第07章_面向对象编程(进阶)拓展练习(关键字:this,继承性和方法重写,关键字:super,多态性,Object类)
第07章_面向对象编程(进阶)拓展练习
01-关键字:this
1、Circle类
-
在com.atguigu.exercise1.bean包中定义一个圆形Circle类。
- 属性:私有化
- r:半径
- 构造方法:
- 无参构造方法
- 满参构造方法
- 成员方法:
- get/set方法
- showArea方法:打印圆形面积
- showPerimeter方法:打印圆形周长
- 属性:私有化
-
在com.atguigu.test01.test包中定义测试类TestCircle:创建Circle对象,并测试。
package com.atguigu.exercise1.bean;
public class Circle {
private double radius;
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public Circle() {
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public void showArea(){
System.out.println("半径为:" + radius + ",面积:" + 3.14 * radius * radius);
}
public void showPerimeter(){
System.out.println("半径为:" + radius + ",周长:" + 2 * 3.14 * radius);
}
}
public class Exercise1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Circle c1 = new Circle(1.2);
c1.showArea();
c1.showPerimeter();
}
}
2、MyDate类
-
在com.atguigu.test02.bean包中定义一个日期MyDate类。
- 属性:
- year:年
- month:月
- day:日
- 构造方法:
- 包含year、month、day三个参数的构造方法
- 成员方法:
- get/set方法
- void showDate方法:打印日期。“日期:xxx年xx月xx日”
- boolean isLeapYear()方法:判断当前日期是否是闰年
- 属性:
-
在com.atguigu.test02.test包中定义测试类:创建MyDate对象,并测试。
-
代码实现,效果如图所示:
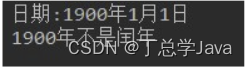
-
提示:
- 闰年:能被4整除且不能被100整除; 能被400整除
public class MyDate {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public MyDate() {
}
public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
public void showDate() {
System.out.println("日期:" + year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日");
}
public boolean isLeapYear() {
return year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0;
}
}
public class Exercise2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyDate my = new MyDate(2019,5,13);
my.showDate();
boolean flag = my.isLeapYear();
System.out.println(my.getYear()+ (flag?"是闰年":"不是闰年"));
}
}
3、Card类
-
在com.atguigu.test03.bean包中定义一个扑克Card类。
- 属性:
- 花色(String hua)
- 点数(String dian)
- 构造方法:
- 包含hua、dian两个参数的构造方法
- 成员方法:
- showCard方法:打印牌面信息。比如:红桃K
- 属性:
-
在com.atguigu.test03.test包中定义测试类,创建Card对象,调用showCard方法。
public class Card {
private String hua;
private String dian;
public Card(String hua, String dian) {
this.hua = hua;
this.dian = dian;
}
public Card() {
}
public String getHua() {
return hua;
}
public void setHua(String hua) {
this.hua = hua;
}
public String getDian() {
return dian;
}
public void setDian(String dian) {
this.dian = dian;
}
public void showCard() {
System.out.println(hua + dian);
}
}
public class Exercise3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Card c = new Card("黑桃", "A");
c.showCard();
}
}
02-继承性和方法重写
4、Person、Student、Teacher类
(1)声明父类:Person类
- 包含属性:姓名,年龄,性别,属性私有化,
- 包含get/set方法
- 包含getInfo()方法:例如:姓名:张三,年龄:23,性别:男
(2)声明子类:Student类,继承Person类
- 新增属性:score成绩,属性私有化,
- 包含get/set方法
- 重写getInfo()方法:例如:姓名:张三,年龄:23,性别:男,成绩:89
(3)声明子类:Teacher类,继承Person类
- 新增属性:salary薪资,属性私有化,
- 包含get/set方法
- 重写getInfo()方法:例如:姓名:张三,年龄:23,性别:男,薪资:10000
(4)在测试类的main方法中创建三个类的对象,并调用相应的方法测试
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private char gender;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public char getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(char gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getInfo() {
return "姓名:" + name + ",年龄:" + age + ",性别:" + gender;
}
}
public class Student extends Person {
private int score;
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String getInfo(){
//方式一:
// return "姓名:" + getName() + ",年龄:" + getAge() + ",性别:" + getGender() + ",成绩:" + score;
//方法二:
return super.getInfo() + ",成绩:" + score;
}
}
public class Teacher extends Person {
private double salary;
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String getInfo(){
return super.getInfo() + ",薪资:" + salary;
}
}
public class Exercise4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person();
p.setName("张三");
p.setAge(23);
p.setGender('男');
System.out.println(p.getInfo());
Student s = new Student();
s.setName("王浩");
s.setAge(20);
s.setGender('男');
s.setScore(90);
System.out.println(s.getInfo());
Teacher t = new Teacher();
t.setName("宋红康");
t.setAge(36);
t.setGender('男');
t.setSalary(50000);
System.out.println(t.getInfo());
}
}
5、DepositCard、CreditCard类
(1)声明一个银行储蓄卡DepositCard类
- 包含属性:账户,余额,属性私有化
- 包含get/set方法
- public void withdraw(double money):取款,
- 取款金额不能为负数,否则提示取款金额不能为负数
- 取款金额不能超过账户余额,否则提示余额不足
- public void save(double money):存款,
- 存款金额不能为负数,否则提示存款金额不能为负数
- public String getInfo() 可以返回账户和余额
(2)声明一个银行信用卡CreditCard类,继承储蓄卡类
-
增加属性:本月可透支总额度,本月已透支金额
-
重写public void withdraw(double money),可透支,
- 取款金额超过账户余额+本月还可透支额度,提示超过可透支额度
- 取款金额在账户余额范围内,不用透支
- 取款金额超过账户余额但在可透支范围内,需要透支
-
重写public void save(double money),
- 存款金额不能为负数,否则提示存款金额不能为负数
- 本次存款金额只够偿还部分已透支金额
- 本次存款金额除了偿还透支金额,还有剩余
(3)在测试类中,分别创建两种卡对象,测试
public class DepositCard {
private String id;
private double balance;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public void withdraw(double money){
if(money<0){
System.out.println("取款金额不能为负数");
return;
}
if(money>balance){
System.out.println("余额不足");
return;
}
balance -= money;
}
public void save(double money){
if(money<0){
System.out.println("存款金额不能为负数");
return;
}
balance += money;
}
public String getInfo(){
return "账号:" + id + ",余额:" + balance;
}
}
public class CreditCard extends DepositCard {
