JDK8新增的时间类
发布时间:2024年01月21日
目录
? ? ? ? 4、DateTimeFormatter用于时间的格式化和解析
内容大纲:
????????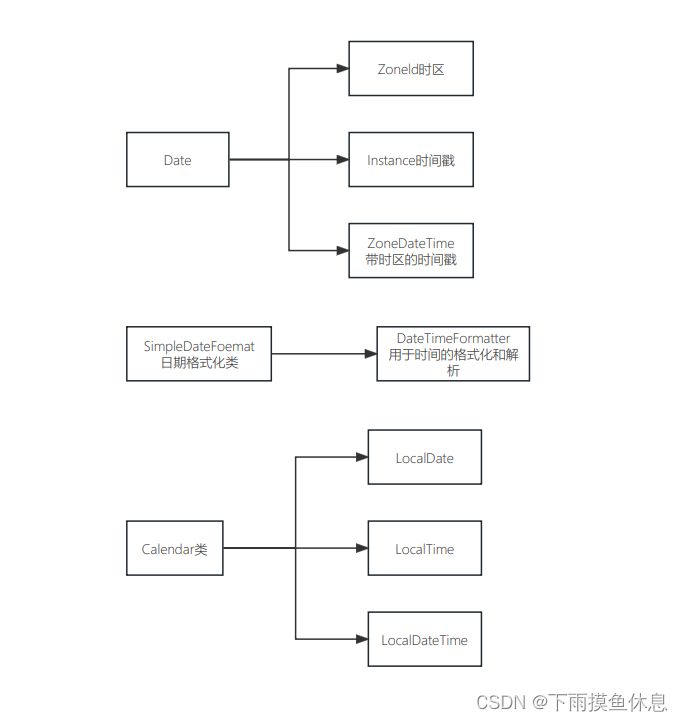
? ? ? ? 1、Zoneld时区
????????????????
| 方法名 | 说明 |
| static Set<String>getArailableZoneIds() | 获取Java中支持的所有时区 |
| static Zoneld systemDefault() | 获取系统默认时区 |
| static Zoneld of(String Zoneld) | 获取一个指定时区 |
? ? ? ? 代码如下:
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.util.Set;
public class Time_zoneIdDEMO {
public static void main(String[] args) {
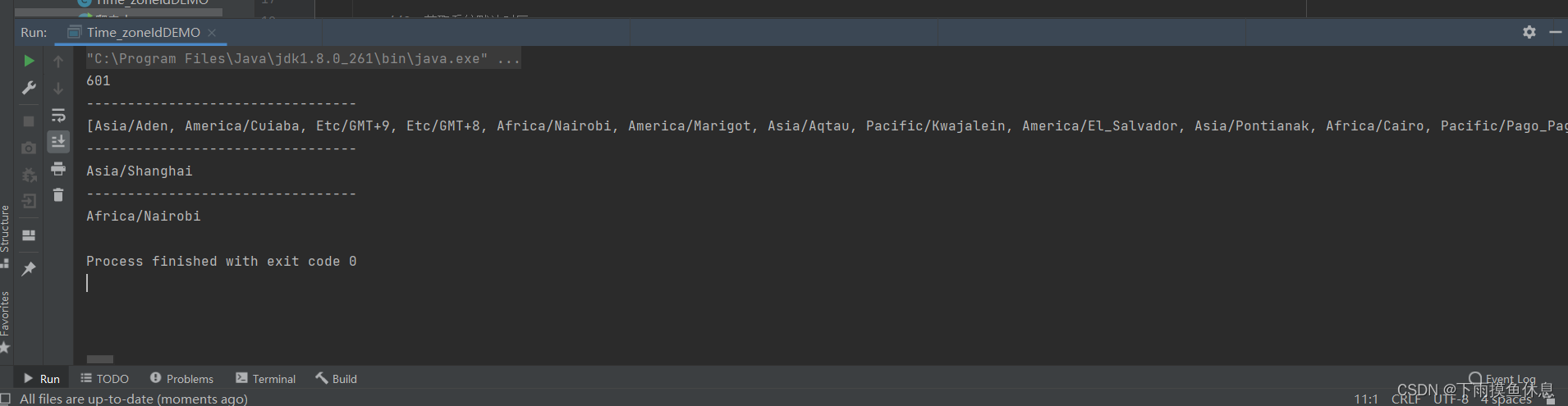
//1、获取所有的时区
Set<String> zoneIds = ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds();
//显示Java给的时区的数量
System.out.println(zoneIds.size());
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
//打印这些时区
System.out.println(zoneIds);
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
//2、获取系统默认时区
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.systemDefault();
System.out.println(zoneId);
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
//3、获取一个指定时区
ZoneId zoneId1 = ZoneId.of("Africa/Nairobi");
System.out.println(zoneId1);
}
}
运行结果如下:
? ? ? ? 2、Instant时间戳
????????????????
