【C++】继承和运算符重载练习题
发布时间:2023年12月25日
运算符重载

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
class Money
{
public:
Money(int y = 0, int j = 0, int f = 0);
Money operator+(Money &);
void Display(string);
private:
int yuan, jiao, fen;
void Optimize();
};
void Money::Optimize()
{
if (fen >= 10)
{
jiao++;
fen -= 10;
}
if (jiao >= 10)
{
yuan++;
jiao -= 10;
}
}
Money::Money(int y, int j, int f)
{
yuan = y;
jiao = j;
fen = f;
Optimize();
}
Money Money::operator+(Money &c2)
{
return Money(yuan + c2.yuan, jiao + c2.jiao, fen + c2.fen);
}
void Money::Display(string str)
{
cout << str << " = " << yuan << "." << jiao << fen << "¥" << endl;
}
int main()
{
Money cost1(300, 5, 6), cost2(105, 7, 6), total1, total2;
// cost1+cost2解释为:cost1.operator+(cost2)
total1 = cost1 + cost2;
total2 = cost1.operator+(cost2);
total1.Display("total1 = cost1 + cost2");
total2.Display("total2 = cost1 + cost2");
// total1 = cost1 + cost2 = 406.32¥ total2 = cost1 + cost2 = 406.32¥
return 0;
}

#include <math.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rational // 声明有理数类
{
public:
Rational(int x = 0, int y = 1); // 构造函数
void Print();
Rational operator+(Rational a); // 重载运算符"+"
Rational operator-(Rational a); // 重载运算符"-"
private:
int num, den;
void Optimi();
}; // 优化有理数函数
// 声明构造函数
Rational::Rational(int x, int y) : num(x), den(y)
{
Optimi();
}
void Rational::Optimi() // 定义有理数优化函数
{
// 最大公约数
int gcd;
if (num == 0) // 若分子为0,则置分母为1后返回
{
den = 1;
return;
}
gcd = (abs(num) > abs(den) ? abs(num) : abs(den));
if (gcd == 0)
return; // 若为0,则返回
int i = gcd;
for (; i > 1; i--) // 用循环找最大公约数
{
if ((num % i == 0) && (den % i == 0))
break;
}
num /= i; // i为最大公约数,将分子、分母均整除它,重新赋值
den /= i;
// 若分子和分母均为负数,则结果为正,所以均改为正
if (num < 0 && den < 0)
{
num = -num;
den = -den;
}
else if (num < 0 || den < 0)
{ // 若分子和分母中只有一个为负数,则调整为分子取负,分母取正
num = -abs(num);
den = abs(den);
}
}
void Rational::Print() // 输出有理数
{
cout << num;
// 当分子不为0且分母不为1时才显示"/分母“
if (num != 0 && den != 1)
cout << "/" << den << "\n";
else
cout << "\n";
}
Rational Rational::operator+(Rational a)
{ // “+”运算符重载函数,根据前面所列的算法写出表达式
Rational r;
r.den = a.den * den;
r.num = a.num * den + a.den * num;
r.Optimi();
return r;
}
Rational Rational::operator-(Rational a)
{ // “-”运算符重载函数,根据前面所列的算法写出表达式
Rational r;
r.den = a.den * den;
r.num = num * a.den - den * a.num;
r.Optimi();
return r;
}
int main()
{
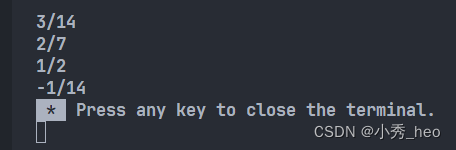
Rational r1(3, 14), r2(4, 14), r3, r4;
r1.Print();
r2.Print();
r3 = r1 + r2; // 使用重载了的运算符“+”
r3.Print();
r4 = r1 - r2; // 使用重载了的运算符“-”
r4.Print();
return 0;
}