private double maxOverdraft;//当月最多可以透支额度
private double overdraft;//本月已透支额度
public double getMaxOverdraft() {
return maxOverdraft;
}
public void setMaxOverdraft(double maxOverdraft) {
this.maxOverdraft = maxOverdraft;
}
public double getOverdraft() {
return overdraft;
}
public void setOverdraft(double overdraft) {
this.overdraft = overdraft;
}
@Override
public void withdraw(double money) {
//超过可透支额度
if(money > getBalance() + maxOverdraft - overdraft){
System.out.println("超过可透支额度");
return;
}
//不用透支
if(money <= getBalance()){
super.withdraw(money);
return;
}
//需要透支
overdraft += money - getBalance();
setBalance(0);
}
@Override
public void save(double money) {
if(money < 0){
System.out.println("存款金额不能为负数");
return;
}
//偿还部分透支金额
if(money <= overdraft){
overdraft -= money;
return;
}
//偿还所有透支金额,还有剩余
setBalance(getBalance() + (money - overdraft));
overdraft = 0;
}
@Override
public String getInfo() {
return super.getInfo() +",本月可透支总额度:" + maxOverdraft + ",本月已透支:" + overdraft +",本月还可透支:" + (maxOverdraft - overdraft);
}
}
//测试1
public class Exercise5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DepositCard d = new DepositCard();
d.setId("11111");
d.setBalance(500);
System.out.println("初始情况:" + d.getInfo());
d.withdraw(200);
System.out.println("取款200后:" + d.getInfo());
d.save(100);
System.out.println("存款100后:" + d.getInfo());
d.save(-100);
System.out.println("存款-100后:" + d.getInfo());
d.withdraw(-100);
System.out.println("取款-100后:" + d.getInfo());
d.withdraw(500);
System.out.println("取款500后:" + d.getInfo());
}
}
//测试2
public class Exercise5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CreditCard d = new CreditCard();
d.setId("11111");
d.setBalance(500);
d.setMaxOverdraft(1000);
System.out.println("初始情况:" + d.getInfo());
d.withdraw(200);
System.out.println("取款200后:" + d.getInfo());
d.withdraw(800);
System.out.println("取款800后:" + d.getInfo());
d.withdraw(500);
System.out.println("取款500后:" + d.getInfo());
d.save(100);
System.out.println("存款100后:" + d.getInfo());
d.save(-100);
System.out.println("存款-100后:" + d.getInfo());
d.withdraw(-100);
System.out.println("取款-100后:" + d.getInfo());
d.withdraw(500);
System.out.println("取款500后:" + d.getInfo());
d.save(2000);
System.out.println("存款2000后:" + d.getInfo());
}
}
6、Employee、Programmer、Designer、Architect类
1、在包中声明员工类、程序员类、设计师类、架构师类
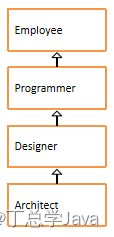
- 员工类属性:编号、姓名、年龄、手机号码
- 程序员类属性:编程语言
- 设计师类属性:奖金
- 架构师类属性:持有股票数量
? 要求:属性私有化,无参有参构造,get/set,getInfo方法(考虑重写)
2、在包中声明测试类Exercise6
创建各种类的对象,并测试
public class Employee {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String tel;
public Employee() {
super();
}
public Employee(int id, String name, int age, String tel) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.tel = tel;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getTel() {
return tel;
}
public void setTel(String tel) {
this.tel = tel;
}
public String getInfo(){
return "编号:" + name + ",姓名:" + name + ",年龄:" + age + ",电话:" + tel;
}
}
public class Programmer extends Employee{
private String language;
public Programmer() {
super();
}
public Programmer(int id, String name, int age, String tel, String language) {
super(id, name, age, tel);
this.language = language;
}
public String getLanguage() {
return language;
}
public void setLanguage(String language) {
this.language = language;
}
@Override
public String getInfo() {
return super.getInfo() + ",编程语言:" + language;
}
}
public class Designer extends Programmer {
private double bonus;
public Designer() {
super();
}
public Designer(int id, String name, int age, String tel, String language, double bonus) {
super(id, name, age, tel, language);
this.bonus = bonus;
}
public double getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
@Override
public String getInfo() {
return super.getInfo() + ",奖金:" + bonus;
}
}
public class Architect extends Designer {
private int stock;
public Architect() {
super();
}
public Architect(int id, String name, int age, String tel, String language, double bonus, int stock) {
super(id, name, age, tel, language, bonus);
this.stock = stock;
}
public int getStock() {
return stock;
}
public void setStock(int stock) {
this.stock = stock;
}
@Override
public String getInfo() {
return super.getInfo() + ",持有股票数:" + stock;
}
}
public class Exercise6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee emp = new Employee(1, "张三", 23, "10086");
Programmer pro = new Programmer(2, "李四", 24, "10010", "java");
Designer de = new Designer(3, "王五", 25, "114", "python", 2000);
Architect a = new Architect(4, "赵六", 26, "110", "java", 3000, 100);
System.out.println(emp.getInfo());
System.out.println(pro.getInfo());
System.out.println(de.getInfo());
System.out.println(a.getInfo());
}
}
7、判断输出结果
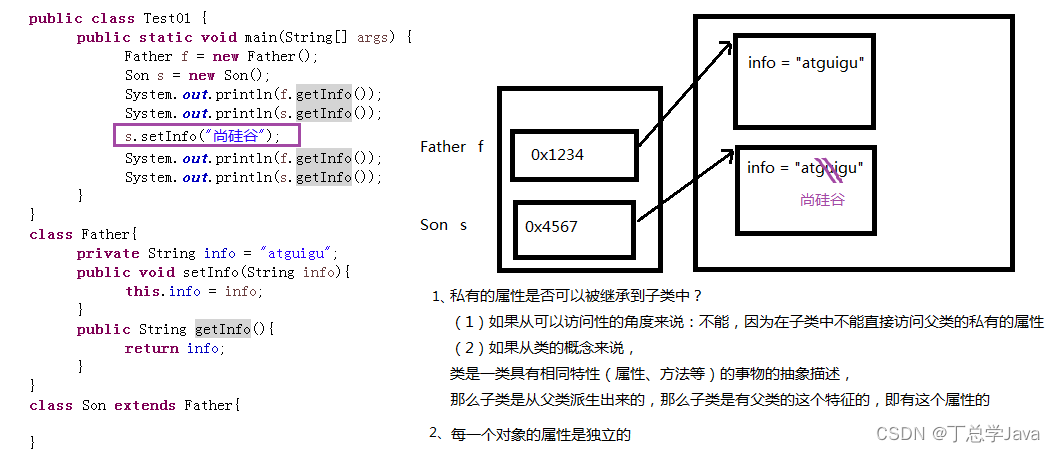
public class Exercise7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f = new Father();
Son s = new Son();
System.out.println(f.getInfo());
System.out.println(s.getInfo());
s.setInfo("尚硅谷");
System.out.println(f.getInfo());
System.out.println(s.getInfo());
}
}
class Father{
private String info = "atguigu";
public void setInfo(String info){
this.info = info;
}
public String getInfo(){
return info;
}
}
class Son extends Father{
}
/*
1、私有的属性是否可以被继承到子类中?