| 方法名 | 说明 |
| static Instant now() | 获取当前时间的Instant对象(标准时间) |
| static Instant ofXxx(long epochMilli) | 根据(s/ms/ns)获取Instant对象 |
| ZonedDateTime atZone(ZoneId zone) | 指定时区 |
| boolean isXxx(Instant other Instant) | 判断系列的方法 |
| Instant minusXxx(long millisToSubtract) | 减少时间系列的方法 |
| Instant plusXxx(long millisToSubtract) | 增加时间系列的方法 |
? ? ? ? 代码如下:
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class Time_instantDEMO {
public static void main(String[] args) {
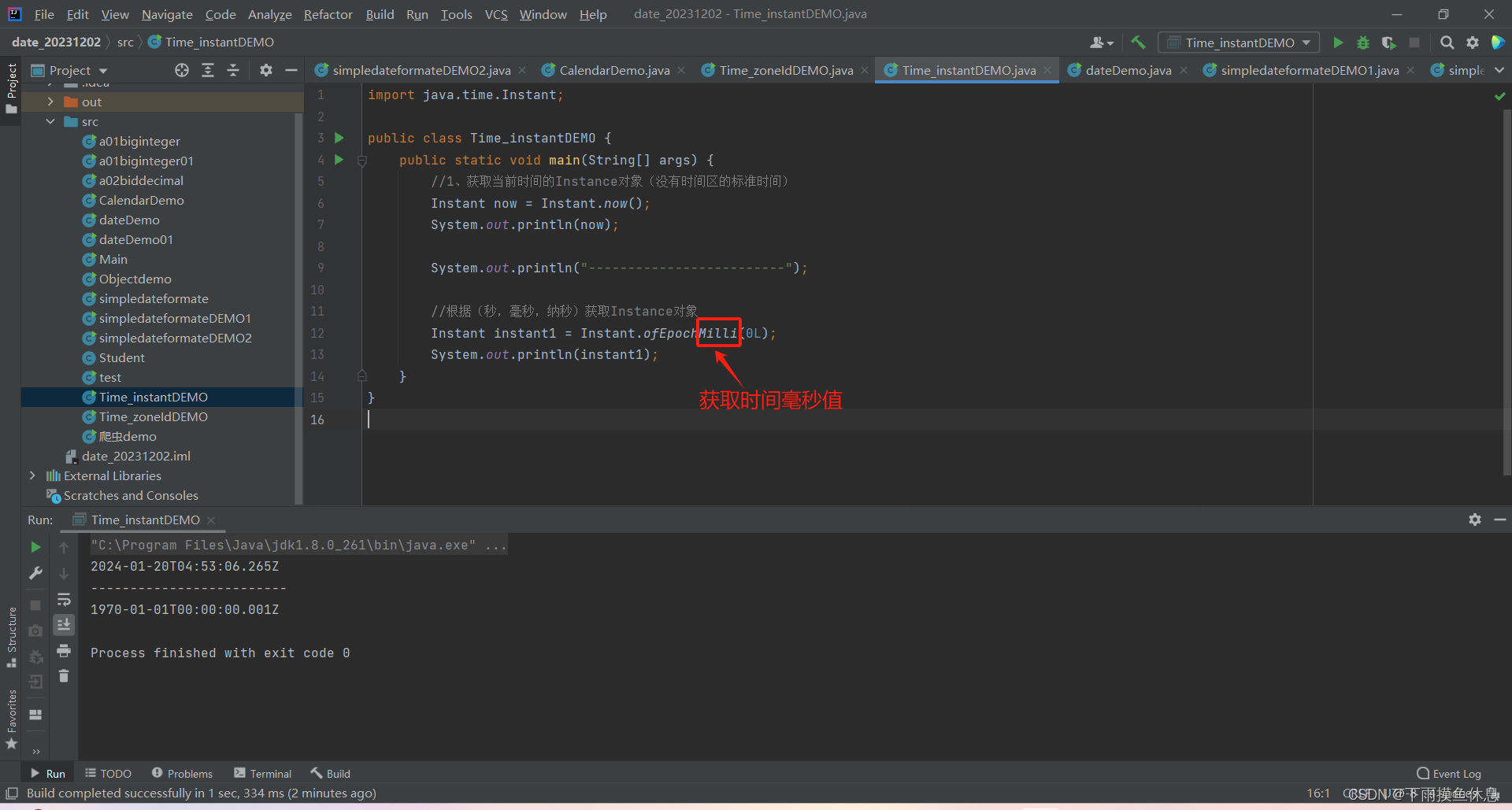
//1、获取当前时间的Instance对象(没有时间区的标准时间)
Instant now = Instant.now();
System.out.println(now);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
//2、根据(秒,毫秒,纳秒)获取Instance对象
Instant instant1 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(0L);
System.out.println(instant1);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
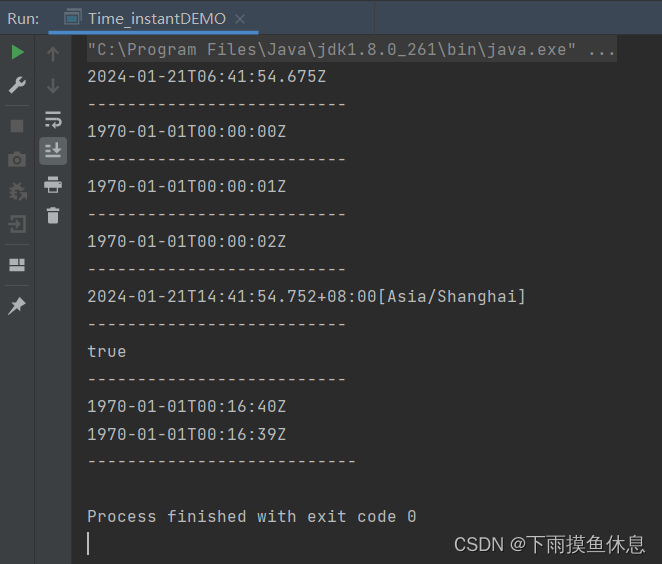
Instant instant2 = Instant.ofEpochSecond(1L);
System.out.println(instant2);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
Instant instant3 = Instant.ofEpochSecond(1L,1000000000L);
System.out.println(instant3);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
//3、获取指定时区时间
ZonedDateTime time = Instant.now().atZone(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
System.out.println(time);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
//4、isXxx判断
Instant instant4 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(0L);
Instant instant5 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(1000L);
boolean falg = instant4.isBefore(instant5);
System.out.println(falg);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
//minusXxx减少时间
Instant instant6 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(1000000L);
System.out.println(instant6);//1970-01-01T00:16:40Z
Instant instant7 = instant6.minusSeconds(1L);
System.out.println(instant7);
System.out.println("---------------------------");
}
}
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 这里需要注意:


? ? ? ? 代码的运行结果如下:
? ? ? ? 3、ZoneDateTime带时区的时间
| 方法名 | 说明 |
| static ZonedDateTime now() | 获取当前时间的zonedDateTime对象 |