#include <math.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class rational // 声明有理数类
{
public:
// 重载函数作为友元函数
rational(int x = 0, int y = 1);
friend rational operator+(rational a, rational b);
// 重载函数作为友元函数
friend rational operator-(rational a, rational b);
void print();
private:
int num, den;
void optimi();
};
rational::rational(int x, int y) : num(x), den(y)
{
optimi();
}
void rational::optimi() // 定义有理数优化函数
{
// 最大公约数
int gcd;
if (num == 0) // 若分子为0,则置分母为1后返回
{
den = 1;
return;
}
gcd = (abs(num) > abs(den) ? abs(num) : abs(den));
if (gcd == 0)
return; // 若为0,则返回
int i = gcd;
for (; i > 1; i--) // 用循环找最大公约数
{
if ((num % i == 0) && (den % i == 0))
break;
}
num /= i; // i为最大公约数,将分子、分母均整除它,重新赋值
den /= i;
// 若分子和分母均为负数,则结果为正,所以均改为正
if (num < 0 && den < 0)
{
num = -num;
den = -den;
}
else if (num < 0 || den < 0)
{ // 若分子和分母中只有一个为负数,则调整为分子取负,分母取正
num = -abs(num);
den = abs(den);
}
}
// 定义作为友元函数的重载函数
rational operator+(rational a, rational b)
{
rational r;
r.den = a.den * b.den;
r.num = a.num * b.den + a.den * b.num;
r.optimi();
return r;
}
// 定义作为友元函数的重载函数
rational operator-(rational a, rational b)
{
rational r;
r.den = a.den * b.den;
r.num = a.num * b.den - a.den * b.num;
r.optimi();
return r;
}
void rational::print() // 输出有理数
{
cout << num;
// 当分子不为0且分母不为1时才显示"/分母“
if (num != 0 && den != 1)
cout << "/" << den << "\n";
else
cout << "\n";
}
int main()
{
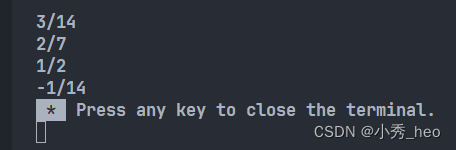
rational r1(3, 14), r2(4, 14), r3, r4;
r1.print();
r2.print();
r3 = r1 + r2; // 使用重载了的运算符“+”
r3.print();
r4 = r1 - r2; // 使用重载了的运算符“-”
r4.print();
return 0;
}

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
Point();
Point(int vx, int vy);
// 前置自增重载为成员函数
Point operator++();
// 前置自减重载为友元函数
friend Point &operator--(Point &p);
void Display();
private:
int x, y;
};
Point::Point()
{
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
Point::Point(int vx, int vy)
{
x = vx;
y = vy;
}
void Point::Display()
{
cout << "(" << x << ", " << y << ")" << endl;
}
Point Point::operator++() // 前置自增
{
if (x < 640)
x++; // 不超过屏幕的横界
if (y < 480)
y++; // 不超过屏幕的竖界
return *this;
}
Point &operator--(Point &p)
// 前置自减重载为友元函数
{
if (p.x > 0)
p.x--;
if (p.y > 0)
p.y--;
return p;
}
int main()
{
Point p1(10, 10), p2(150, 150);
cout << "p1=";
p1.Display();
++p1; // 测试前置自增
cout << "++p1=";
p1.Display();
cout << "p2=";
p2.Display();
--p2; // 测试前置自减
cout << "--p2=";
p2.Display();
return 0;
}

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
Point();
Point(int vx, int vy);
Point &operator++(); // 重载前置自增为类的成员函数
Point &operator++(int); // 重载后置自增为类的成员函数
// 重载前置自减为类的友元函数
friend Point& operator--(Point & p1);
// 重载后置自减为类的友元函数
friend Point& operator--(Point &p1, int);
void display();
private:
int x, y;
};
Point::Point()
{
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
Point::Point(int vx, int vy)
{
x = vx;
y = vy;
}
void Point::display()
{
cout << " (" << x << "," << y << ") " << endl;
}
Point &Point::operator++() // 前置自增
{
if (x < 640)
x++; // 不超过屏幕的横界
if (y < 480)
y++; // 不超过屏幕的竖界 return *this;
return *this;
}
Point &Point::operator++(int) // 后置自增
{ // 先将当前对象通过复制构造函数临时保存起来
Point temp(*this);
if (x < 640)
x++; // 不超过屏幕的横界
if (y < 480)
y++; // 不超过屏幕的竖界
return temp;
}
Point &operator--(Point &p) // 前置自减
{
if (p.x > 0)
p.x--;
if (p.y > 0)
p.y--;
return p;
}
Point& operator--(Point &p, int) // 后置自减
{ // 先将当前对象通过复制构造函数临时保存起来
Point temp(p);
if (p.x > 0)
p.x--;
if (p.y > 0)
p.y--;
return temp;
}
int main()
{
Point p1(10, 10), p2(150, 150), p3(20, 20),
p4(160, 160), p5;
cout << "p1=";
p1.display();
++p1; // 测试前置自增
cout << "++p1=";
p1.display();
cout << "p3=";
p3.display();
p5 = p3++; // 测试后置自增
cout << " p3++=";
p3.display();
cout << "p5=p3++=";
p5.display();
cout << "p2=";
p2.display();
--p2; // 测试前置自减
cout << "--p2=";
p2.display();
cout << "p4=";
p4.display();
p5 = p4--; // 测试后置自增
cout << " p4--=";
p4.display();
cout << " p5= p4--=";
p5.display();
return 0;
}