(1)如果从可以访问性的角度来说:不能,因为在子类中不能直接访问父类的私有的属性,但是可以通过get/set操作
(2)如果从类的概念来说,
类是一类具有相同特性(属性、方法等)的事物的抽象描述,
那么子类是从父类派生出来的,那么子类是有父类的这个特征的,即有这个属性的
2、每一个对象的非静态属性是独立的,其中一个对象修改和另一个对象是无关的
*/
03-关键字:super
8、判断运行结果
public class Exercise8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Child("mike");
}
}
class People {
private String name;
public People() {
System.out.print("1");
}
public People(String name) {
System.out.print("2");
this.name = name;
}
}
class Child extends People {
People father;
public Child(String name) {
System.out.print("3");
father = new People(name + " F");
}
public Child() {
System.out.print("4");
}
}
9、判断运行结果
public class Exercise9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f = new Father();
Child c = new Child();
}
}
class Father {
public Father(){
System.out.println("father()...");
}
}
class Child extends Father{
public Child(){
System.out.println("child()...");
}
}
10、判断运行结果
public class Exercise10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new A(new B());
}
}
class A {
public A() {
System.out.println("A");
}
public A(B b) {
this();
System.out.println("AB");
}
}
class B {
public B() {
System.out.println("B");
}
}
11、判断运行结果
public class Son extends Father{
private String name = "son";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Son son = new Son();
System.out.println(son.getName());
}
}
class Father {
private String name = "father";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
/*
* 当父类与子类有同名的属性时:
* 通过子类对象调用getName()访问的是父类的name还是子类的name,
* 那么要看子类是否重写,如果没有重写,就是父类的,重写了就是子类的。
*/
12、判断运行结果
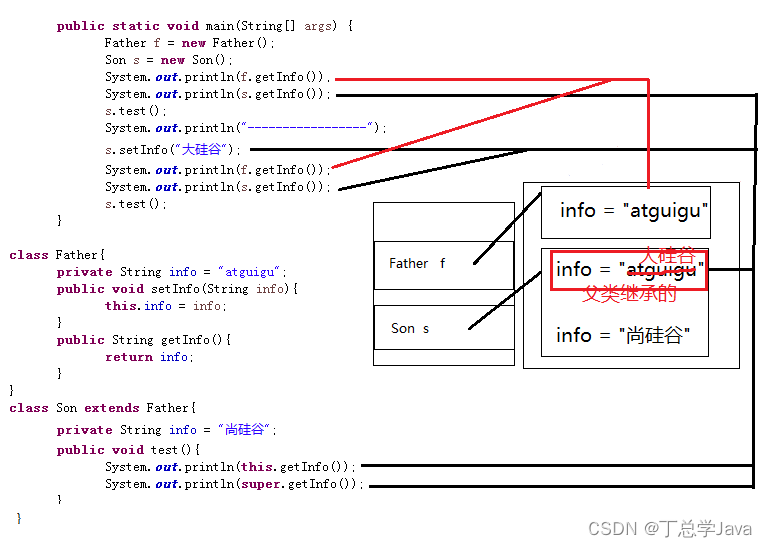
public class Exercise12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f = new Father();
Son s = new Son();
System.out.println(f.getInfo());
System.out.println(s.getInfo());
s.test();
System.out.println("-----------------");
s.setInfo("大硅谷");
System.out.println(f.getInfo());
System.out.println(s.getInfo());
s.test();
}
}
class Father{
private String info = "atguigu";
public void setInfo(String info){
this.info = info;
}
public String getInfo(){
return info;
}
}
class Son extends Father{
private String info = "尚硅谷";
public void test(){
System.out.println(this.getInfo());
System.out.println(super.getInfo());
}
}
/*
1、私有的属性是否可以被继承到子类中?
(1)如果从可以访问性的角度来说:不能,因为在子类中不能直接访问父类的私有的属性,但是可以通过get/set操作
(2)如果从类的概念来说,
类是一类具有相同特性(属性、方法等)的事物的抽象描述,
那么子类是从父类派生出来的,那么子类是有父类的这个特征的,即有这个属性的
2、每一个对象的非静态属性是独立的,其中一个对象修改和另一个对象是无关的
3、当子类有与父类的属性同名时,那么通过子类对象调用get/set方法操作的是父类继承还是子类自己的属性呢?
要看子类是否重写:
如果没有重写,操作的都是父类的,不管是直接getInfo()还是this.getInfo(),还是super.getInfo()
如果重写了,如果通过子类对象调用,操作的是子类的,例如:getInfo()还是this.getInfo(),
如果通过super.调用的,操作的是父类的。
*/
13、判断运行结果
public class Exercise13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f = new Father();
Son s = new Son();
System.out.println(f.getInfo());
System.out.println(s.getInfo());
s.test();
System.out.println("-----------------");
s.setInfo("大硅谷");
System.out.println(f.getInfo());
System.out.println(s.getInfo());
s.test();
}
}
class Father{
private String info = "atguigu";
public void setInfo(String info){
this.info = info;
}
public String getInfo(){
return info;
}
}
class Son extends Father{
private String info = "尚硅谷";
public void setInfo(String info){
this.info = info;
}
public String getInfo(){
return info;
}
public void test(){
System.out.println(this.getInfo());
System.out.println(super.getInfo());
}
}
/*
1、私有的属性是否可以被继承到子类中?
(1)如果从可以访问性的角度来说:不能,因为在子类中不能直接访问父类的私有的属性,但是可以通过get/set操作
(2)如果从类的概念来说,
类是一类具有相同特性(属性、方法等)的事物的抽象描述,
那么子类是从父类派生出来的,那么子类是有父类的这个特征的,即有这个属性的
2、每一个对象的非静态属性是独立的,其中一个对象修改和另一个对象是无关的
3、当子类有与父类的属性同名时,那么通过子类对象调用get/set方法操作的是父类继承还是子类自己的属性呢?
要看子类是否重写:
如果没有重写,操作的都是父类的,不管是直接getInfo()还是this.getInfo(),还是super.getInfo()
如果重写了,如果通过子类对象调用,操作的是子类的,例如:getInfo()还是this.getInfo(),
如果通过super.调用的,操作的是父类的。
*/
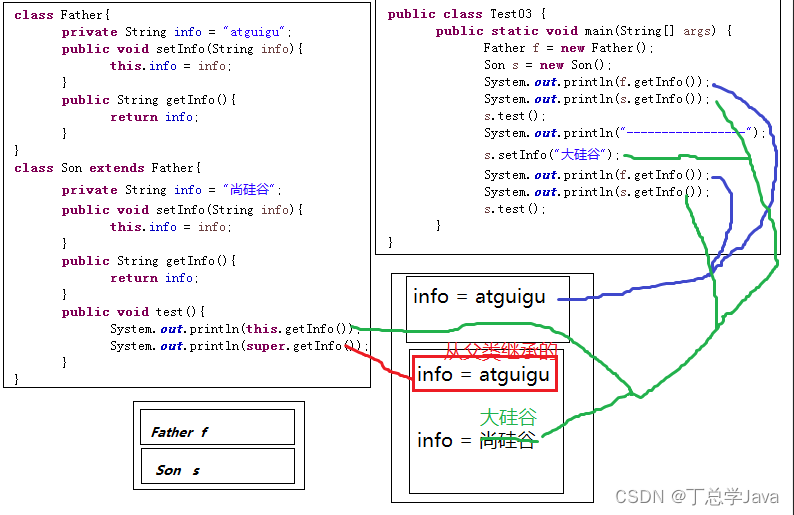
14、是否可通过编译
如下代码是否可以编译通过,如果能,结果是什么,如果不能,为什么?