| static ZonedDateTime odXxx() | 获取指定时间的ZonedDateTime对象 |
| ZonedDateTime withXxx(时间) | 修改时间系列的方法 |
| ZonedDateTime minusXxx(时间) | 减少时间系列的方法 |
| ZonedDateTime plusXxx(时间) | 增加时间系列的方法 |
? ? ? ? 代码如下:
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class Zonedatetime {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
static ZonedDateTime now() 获取当前时间的ZonedDateTime对象
static ZonedDateTime ofXxxx(。。。) 获取指定时间的ZonedDateTime对象
ZonedDateTime withXxx(时间) 修改时间系列的方法
ZonedDateTime minusXxx(时间) 减少时间系列的方法
ZonedDateTime plusXxx(时间) 增加时间系列的方法
*/
//1.获取当前时间对象(带时区)
ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now();
System.out.println(now);
//2.获取指定的时间对象(带时区)1/年月日时分秒纳秒方式指定
ZonedDateTime time1 = ZonedDateTime.of(2023, 10, 1,
11, 12, 12, 0, ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
System.out.println(time1);
//通过Instant + 时区的方式指定获取时间对象
Instant instant = Instant.ofEpochMilli(0L);
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai");
ZonedDateTime time2 = ZonedDateTime.ofInstant(instant, zoneId);
System.out.println(time2);
//3.withXxx 修改时间系列的方法
ZonedDateTime time3 = time2.withYear(2000);
System.out.println(time3);
//4. 减少时间
ZonedDateTime time4 = time3.minusYears(1);
System.out.println(time4);
//5.增加时间
ZonedDateTime time5 = time4.plusYears(1);
System.out.println(time5);
}
}
? ? ? ? 运行结果如下:

? ? ? ? 4、DateTimeFormatter用于时间的格式化和解析
| 方法名 | 说明 |
| static DateTimeFormatter ofPattern(格式) | 获取个数对象 |
| String format(时间对象) | 按照指定方式格式化 |
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 这个代码相对于上面的就简单许多了
代码如下:
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class Datetimeformatter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
static DateTimeFormatter ofPattern(格式) 获取格式对象
String format(时间对象) 按照指定方式格式化
*/
//获取时间对象
ZonedDateTime time = Instant.now().atZone(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
// 解析/格式化器
DateTimeFormatter dtf1=DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm;ss EE a");
// 格式化
System.out.println(dtf1.format(time));
}
}运行结果如下:

????????5、Calendar类:
????????????????
| 方法名 | 说明 |
| static XXX now() | 获取当前的对象 |