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <cstring>
#include <cassert>
class String // 自定义字符串类
{
public:
String(); // 默认构造函数
String(const char *src); // 带参数的构造函数
~String(); // 析构函数
const char *ToString() const { return str; }
unsigned int Length() const { return len; }
String &operator=(const String &right);
// 赋值运算符重载函数
private:
char *str;
unsigned int len; // 存放字符串的长度
};
String::String() // 默认构造函数
{
len = 0;
str = new char[len + 1];
str[0] = '\0';
}
String::String(const char *src) // 带参数的构造函数
{
len = strlen(src);
str = new char[len + 1];
if (!str)
{
cerr << "Allocation Error!\n";
exit(1);
}
strcpy(str, src);
}
String::~String() // 析构函数
{
delete str;
str = NULL;
}
String &String::operator=(const String &right)
// 赋值运算符重载函数
{
if (&right != this)
{
int length = right.Length();
if (len < length)
{
delete[] str;
str = new char[length + 1];
assert(str != 0);
}
int i;
for (i = 0; right.str[i] != '\0'; i++)
str[i] = right.str[i];
str[i] = '\0';
len = length;
}
return *this;
}
int main()
{
String str1("Hi!"), str2("Hello!");
cout << "str1: " << str1.ToString() << endl;
cout << "str2: " << str2.ToString() << endl;
str1 = str2;
cout << "str1: " << str1.ToString() << endl;
return 0;
}

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Timer
{
public:
Timer();
Timer(int h, int m = 0);
friend Timer operator+(Timer &t1, Timer &t2);
friend Timer operator-(Timer &t1, Timer &t2);
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out,
Timer &t);
friend istream &operator>>(istream &in,
Timer &t);
private:
int hours;
int minutes;
};
Timer::Timer()
{
hours = minutes = 0;
}
Timer::Timer(int h, int m)
{
hours = h;
minutes = m;
}
Timer operator+(Timer &t1, Timer &t2)
{
Timer sum;
sum.minutes = t1.minutes + t2.minutes;
sum.hours = t1.hours + t2.hours + sum.minutes / 60;
sum.minutes %= 60;
return sum;
}
Timer operator-(Timer &t1, Timer &t2)
{
Timer dif;
int x1, x2;
x1 = t2.hours * 60 + t2.minutes;
x2 = t1.hours * 60 + t1.minutes;
dif.minutes = (x2 - x1) % 60;
dif.hours = (x2 - x1) / 60;
return dif;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, Timer &t)
{
out << t.hours << "hours," << t.minutes << "minutes";
return out;
}
istream &operator>>(istream &in, Timer &t)
{
cout << "Input hours and minutes:";
in >> t.hours >> t.minutes;
return in;
}
int main()
{
Timer t1, t2, t3, t4;
cin >> t1 >> t2;
cout << "t1 = " << t1 << "\n";
cout << "t2 = " << t2 << "\n";
t3 = t1 + t2;
cout << "t3 = t1 + t2 = " << t3 << "\n";
t4 = t1 - t2;
cout << "t4 = t1 - t2 = " << t4 << "\n";
return 0;
}


#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Complex
{
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, Complex &c);
friend istream &operator>>(istream &in, Complex &c);
public:
Complex(double r = 1, double m = 1)
{
real = r;
imag = m;
}
Complex operator+(Complex b)
{
Complex c;
c.real = real + b.real;
c.imag = imag + b.imag;
return c;
}
private:
double real, imag;
};
ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, Complex &c)
{
if (c.imag > 0)
out << c.real << "+" << c.imag << "i" << endl;
else
out << c.real << "+(" << c.imag << ")i" << endl;
return out;
}
istream &operator>>(istream &in, Complex &c)
{
cout << "请输入复数的实部和虚部:" << endl;
in >> c.real >> c.imag;
return in;
}
int main()
{
Complex a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b;
c = a + b;
cout << "两个复数之和为:" << c << endl;
return 0;
}