public class Person{
public Person(){
System.out.println("this is a Person.");
}
}
public class Teacher extends Person{
private String name = "tom";
public Teacher(){
System.out.println("this is a teacher.");
super();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Teacher tea = new Teacher();
System.out.println(this.name);
}
}
剖析:
public class Teacher extends Person{
private String name = "tom";
public Teacher(){
System.out.println("this is a teacher.");
// super();//错误,super()必须在构造器首行
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Teacher tea = new Teacher();
// System.out.println(this.name);//错误,static方法中不能使用this
}
}
15、Person、Student、Teacher类
(1)声明父类:Person类
- 包含属性:姓名,年龄,性别,属性私有化
- 包含get/set方法
- 提供无参构造public Person()
- 提供有参构造public Person(String name, int age, char gender)
- 包含getInfo()方法:例如:姓名:张三,年龄:23,性别:男
(2)声明子类:Student类,继承Person类
- 新增属性:score成绩,属性私有化
- 包含get/set方法
- 提供无参构造public Student()
- 提供有参构造public Student(String name, int age, char gender, int score)
- 重写getInfo()方法:例如:姓名:张三,年龄:23,性别:男,成绩:89
(3)声明子类:Teacher类,继承Person类
- 新增属性:salary薪资,属性私有化
- 包含get/set方法
- 提供无参构造public Teacher()
- 提供有参构造public Teacher(String name, int age, char gender, double salary)
- 重写getInfo()方法:例如:姓名:张三,年龄:23,性别:男,薪资:10000
(4)在测试类的main方法中用有参构造创建三个类的对象,并调用相应的方法测试
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private char gender;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age, char gender) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public char getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(char gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getInfo() {
return "姓名:" + name + ",年龄:" + age + ",性别:" + gender;
}
}
public class Student extends Person {
private int score;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, char gender, int score) {
super(name, age, gender);
this.score = score;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String getInfo(){
return super.getInfo() + ",成绩:" + score;
}
}
public class Teacher extends Person {
private double salary;
public Teacher() {
}
public Teacher(String name, int age, char gender, double salary) {
super(name, age, gender);
this.salary = salary;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String getInfo(){
return super.getInfo() + ",薪资:" + salary;
}
}
public class Exercise15 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person("张三",23,'男');
System.out.println(p.getInfo());
Student s = new Student("王浩",20,'男',90);
System.out.println(s.getInfo());
Teacher t = new Teacher("宋红康",37,'男',50000);
System.out.println(t.getInfo());
}
}
05-多态性
16、Graphic、Circle、Rectangle类
(1)父类Graphic图形
- public double area()方法:返回0.0
- public double perimeter()方法:返回0.0
- public String getInfo()方法,返回图形面积和图形周长
(2)子类Circle圆类继承Graphic图形
- 包含属性:radius,属性私有化
- 包含get/set方法
- 重写area()求面积方法
- 重写perimeter()求周长方法
- 重写getInfo()方法,返回圆的半径,面积和周长
(3)子类矩形Rectangle继承Graphic图形
- 包含属性:length、width,属性私有化
- 包含get/set方法
- 重写area()求面积方法
- 重写perimeter()求周长方法
- 重写getInfo()方法,返回长和宽,面积、周长信息
(4)在测试类的main方法中创建多个圆和矩形对象放到Graphic[]类型的数组中,并按照面积从小到大排序输出。
public class Graphic {
public double area(){
return 0.0;
}
public double perimeter(){
return 0.0;
}
public String getInfo() {
return "面积:" + area() + ",周长:" + perimeter();
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Graphic{
private double length;
private double width;
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
@Override
public double area(){
return length * width;
}
@Override
public double perimeter(){
return 2 * (length + width);
}
@Override
public String getInfo() {
return "矩形长:" + length + ",宽:" + width +"," + super.getInfo();
}
}
public class Circle extends Graphic{
private double radius;
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public double area(){
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
@Override
public double perimeter(){
return 2 * Math.PI * radius;
}
@Override
public String getInfo() {
return "圆半径:" + radius +"," + super.getInfo();
}
}
public class Exercise16 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用一个数组用来存储各种图形的对象,并且按照各种图形的面积进行排序
Circle c1 = new Circle();
c1.setRadius(2.5);
Circle c2 = new Circle();
c2.setRadius(1.5);
Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle();
r1.setLength(5);
r1.setWidth(1);
Rectangle r2 = new Rectangle();
r2.setLength(4);
r2.setWidth(2);
Graphic[] shapes = new Graphic[4];
shapes[0] = c1;
shapes[1] = c2;
shapes[2] = r1;
shapes[3] = r2;
System.out.println("排序前:");
for (int i = 0; i < shapes.length; i++) {
System.out.println(shapes[i].getInfo());
}
//按照面积排序
for (int i = 1; i < shapes.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < shapes.length - i; j++) {
if(shapes[j].area() > shapes[j+1].area()){
Graphic temp = shapes[j];
shapes[j] = shapes[j+1];
shapes[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println("排序后:");
for (int i = 0; i < shapes.length; i++) {
System.out.println(shapes[i].getInfo());
}
}
}
17、Employee、SalaryEmployee、HourEmployee、Manager类
(1)声明一个父类Employee员工类型,
- 有姓名属性,私有化,提供get/set方法
- 提供有参构造public Employee(String name)
- public double earning():代表实发工资,返回0.0
- public String getInfo():显示姓名和实发工资
(2)声明MyDate类型
- 有int类型的年,月,日属性,私有化,提供get/set方法
- 提供有参构造public MyDate(int year, int month, int day)
- 提供public String getInfo(),返回“xxxx年xx月xx日”
(3)声明一个子类SalaryEmployee正式工,继承父类Employee
- 增加属性,double类型的薪资,MyDate类型的出生日期,私有化,提供get/set方法
- 提供有参构造public SalaryEmployee(String name, double salary, MyDate birthday)
- 提供有参构造public SalaryEmployee(String name,double salary, int year, int month ,int day)
- 重写方法,public double earning()返回实发工资, 实发工资 = 薪资
- 重写方法,public String getInfo():显示姓名和实发工资、生日
(4)声明一个子类HourEmployee小时工,继承父类Employee
- 有属性,double类型的工作小时数和每小时多少钱
- 提供有参构造public HourEmployee(String name, double moneyPerHour)
- 提供有参构造public HourEmployee(String name, double moneyPerHour, double hour)
- 重写方法,public double earning()返回实发工资, 实发工资 = 每小时多少钱 * 小时数
- 重写方法,public String getInfo():显示姓名和实发工资,时薪,工作小时数
(5)声明一个子类Manager经理,继承SalaryEmployee
- 增加属性:奖金比例,私有化,提供get/set方法
- 提供有参构造public Manager(String name, double salary, MyDate birthday, double bonusRate)
- 提供有参构造public Manager(String name,double salary, int year, int month ,int day, double bonusRate)
- 重写方法,public double earning()返回实发工资, 实发工资 = 薪资 *(1+奖金比例)
- 重写方法,public String getInfo():显示姓名和实发工资,生日,奖金比例
(6)声明一个员工数组,存储各种员工,你现在是人事,遍历查看每个人的详细信息,并统计实发工资总额,通知财务准备资金。
(7)从键盘输入当期月份值,如果他是正式工(包括SalaryEmployee和Manager),并且是本月生日的,通知领取生日礼物。
public class Employee {
private String name;
public Employee(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double earning(){
