半径滤波为主的去除离散点。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 山西电力市场日前价格预测【2024-01-14】
- 【LeetCode刷题笔记】344.反转字符串
- AdaBoost提升方法
- 项目排期(100%用例) C卷 (Java&&Python&&C++&&Node.js&&C语言)
- ES6学习(四):promise的使用和实例方法
- WebService
- MFC 菜单
- C语言实用第三方库Melon开箱即用之多线程模型
- BootStrap 实现轮播图
- SpringMVC- ThreadLocal变量的注意点