| static XXX of() | 获取指定的时间对象 |
| get开头的方法 | 获取日历中的年,月,日,时,分,秒等信息 |
| isBefore,isAfter | 比较两个LocalDate |
| with开头的 | 修改时间系列的方法 |
| minus开头的 | 减少时间系列的方法 |
| plus开头的 | 增加时间系列的方法 |
| public LocalDate toLocalDate() | LocalDateTime转换成LocalDate对象 |
| public LocalTime toLocalTime() | LocalDateTime转换成LocalTime对象 |
代码如下:
import java.time.DayOfWeek;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.Month;
import java.time.MonthDay;
public class _LocalDate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取当前时间的日历对象(包含 年月日)
LocalDate nowDate = LocalDate.now();
//System.out.println("今天的日期:" + nowDate);
//2.获取指定的时间的日历对象
LocalDate ldDate = LocalDate.of(2023, 1, 1);
System.out.println("指定日期:" + ldDate);
System.out.println("=============================");
//3.get系列方法获取日历中的每一个属性值//获取年
int year = ldDate.getYear();
System.out.println("year: " + year);
//获取月//方式一:
Month m = ldDate.getMonth();
System.out.println(m);
System.out.println(m.getValue());
//方式二:
int month = ldDate.getMonthValue();
System.out.println("month: " + month);
//获取日
int day = ldDate.getDayOfMonth();
System.out.println("day:" + day);
//获取一年的第几天
int dayofYear = ldDate.getDayOfYear();
System.out.println("dayOfYear:" + dayofYear);
//获取星期
DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = ldDate.getDayOfWeek();
System.out.println(dayOfWeek);
System.out.println(dayOfWeek.getValue());
//is开头的方法表示判断
System.out.println(ldDate.isBefore(ldDate));
System.out.println(ldDate.isAfter(ldDate));
//with开头的方法表示修改,只能修改年月日
LocalDate withLocalDate = ldDate.withYear(2000);
System.out.println(withLocalDate);
//minus开头的方法表示减少,只能减少年月日
LocalDate minusLocalDate = ldDate.minusYears(1);
System.out.println(minusLocalDate);
//plus开头的方法表示增加,只能增加年月日
LocalDate plusLocalDate = ldDate.plusDays(1);
System.out.println(plusLocalDate);
//-------------
// 判断今天是否是你的生日
LocalDate birDate = LocalDate.of(2000, 1, 1);
LocalDate nowDate1 = LocalDate.now();
MonthDay birMd = MonthDay.of(birDate.getMonthValue(), birDate.getDayOfMonth());
MonthDay nowMd = MonthDay.from(nowDate1);
System.out.println("今天是你的生日吗? " + birMd.equals(nowMd));//今天是你的生日吗?