return 0.0;
}
public String getInfo(){
return "姓名:" + name + ",实发工资:" + earning();
}
}
public class MyDate {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
public String getInfo(){
return year + "年" + month + "月" + day +"日";
}
}
public class SalaryEmployee extends Employee {
private double salary;
private MyDate birthday;
public SalaryEmployee(String name, double salary, MyDate birthday) {
super(name);
this.salary = salary;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public SalaryEmployee(String name, double salary,int year, int month, int day) {
super(name);
this.salary = salary;
this.birthday = new MyDate(year, month ,day);
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public MyDate getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(MyDate birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public double earning() {
return salary;
}
@Override
public String getInfo() {
return super.getInfo() +",生日:" + birthday.getInfo();
}
}
public class HourEmployee extends Employee {
private double hour;
private double moneyPerHour;
public HourEmployee(String name, double hour) {
super(name);
this.hour = hour;
}
public HourEmployee(String name, double hour, double moneyPerHour) {
super(name);
this.hour = hour;
this.moneyPerHour = moneyPerHour;
}
public double getHour() {
return hour;
}
public void setHour(double hour) {
this.hour = hour;
}
public double getMoneyPerHour() {
return moneyPerHour;
}
public void setMoneyPerHour(double moneyPerHour) {
this.moneyPerHour = moneyPerHour;
}
@Override
public double earning() {
return hour * moneyPerHour;
}
@Override
public String getInfo() {
return super.getInfo() +",时薪:" + moneyPerHour +",工作小时数:" + hour;
}
}
public class Manager extends SalaryEmployee {
private double bonusRate;
public Manager(String name, double salary, MyDate birthday, double bonusRate) {
super(name, salary, birthday);
this.bonusRate = bonusRate;
}
public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day, double bonusRate) {
super(name, salary, year, month, day);
this.bonusRate = bonusRate;
}
public double getBonusRate() {
return bonusRate;
}
public void setBonusRate(double bonusRate) {
this.bonusRate = bonusRate;
}
@Override
public double earning() {
return super.earning() * (1 + bonusRate);
}
@Override
public String getInfo() {
return super.getInfo() +",奖金比例:" + bonusRate;
}
}
public class Exercise17 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee[] all = new Employee[3];
all[0] = new SalaryEmployee("张三",15000,new MyDate(1995,5,1));
all[1] = new Manager("老王",20000,1990,6,1,0.1);
all[2] = new HourEmployee("李四",50,100);
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) {
System.out.println(all[i].getInfo());
sum += all[i].earning();
}
System.out.println("实发工资总额:" + sum);
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入月份:");
int month = input.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) {
if(all[i] instanceof SalaryEmployee){
SalaryEmployee s = (SalaryEmployee) all[i];
if(s.getBirthday().getMonth() == month){
System.out.println(s.getName() + "生日快乐,请到人事部门领取生日大礼包");
}
}
}
input.close();
}
}
18、Person、Man、Woman等类
案例:
? 1、在包中声明人Person、男人Man、女人Woman类
? (1)在Person类中,包含
? ①public void eat():打印吃饭
? ②public void toilet():打印上洗手间
? (2)在Man类中,包含
? ①重写上面的方法
? ②增加 public void smoke():打印抽烟
? (3)在Woman类中,包含
? ①重写上面的方法
? ②增加 public void makeup():打印化妆
? 2、在包中声明测试类Test09
? (1)public static void meeting(Person… ps)
? 在该方法中,每一个人先吃饭,然后上洗手间,然后如果是男人,随后抽根烟,如果是女人,随后化个妆
? (2)public static void main(String[] args)
? 在主方法中,创建多个男人和女人对象,并调用meeting()方法进行测试
public class Person {
public void eat(){
System.out.println("吃饭");
}
public void toilet(){
System.out.println("上洗手间");
}
}
public class Man extends Person{
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("细嚼慢咽吃饭");
}
@Override
public void toilet() {
System.out.println("站着上洗手间");
}
public void smoke(){
System.out.println("抽烟爽爽");
}
}
public class Woman extends Person{
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("狼吞虎咽吃饭");
}
@Override
public void toilet() {
System.out.println("坐着上洗手间");
}
public void makeup(){
System.out.println("化妆美美");
}
}
public class Exercise18 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
meeting(new Woman(),new Man(), new Woman(), new Man());
}
public static void meeting(Person... ps){
for (int i = 0; i < ps.length; i++) {
ps[i].eat();
ps[i].toilet();
if(ps[i] instanceof Woman){
((Woman)ps[i]).makeup();
}else if(ps[i] instanceof Man){
((Man)ps[i]).smoke();
}
}
}
}
19、Person、Man、Woman类及数组
(1)在Person类中,包含
- 属性:姓名,年龄,职业
- public void eat():打印xx吃饭,xx代表姓名
- public void toilet():打印xx上洗手间
- public String getInfo():返回姓名、年龄、职业信息。
(2)在Man类中,包含
- 重写eat():xx狼吞虎咽吃饭
- 增加 public void smoke():打印xx抽烟
(3)在Woman类中,包含
- 重写eat():xx细嚼慢咽吃饭
- 增加 public void makeup():打印xx化妆
(4)周末一群男男女女相亲,在测试类创建不同对象放在Person[]数组中,
- 遍历数组,自我介绍,
- 再次遍历数组,调用吃饭方法
- 吃完饭,最后遍历数组,都去上厕所,男的上完厕所抽烟,女的上完厕所补妆。
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private String job;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getJob() {
return job;
}
public void setJob(String job) {
this.job = job;
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println(name + "吃饭");
}
public void toilet() {
System.out.println(name + "上洗手间");
}
public String getInfo() {
return "姓名:" + name + ",年龄:" + age + ",职业:" + job;
}
}
public class Man extends Person {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(getName() + "狼吞虎咽的吃饭");
}
public void smoke(){
System.out.println(getName() + "抽烟");
}
}
public class Woman extends Person{
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(getName() + "细嚼慢咽的吃饭");
}
public void makeup(){
System.out.println(getName() + "化妆");
}
}
public class Exercise19 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] arr = new Person[4];
arr[0] = new Man();
arr[0].setName("张三");
arr[0].setAge(23);
arr[0].setJob("Java中级工程师");
arr[1] = new Man();
arr[1].setName("李四");
arr[1].setAge(24);
arr[1].setJob("大数据工程师");
arr[2] = new Woman();
arr[2].setName("翠花");
arr[2].setAge(22);
arr[2].setJob("UI设计师");
arr[3] = new Woman();
arr[3].setName("如花");
arr[3].setAge(23);
arr[3].setJob("前端设计师");
System.out.println("------------初次见面--------------");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i].getInfo());
}
System.out.println("-------------开始聚餐--------------");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i].eat();
}
System.out.println("---------------饭后休息-------------");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i].toilet();
