2023-12-20 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先和二叉搜索树中的插入操作和删除二叉搜索树中的节点
发布时间:2023年12月21日
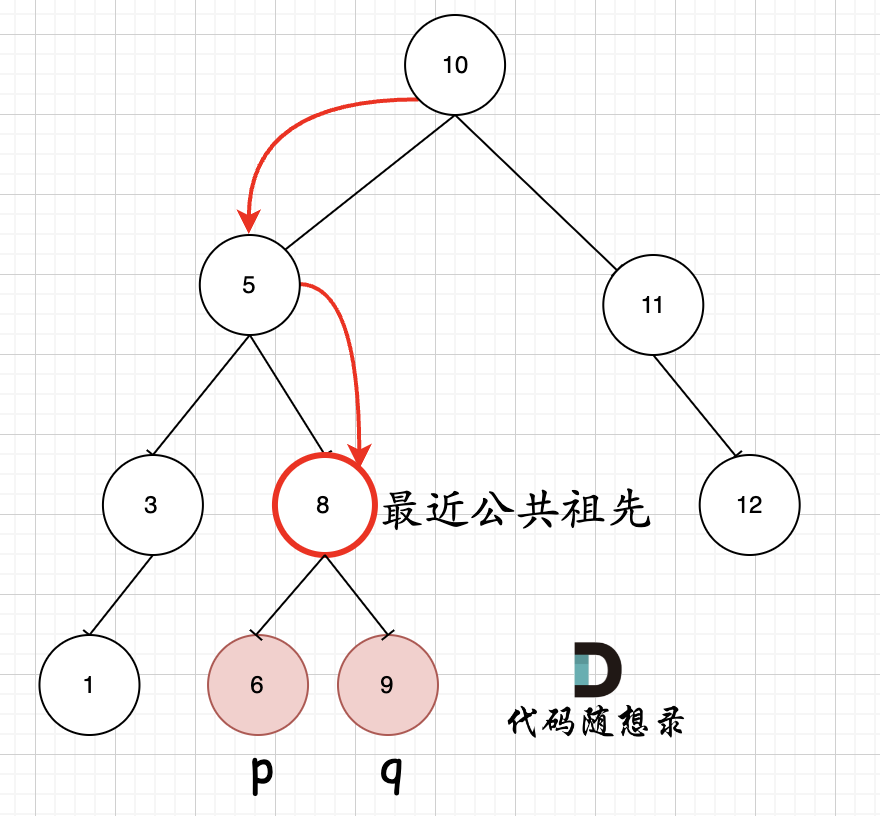
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
思想:和二叉树的公共最近祖先节点的思路基本一致的!就是不用从下往上遍历处理!可以利用的二叉搜索树的特点从上往下处理了!而且最近公共节点肯定是第一个出现在【q,p】这个区间的内的!
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
return self.lowestCommonAncestor1(root, p, q)
def lowestCommonAncestor1(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
# 二叉搜索树,是有序的,不同于二叉树的公共祖先需要从下往上遍历
# 而且公共节点一定会出现在【p,q】之前,我们递归遍历,最先出现在这个区间就是公共祖先节点了
if root is None:
return root
# 处理中节点了
if root.val > q.val and root.val > p.val: # 处理左节点
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
if left is not None:
# if not left: 这种用来判断节点不对的!
return left
if root.val < q.val and root.val < p.val:
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if right is not None:
return right
return root
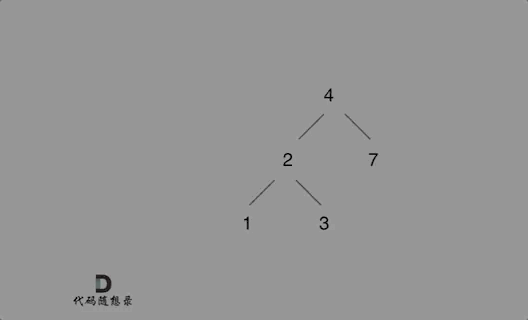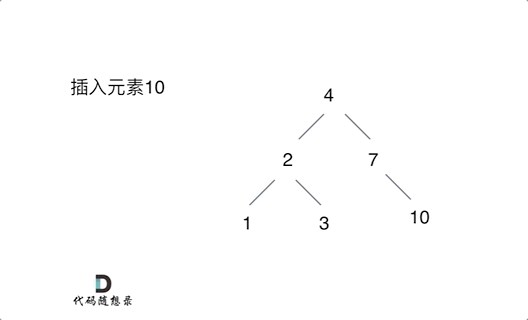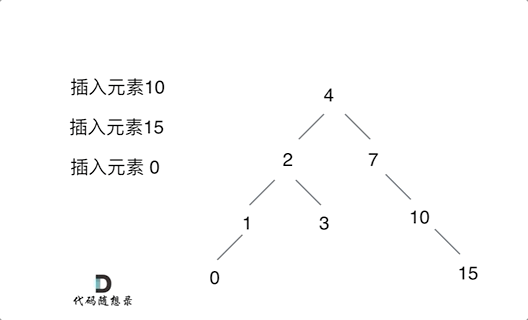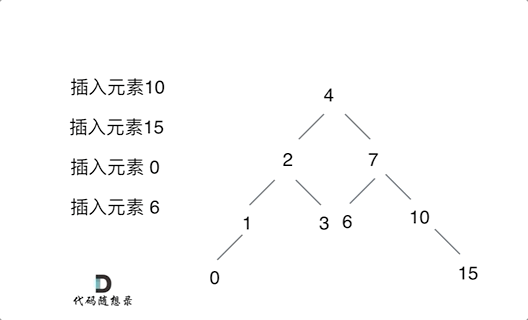
701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
思路:只要按照二叉搜索树的规则去遍历,遇到空节点就插入节点就可以了!通过递归函数返回值完成了新加入节点的父子关系赋值操作了,下一层将加入节点返回,本层用root->left或者root->right将其接住
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def insertIntoBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], val: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if root is None:
node = TreeNode(val)
# root = node
return node
if root.val > val:
root.left = self.insertIntoBST(root.left, val) # 左
if root.val < val:
root.right = self.insertIntoBST(root.right, val) # 有