继承
- 分别定义教师类Teacher和干部类Cadre,采用多重继承的方式由这两个类派生出新类Teacher_Cadre (教师兼干部类)。要求:(1)在两个基类中都包含姓名、年龄、性别、地址、电话数据成员。(2)在Teacher类中还包含数据成员职称title,在Cadre类中还包含数据成员职务post,在Teacher_Cadre类中还包含数据成员工资wage.(3)对两个基类中的姓名、年龄、性别、地址、电话数据成员用相同的名字,在访问这类数据成员时,指定作用域。(4)在类体中声明成员函数,在类外定义成员函数。(5)在派生类Teacher_Cadre的成员函数show中调用Teacher类中的display函数,输出姓名、年龄、性别、地址、电话,然后再用cout语句输出职务和工资。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Teacher
{
protected:
string name;
int age;
string gender;
string address;
string phone;
string title;
public:
Teacher(string n, int a, string g, string ad, string p, string t);
void display();
};
Teacher::Teacher(string n, int a, string g, string ad, string p, string t)
{
name = n;
age = a;
gender = g;
address = ad;
phone = p;
title = t;
}
void Teacher::display()
{
cout << "Name: " << name << endl;
cout << "Age: " << age << endl;
cout << "Gender: " << gender << endl;
cout << "Address: " << address << endl;
cout << "Phone: " << phone << endl;
cout << "Title: " << title << endl;
}
class Cadre
{
protected:
string name;
int age;
string gender;
string address;
string phone;
string post;
public:
Cadre(string n, int a, string g, string ad, string p, string pst);
void display();
};
Cadre::Cadre(string n, int a, string g, string ad, string p, string pst)
{
name = n;
age = a;
gender = g;
address = ad;
phone = p;
post = pst;
}
void Cadre::display()
{
cout << "Name: " << name << endl;
cout << "Age: " << age << endl;
cout << "Gender: " << gender << endl;
cout << "Address: " << address << endl;
cout << "Phone: " << phone << endl;
cout << "Post: " << post << endl;
}
class Teacher_Cadre : public Teacher, public Cadre
{
private:
float wage;
public:
Teacher_Cadre(string n, int a, string g, string ad, string p, string t, string pst, float w);
void show();
};
Teacher_Cadre::Teacher_Cadre(string n, int a, string g, string ad, string p, string t, string pst, float w) : Teacher(n, a, g, ad, p, t), Cadre(n, a, g, ad, p, pst)
{
wage = w;
}
void Teacher_Cadre::show()
{
Teacher::display();
cout << "Post: " << Cadre::post << endl;
cout << "Wage: " << wage << endl;
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
Teacher_Cadre tc("张三", 30, "男", "北京", "123456789", "教授", "部门主管", 5000.50);
tc.show();
return 0;
}