if(arr[i] instanceof Man){
Man man = (Man) arr[i];
man.smoke();
}else if(arr[i] instanceof Woman){
Woman woman = (Woman) arr[i];
woman.makeup();
}
}
}
}
20、普通员工、程序员、设计师、架构师
(1)普通员工Employee类
- 包含编号、姓名、年龄、工资,属性私有化
- 提供无参构造
- 提供有参构造Employee(int id, String name, int age, double salary)
- 提供get/set方法
- 提供String say()方法:返回员工基本信息
- 提供String getInfo()方法:返回员工基本信息
(2)程序员Programmer类,继承普通员工类
- 提供无参构造
- 提供有参构造Programmer(int id, String name, int age, double salary)
- 重写String getInfo()方法,增加职位“程序员”信息
(3)设计师Designer类,继承程序员类
- 增加奖金属性
- 提供无参构造
- 提供有参构造Designer(int id, String name, int age, double salary, double bonus)
- 重写String getInfo()方法,增加职位“设计师”和奖金信息
(4)架构师Architect类,继承设计师类
- 增加股票属性
- 提供无参构造
- 提供有参构造Architect(int id, String name, int age, double salary, double bonus, int stock)
- 重写String getInfo()方法,增加职位“架构师”和奖金、股票信息
(5)在测试类中创建员工数组,并存储1个普通员工对象,2个程序员对象,1个架构师对象,1个设计师对象
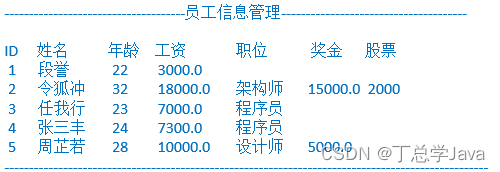

public class Employee {
private int id;
private String name;// : 姓名
private int age;// : 年龄
private double salary;// : 工资
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(int id, String name, int age, double salary) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String say(){
return id + "\t\t" + name + "\t" + age + "\t\t" + salary;
}
public String getInfo() {
return say();
}
}
public class Programmer extends Employee {
public Programmer() {
}
public Programmer(int id, String name, int age, double salary) {
super(id, name, age, salary);
}
@Override
public String getInfo() {
return super.say() + "\t\t程序员";
}
}
public class Designer extends Programmer {
private double bonus;// : 奖金
public Designer() {
}
public Designer(int id, String name, int age, double salary, double bonus) {
super(id, name, age, salary);
this.bonus = bonus;
}
public double getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
@Override
public String getInfo() {
return super.say() + "\t\t设计师" + "\t" + bonus;
}
}
public class Architect extends Designer {
private int stock;// : 股票
public Architect() {
}
public Architect(int id, String name, int age, double salary, double bonus, int stock) {
super(id, name, age, salary, bonus);
this.stock = stock;
}
public int getStock() {
return stock;
}
public void setStock(int stock) {
this.stock = stock;
}
@Override
public String getInfo() {
return super.say() + "\t\t架构师" + "\t" + getBonus() + "\t" + stock;
}
}
public class Exercise20 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee[] arr = new Employee[5];
arr[0] = new Employee(1,"段誉",22,3000);
arr[1] = new Architect(2,"令狐冲",32,18000,15000,2000);
arr[2] = new Programmer(3,"任我行",23,7000);
arr[3] = new Programmer(4,"张三丰",24,7300);
arr[4] = new Designer(5,"周芷若",28,10000,5000);
System.out.println("----------------员工信息管理-------------------");
System.out.println("编号\t姓名\t年龄\t工资\t\t职位\t奖金\t股票");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i].setId(i+1);
System.out.println(arr[i].getInfo());
}
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------");
}
}
21、判断运行结果
如下代码是否可以编译通过,如果能,结果是什么,如果不能,为什么?
public class Father{
private String name = "atguigu";
int age = 0;
}
public class Child extends Father{
public String grade;
public static void main(String[] args){
Father f = new Child();
System.out.println(f.name);
}
}
public class Child extends Father{
public String grade;
public static void main(String[] args){
Father f = new Child();
// System.out.println(f.name);//编译错误,因为name私有化
}
}
22、判断运行结果
public class Exercise22 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f = new Father();
Father s = new Son();
Father d = new Daughter();
MyClass my = new MyClass();
/*
第一个问题,my有没有多态引用?没有,从my角度来说,不需要考虑多态现象。
第二个问题,my调用的method方法,去哪个类找?只MyClass类中找就可以,和其他类无关。
第三个问题,method方法有三个形式,即重载的形式,那么怎么确定调用的是哪一个?
重载方法找寻原则:
A:先找最匹配的
什么叫最匹配的?
实参的“编译时”类型和形参的“声明”类型一致,个数也一致。
B:再找唯一可以兼容的
什么叫兼容?
实参的“编译时”类型 < 形参的“声明”类型
形参是可变参数的话,实参的个数在它允许的范围内
*/
my.method(f);//father
/*
实参f的编译时类型是 Father,和哪个方法的形参最匹配呢?public void method(Father f) 就它了
*/
my.method(s);//father
/*
实参s的编译时类型是 Father,和哪个方法的形参最匹配呢?public void method(Father f) 就它了
*/
my.method(d);//father
/*
实参d的编译时类型是 Father,和哪个方法的形参最匹配呢?public void method(Father f) 就它了
*/
}
}
class MyClass{
public void method(Father f) {
System.out.println("father");
}
public void method(Son s) {
System.out.println("son");
}
public void method(Daughter f) {
System.out.println("daughter");
}
}
class Father{
}
class Son extends Father{
}
class Daughter extends Father{
}
23、判断运行结果
public class Exercise23 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f = new Father();
Son s = new Son();
Daughter d = new Daughter();
MyClass my = new MyClass();//my没有多态引用,只看MyClass类就可以了
my.method(f);//father
/*
实参f的编译时类型仍然是Father,找最匹配的public void method(Father f)
*/
my.method(s);//son
/*
实参s的编译时类型是Son,找最匹配的public void method(Son s)
*/
my.method(d);//father
/*'
实参d的编译时类型是Daughter,找最匹配,没有,找兼容的,public void method(Father f)
*/
}
}
class MyClass{
public void method(Father f) {
System.out.println("father");
}
public void method(Son s) {
System.out.println("son");
}
}
class Father{
}
class Son extends Father{
}
class Daughter extends Father{
}
24、判断运行结果
public class Exercise24 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f = new Father();
Son s = new Son();
Daughter d = new Daughter();
MyClass my = new MySub();//my有多态引用了,而且method是虚方法
/*
如何确定它执行的是哪个方法呢?
(1)编译时,去my的编译时类型MyClass中找合适的方法
(2)运行时,去my的运行时类型MySub中看是否有对刚刚找到的方法进行了“重写”
*/
my.method(f);//father
/*
(1)编译时,去my的编译时类型MyClass中找合适的方法
实参f的编译时类型是Father,找最匹配的public void method(Father f)
(2)运行时,去my的运行时类型MySub中看是否有对刚刚找到的方法进行了“重写”
没有重写
仍然执行刚刚在MyClass中找到的合适的方法
*/
my.method(s);//son
/*
(1)编译时,去my的编译时类型MyClass中找合适的方法
实参s的编译时类型是Son,找最匹配的public void method(Son s)
(2)运行时,去my的运行时类型MySub中看是否有对刚刚找到的方法进行了“重写”
没有重写
仍然执行刚刚在MyClass中找到的合适的方法
*/
my.method(d);//father
/*
(1)编译时,去my的编译时类型MyClass中找合适的方法
实参s的编译时类型是Daughter,找最匹配的,没有,找兼容的,public void method(Father f)
(2)运行时,去my的运行时类型MySub中看是否有对刚刚找到的方法进行了“重写”
没有重写
仍然执行刚刚在MyClass中找到的合适的方法
*/
}
}
class MyClass{
public void method(Father f) {
System.out.println("father");
}
public void method(Son s) {
System.out.println("son");
}
}
class MySub extends MyClass{
public void method(Daughter d) {//这个不是重写,因为形参列表不同
System.out.println("daughter");
}
}
class Father{
}
class Son extends Father{
}
class Daughter extends Father{
}
25、判断运行结果
public class Exercise25 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f = new Father();
Son s = new Son();
Daughter d = new Daughter();
MyClass my = new MySub();//my有多态引用了,而且method是虚方法
/*
如何确定它执行的是哪个方法呢?