# 中
return root
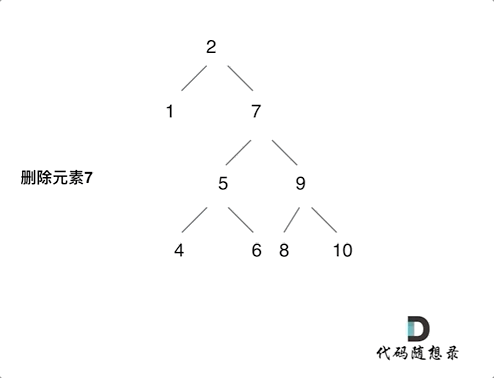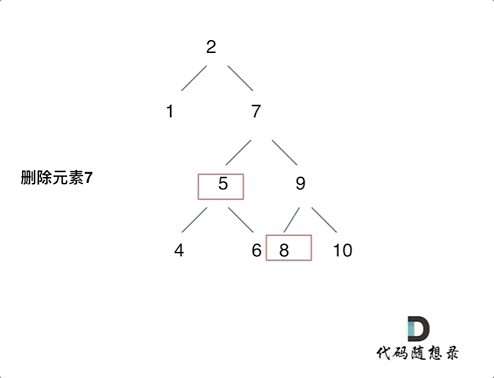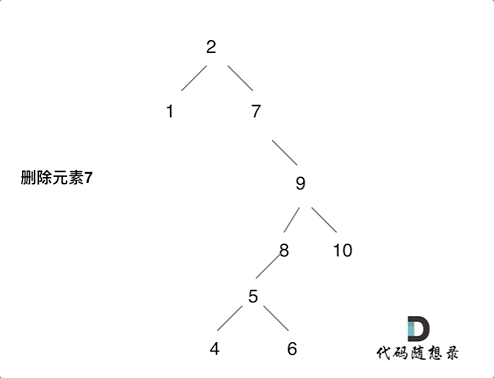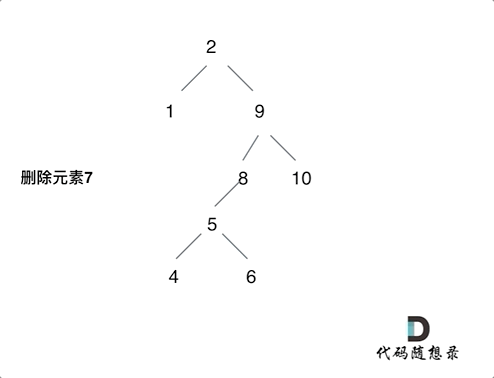
450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
思路:对于这种增删的,使用root.left and root.right来接受返回的节点值的!返回值来加入新节点, 这里也可以通过递归返回值删除节点!搜索树不用限定是用前中后序遍历,根据搜索树有序规则遍历就好了!但是还是要有递归三部曲的!!
- 确定单层递归的逻辑
这里就把二叉搜索树中删除节点遇到的情况都搞清楚。
有以下五种情况:
- 第一种情况:没找到删除的节点,遍历到空节点直接返回了
- 找到删除的节点
- 第二种情况:左右孩子都为空(叶子节点),直接删除节点, 返回NULL为根节点
- 第三种情况:删除节点的左孩子为空,右孩子不为空,删除节点,右孩子补位,返回右孩子为根节点
- 第四种情况:删除节点的右孩子为空,左孩子不为空,删除节点,左孩子补位,返回左孩子为根节点
- 第五种情况:左右孩子节点都不为空,则将删除节点的左子树头结点(左孩子)放到删除节点的右子树的最左面节点的左孩子上,返回删除节点右孩子为新的根节点。
第五种情况有点难以理解,看下面动画:
class Solution:
def deleteNode(self, root, key):
if root is None:
return root
# 单层逻辑
if root.val == key:
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
return None
elif root.left is None:
return root.right
elif root.right is None:
return root.left
else:
cur = root.right
while cur.left is not None:
cur = cur.left
cur.left = root.left
return root.right
if root.val > key: # 左
root.left = self.deleteNode(root.left, key)
if root.val < key: # 右
root.right = self.deleteNode(root.right, key)
return root
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/niuzai_/article/details/135118078
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Jmeter接口测试断言
- 计算机Java项目|java游戏账号交易系统
- JVM虚拟机系统性学习-JVM调优之GC日志分析
- Camtasia2024最新版本如何进行电脑录制屏幕?
- 实验九 基于FPGA的计数译码显示电路设计
- 高级别智能驾驶业务系列:港口作业仿真系统
- 机器学习与深度学习——使用paddle实现随机梯度下降算法SGD对波士顿房价数据进行线性回归和预测
- dp专题13 零钱兑换II
- 【爬虫课堂】如何高效使用短效代理IP进行网络爬虫
- 【MAUI】完整的登录界面~源码