- 编写一个程序实现小型公司的人员信息管理系统。该公司雇员(Employee)包括经理(Manager),技术人员(Technician)、销售员(Salesman)和销售部经理(SalesManager)。要求存储这些人员的姓名、编号、级别、当月薪水,计算月薪并显示全部信息。程序要对所有人员有提升级别的功能。为简单起见,所有人员的初始级别均为 1,然后进行升级,经理升为4级,技术人员和销售部经理升为3级,销售员仍为1级。月薪计算办法是:经理拿固定月薪 8000 元,技术人员按每小时 100 元领取月薪,销售员按该当月销售额4%提成,销售经理既拿固定月工资也领取销售提成,固定月工资为5000元,销售提成为所管辖部门当月销售额的 5‰。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Employee
{
protected:
string name;
int id;
int level;
float monthlySalary;
public:
Employee(string name, int id)
{
this->name = name;
this->id = id;
this->level = 1;
this->monthlySalary = 0;
}
void display()
{
cout << "姓名:" << name << endl;
cout << "编号:" << id << endl;
cout << "级别:" << level << endl;
cout << "当月薪水:" << monthlySalary << "元" << endl;
}
};
class Manager : public Employee
{
public:
Manager(string name, int id) : Employee(name, id)
{
monthlySalary = 8000;
}
void promote()
{
level = 4;
}
};
class Technician : public Employee
{
private:
int workedHours;
public:
Technician(string name, int id) : Employee(name, id)
{
monthlySalary = 0;
workedHours = 0;
}
void setWorkedHours(int hours)
{
workedHours = hours;
monthlySalary = workedHours * 100;
}
void promote()
{
level = 3;
}
};
class Salesman : public Employee
{
private:
float salesAmount;
public:
Salesman(string name, int id) : Employee(name, id)
{
monthlySalary = 0;
salesAmount = 0;
}
void setSalesAmount(float amount)
{
salesAmount = amount;
monthlySalary = salesAmount * 0.04;
}
void promote()
{
level = 1;
}
};
class SalesManager : public Employee
{
private:
float salesAmount;
public:
SalesManager(string name, int id) : Employee(name, id)
{
monthlySalary = 5000;
salesAmount = 0;
}
void setSalesAmount(float amount)
{
salesAmount = amount;
monthlySalary += salesAmount * 0.005;
}
void promote()
{
level = 3;
}
};
int main()
{
// 创建员工对象
Manager manager("经理", 1);
Technician technician("技术人员", 2);
Salesman salesman("销售员", 3);
SalesManager salesManager("销售部经理", 4);
// 设置员工的相关信息
technician.setWorkedHours(80);
salesman.setSalesAmount(20000);
salesManager.setSalesAmount(50000);
// 显示员工信息
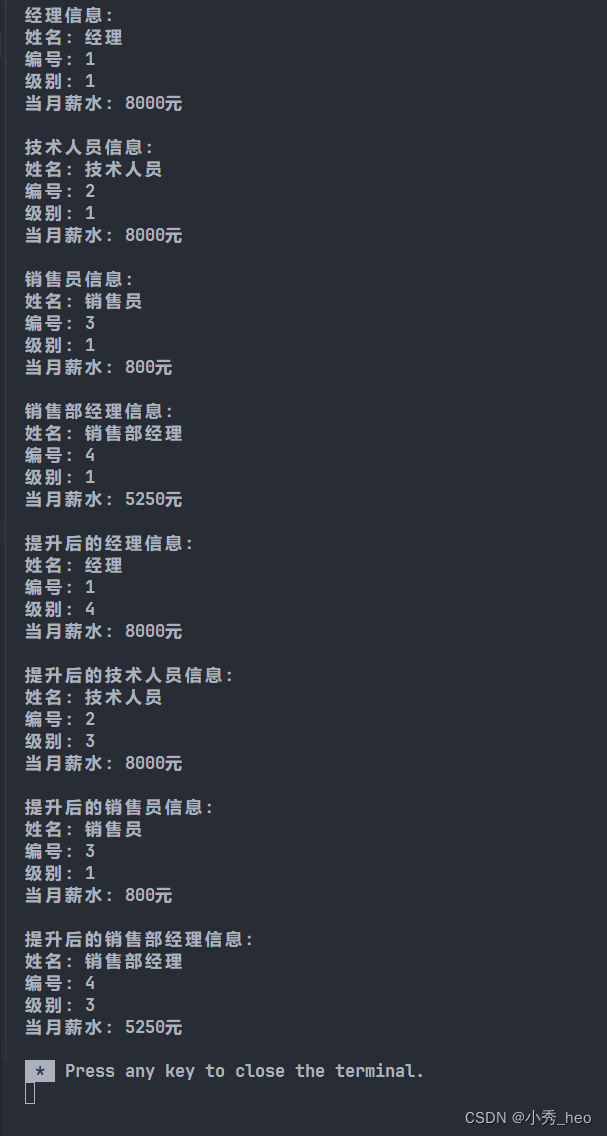
cout << "经理信息:" << endl;
manager.display();
cout << endl;
cout << "技术人员信息:" << endl;
technician.display();
cout << endl;
cout << "销售员信息:" << endl;
salesman.display();
cout << endl;
cout << "销售部经理信息:" << endl;
salesManager.display();
cout << endl;
// 提升级别
manager.promote();
technician.promote();
salesManager.promote();
// 显示提升后的员工信息
cout << "提升后的经理信息:" << endl;
manager.display();
cout << endl;
cout << "提升后的技术人员信息:" << endl;
technician.display();
cout << endl;
cout << "提升后的销售员信息:" << endl;
salesman.display();
cout << endl;
cout << "提升后的销售部经理信息:" << endl;
salesManager.display();
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/XiugongHao/article/details/135146513
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 01.15
- macOS系统打开Linux的方法
- Android 获得通讯录并展示
- 什么是虚拟DOM?为什么虚拟DOM性能更优秀?
- 实战 | 公益SRC上分技巧
- [德人合科技]——设计公司 \ 设计院图纸文件数据 | 资料透明加密防泄密软件
- 企业电子招投标系统源码之电子招投标系统建设的重点和未来趋势
- ESP32-CAM带摄像头的开发板使用-环境安装
- C语言K&R圣经笔记 4.10递归 4.11 C预处理
- 医院信息化云HIS平台源码 基于电子病历的医院信息化标准建设