(1)编译时,去my的编译时类型MyClass中找合适的方法
(2)运行时,去my的运行时类型MySub中看是否有对刚刚找到的方法进行了“重写”
*/
my.method(f);//daughter
/*
(1)编译时,去my的编译时类型MyClass中找合适的方法
实参f的编译时类型是Father,找最匹配的public void method(Father f)
(2)运行时,去my的运行时类型MySub中看是否有对刚刚找到的方法进行了“重写”
有重写
一定是执行重写后的代码
*/
my.method(s);//son
/*
(1)编译时,去my的编译时类型MyClass中找合适的方法
实参s的编译时类型是Son,找最匹配的public void method(Son s)
(2)运行时,去my的运行时类型MySub中看是否有对刚刚找到的方法进行了“重写”
没有重写
仍然执行刚刚在MyClass中找到的合适的方法
*/
my.method(d);//daughter
/*
(1)编译时,去my的编译时类型MyClass中找合适的方法
实参s的编译时类型是Daughter,找最匹配的,没有,找兼容的,public void method(Father f)
(2)运行时,去my的运行时类型MySub中看是否有对刚刚找到的方法进行了“重写”
有重写
执行的是重写的方法体 daughter
*/
}
}
class MyClass{
public void method(Father f) {
System.out.println("father");
}
public void method(Son s) {
System.out.println("son");
}
}
class MySub extends MyClass{//有变化
public void method(Father d) {//是重写
System.out.println("daughter");
}
}
class Father{
}
class Son extends Father{
}
class Daughter extends Father{
}
26、判断运行结果
考核点:属性与多态无关
public class Exercise26 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new B();
System.out.println(a.num);
System.out.println(((B)a).num);
System.out.println(((A)((B)a)).num);
System.out.println("-------------------");
B b = new B();
System.out.println(b.num);
System.out.println(((A)b).num);
System.out.println(((B)((A)b)).num);
}
}
class A{
int num = 1;
}
class B extends A{
int num = 2;
}
/*
* 多态性现象:编译时类型与运行时类型不一致
* 但是多态性是针对方法来说,方法有动态绑定一说。
* 属性没有多态性。属性都是按照编译时类型处理的。
*/
public class Exercise26 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new B();
System.out.println(a.num);//a编译时类型就是A 1
System.out.println(((B)a).num);//编译后,因为a被强制成B类,是B类型 2
System.out.println(((A)((B)a)).num);//编译后,a转成B又转成A,是A类型 1
System.out.println("-------------------");
B b = new B();
System.out.println(b.num);//b编译时类型就是B 2
System.out.println(((A)b).num);//b被强制升级为A类型,按A类型处理, 1
System.out.println(((B)((A)b)).num);//b先转A又转B,最终是B类型 2
}
}
class A{
int num = 1;
}
class B extends A{
int num = 2;
}
27、判断运行结果
考核点:实例初始化方法,属性与多态无关
public class Exercise27 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f = new Son();
System.out.println(f.x);
}
}
class Father{
int x = 10;
public Father(){
this.print();
x = 20;
}
public void print(){
System.out.println("Father.x = " + x);
}
}
class Son extends Father{
int x = 30;
public Son(){
this.print();
x = 40;
}
public void print(){
System.out.println("Son.x = " + x);
}
}
/*
* 1、Father f = new Son();
* 实例初始化的过程:
* (1)父类的实例初始化
* <init>(){
* x = 10;//父类的x
* this.print();//子类的print,因为this代表的是正在创建的子类对象,而子类重写了print,所以是子类的print'
* System.out.println("Son.x = " + x);//子类的x,此时还没有赋值,那么是默认值x=0
x = 20;//父类的x
* }
* (2)子类的实例初始化
* <init>(){
* x = 30;//子类的x
* this.print();//子类的print
* System.out.println("Son.x = " + x);//子类的x,此时已经赋值x=30
x = 40;//子类的x
* }
*
* 2、执行System.out.println(f.x);
* 属性没有多态性,只看编译时类型,那么此时f.x表示父类的x
*/
public class Exercise27 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Father f = new Son();
System.out.println(f.x);
}
}
class Father{
int x = 10;
public Father(){
this.print();
x = 20;
}
public void print(){
System.out.println("Father.x = " + x);
}
}
class Son extends Father{
int x = 30;
public Son(){
this.print();
x = 40;
}
public void print(){
System.out.println("Son.x = " + x);
}
}
28、判断运行结果
考核点:多态,重写,实例初始化过程
public class Exercise28 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Base b1 = new Base();
Base b2 = new Sub();
}
}
class Base {
Base() {
method(100);
}
public void method(int i) {
System.out.println("base : " + i);
}
}
class Sub extends Base {
Sub() {
super.method(70);
}
public void method(int j) {
System.out.println("sub : " + j);
}
}
/*
* 1、Base b1 = new Base();
* 父类的实例初始化,和子类无关
*
* <init>(){
* method(100);
* System.out.println("base : " + i); base:100
* }
*
* 2、Base b2 = new Sub();
* (1) 父类的实例初始化
*
* <init>(){
* method(100);//执行了子类重写的method()
* System.out.println("sub : " + j); sub:100
* }
*
* (2)子类的实例初始化
* <init>(){
* super.method(70);
* System.out.println("base : " + i); base:70
* }
*/
public class Exercise28 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Base b1 = new Base();
Base b2 = new Sub();
}
}
class Base {
Base() {
method(100);
}
public void method(int i) {
System.out.println("base : " + i);
}
}
class Sub extends Base {
Sub() {
super.method(70);
}
public void method(int j) {
System.out.println("sub : " + j);
}
}
29、判断运行结果
考核知识点:多态、重载、重写
public class Exercise29 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a1 = new A();
A a2 = new B();
B b = new B();
C c = new C();
D d = new D();
System.out.println("(1)" + a1.show(b));
System.out.println("(2)" + a2.show(d));
System.out.println("(3)" + b.show(c));
System.out.println("(4)" + b.show(d));
}
}
class A{
public String show(D obj){
return ("A and D");
}
public String show(A obj){
return "A and A";
}
}
class B extends A{
public String show(B obj){
return "B and B";
}
public String show(A obj){
return "B and A";
}
}
class C extends B{
}
class D extends B{
}
/*
* 1、分析方法列表和继承关系
* A类:
* public String show(D obj)
* public String show(A obj)
* B类:
* public String show(D obj)继承的
* public String show(A obj)重写
* public String show(B obj)自定义的
* C->B->A
* D->B->A
*
* 2、方法重载:找最合适的形参类型
* 3、方法重写:如果子类重写,就执行重写的
* 4、分析执行结果
* a1.show(b):a1没有多态引用,直接找A类的方法,b是B类对象,只能选择public String show(A obj) A and A
* a2.show(d):a2多态引用,执行子类的方法,d是D类对象,选最合适的public String show(D obj) A and D
* b.show(c):b没有多态引用,直接找B类的方法,c是C类的对象,选择最合适的public String show(B obj) B and B