}
}运行结果如下:

? ? ? ? 6、工具类
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Duration:用于计算两个“时间”间隔(秒,纳秒)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Period:用于计算两个“日期”间隔(年,月,日)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ChronoUnit:用于计算两个“日期”间隔(所有单位)
? ? ? ? Duration代码:
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class DurationDEMO {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 本地日期时间对象。
LocalDateTime today = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(today);
// 出生的日期时间对象
LocalDateTime birthDate = LocalDateTime.of(2000, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0);
System.out.println(birthDate);
Duration duration = Duration.between(birthDate, today);//第二个参数减第一个参数
System.out.println("相差的时间间隔对象:" + duration);
System.out.println("============================================");
System.out.println(duration.toDays());//两个时间差的天数
System.out.println(duration.toHours());//两个时间差的小时数
System.out.println(duration.toMinutes());//两个时间差的分钟数
System.out.println(duration.toMillis());//两个时间差的毫秒数
System.out.println(duration.toNanos());//两个时间差的纳秒数
}
}运行结果如下:

? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Period代码如下:
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.Period;
public class PeriodDEMO {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 当前本地 年月日
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println(today);
// 生日的 年月日
LocalDate birthDate = LocalDate.of(2000, 1, 1);
System.out.println(birthDate);
Period period = Period.between(birthDate, today);//第二个参数减第一个参数
System.out.println("相差的时间间隔对象:" + period);
System.out.println(period.getYears());
System.out.println(period.getMonths());
System.out.println(period.getDays());
System.out.println(period.toTotalMonths());
}
}运行结果如下:

? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ChronoUnit代码如下:
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
public class ChronoUnitDEMO {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 当前时间
LocalDateTime today = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(today);
// 生日时间
LocalDateTime birthDate = LocalDateTime.of(2000, 1, 1,
0, 0, 0);
System.out.println(birthDate);
System.out.println("相差的年数:" + ChronoUnit.YEARS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的月数:" + ChronoUnit.MONTHS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的周数:" + ChronoUnit.WEEKS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的天数:" + ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的时数:" + ChronoUnit.HOURS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的分数:" + ChronoUnit.MINUTES.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的秒数:" + ChronoUnit.SECONDS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的毫秒数:" + ChronoUnit.MILLIS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的微秒数:" + ChronoUnit.MICROS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的纳秒数:" + ChronoUnit.NANOS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的半天数:" + ChronoUnit.HALF_DAYS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的十年数:" + ChronoUnit.DECADES.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的世纪(百年)数:" + ChronoUnit.CENTURIES.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的千年数:" + ChronoUnit.MILLENNIA.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的纪元数:" + ChronoUnit.ERAS.between(birthDate, today));
}
}运行结果如下:

文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_78496658/article/details/135729050
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Spring Boot开发Spring Security
- 企业出海-如何保护客户账户安全?
- AI跟踪报道第25期-新加坡内哥谈技术-本周AI发展更新-酷炫来袭
- 软件体系结构与风格复习一
- 【C++记忆站】auto关键字(C++11)
- 【高危】Apache Solr 环境变量信息泄漏漏洞
- Spring Security-动态权限控制(2)
- node.js(express.js)+mysql实现登录功能
- 铭飞CMS cms/content/list接口存在SQL注入 附POC
- 【产品经理】用户研究与需求分析