* b.show(d):b没有多态引用,直接找B类的方法,d是D类对象,选最合适的public String show(D obj) A and D
*/
public class Exercise29 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a1 = new A();
A a2 = new B();
B b = new B();
C c = new C();
D d = new D();
System.out.println("(1)" + a1.show(b));
System.out.println("(2)" + a2.show(d));
System.out.println("(3)" + b.show(c));
System.out.println("(4)" + b.show(d));
}
}
class A {
public String show(D obj) {
return ("A and D");
}
public String show(A obj) {
return "A and A";
}
}
class B extends A {
public String show(B obj) {
return "B and B";
}
public String show(A obj) {
return "B and A";
}
}
class C extends B {
}
class D extends B {
}
30、判断运行结果
考核知识点:多态、重载、重写
public class Exercise30 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a1 = new A();
A a2 = new B();
B b = new B();
C c = new C();
D d = new D();
System.out.println("(1)" + a1.show(b));
System.out.println("(2)" + a2.show(d));
System.out.println("(3)" + b.show(c));
System.out.println("(4)" + b.show(d));
}
}
class A {
public String show(C obj) {
return ("A and C");
}
public String show(A obj) {
return "A and A";
}
}
class B extends A {
public String show(B obj) {
return "B and B";
}
public String show(A obj) {
return "B and A";
}
}
class C extends B {
}
class D extends B {
}
/*
* 1、分析每个类的方法列表和继承关系
* A类:
* public String show(C obj)
* public String show(A obj)
* B类:
* public String show(C obj)继承的
* public String show(A obj)重写
* public String show(B obj)自定义的
* C->B->A
* D->B->A
*
* 2、方法重载:找最合适的形参类型
* 3、方法重写:如果子类重写,就执行重写的
* 4、如果特殊的重载,那么多态时,编译时先从父类中查找最合适的形参类型,然后如果子类如果有重写,执行子类重写的,如果没有重写,执行父类的。
* 5、分析执行结果
* a1.show(b):a1没有多态引用,直接找A类的方法,b是B类对象,只能选择public String show(A obj) A and A
* a2.show(d):a2多态引用,执行子类的方法,d是D类对象,但是因为此时编译时按A类编译,所以在编译期间先确定是调用
* public String show(A obj),而后执行子类重写的public String show(A obj) B and A
* 而不是直接选最合适的public String show(B obj)
* b.show(c):b没有多态引用,直接找B类的方法,c是C类的对象,选择最合适的public String show(C obj) A and C
* b.show(d):b没有多态引用,直接找B类的方法,d是D类对象,选最合适的public String show(B obj) B and B
*/
public class Exercise30 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a1 = new A();
A a2 = new B();
B b = new B();
C c = new C();
D d = new D();
System.out.println("(1)" + a1.show(b));
System.out.println("(2)" + a2.show(d));
System.out.println("(3)" + b.show(c));
System.out.println("(4)" + b.show(d));
}
}
class A {
public String show(C obj) {
return ("A and C");
}
public String show(A obj) {
return "A and A";
}
}
class B extends A {
public String show(B obj) {
return "B and B";
}
public String show(A obj) {
return "B and A";
}
}
class C extends B {
}
class D extends B {
}
31、判断运行结果
考核点:属性与多态无关
public class Exercise31 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Base b = new Sub();
System.out.println(b.x);
}
}
class Base{
int x = 1;
}
class Sub extends Base{
int x = 2;
}
/*
* 属性没有多态性,只看编译时类型
*/
public class Exercise31 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Base b = new Sub();
System.out.println(b.x);
}
}
class Base{
int x = 1;
}
class Sub extends Base{
int x = 2;
}
32、判断运行结果
/*
下面这些代码,调用的都是成员变量,不是虚方法。
只看变量或对象的“编译时类型”就可以了。
什么是编译时类型?
(1)对于变量来说,变量声明时,左边的类型就是它的编译时类型
(2)对于强制类型转换来说,()中写的类型是什么,它的编译时类型就是什么。如果有连续多次的强制类型转换,看最后一次。
*/
public class Exercise32 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new B();
System.out.println(a.num);//a变量的编译时类型是A
//1
System.out.println(((B)a).num);//((B)a),的编译时类型就是B
//2
System.out.println(((A)((B)a)).num);//((A)((B)a)),最后的类型是(A),它的编译时类型就是A
//1
System.out.println("-------------------");
B b = new B();
System.out.println(b.num);//b变量的编译时类型是B
//2
System.out.println(((A)b).num);//((A)b),编译时类型是A
//1
System.out.println(((B)((A)b)).num);//((B)((A)b)),编译时类型B
//2
}
}
class A{
int num = 1;
}
class B extends A{
int num = 2;
}
06-Object类
33、Triangle类
声明三角形类Triangle
(1)属性:double类型的a,b,c,代表三角形的三条边,要求属性使用final声明,并且私有化
(2)提供有参构造,并且在构造器中检查a,b,c是否可以构成三角形,如果a,b,c可以构成三角形则正常赋值,否则提示错误,并且a,b,c赋值为0
(3)生成a,b,c的get方法
(4)重写toString方法,并返回三角形信息,例如:“三角形三边是:3.0,4.0,5.0,面积是6.0,周长是:12.0”
(5)重写hashCode和equals方法
(6)编写 public double getArea():求面积方法
(7)编写 public double getPiremeter():求周长方法
在测试类的main中创建两个三角形对象,a,b,c分为赋值为3,4,5,调用equals方法比较两个对象是否相等,打印两个对象看结果。
public class Triangle {
private final double a;
private final double b;
private final double c;
public Triangle(double a, double b, double c) {
if(a<=0 || b<=0 || c<=0 || a+b<=c || a+c<=b || b+c<=a){
System.out.println(a+ "," +b +"," + c +"无法构成三角形");
this.a = 0;
this.b = 0;
this.c = 0;
}else{
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
}
public double getA() {
return a;
}
public double getB() {
return b;
}
public double getC() {
return c;
}
public double area(){
double p = (a+b+c)/2;
return Math.sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c));
}
public double perimeter(){
return a+b+c;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "三角形三边是:"+ a+ "," +b +"," + c +",面积是" + area() +",周长是:" + perimeter();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Triangle triangle = (Triangle) o;
return Double.compare(triangle.a, a) == 0 &&
Double.compare(triangle.b, b) == 0 &&
Double.compare(triangle.c, c) == 0;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(a, b, c);
}
}
public class Exercise33 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Triangle t1 = new Triangle(3,4,5);
Triangle t2 = new Triangle(3,4,5);
System.out.println(t1.equals(t2));
System.out.println(t1);
System.out.println(t2);
}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!