相位相关匹配法的opencv C++实现
前言:一个图像拼接的小项目,用途场景,显微图像的拼接,或者只包含x,y平移的图像拼接。本来是显微镜拼接工具,MIST的核心拼接代码,matlab版的,已经开源。下面是地址,
GitHub - usnistgov/MIST at mist-matlab
?源码是一个显微镜的拼接工具,序列扫描,2D扫描的图像拼接,下面实现的只是两张图像的拼接,并且需要先验知识,输入图像1与输入图像2的相对位置,1在2的北边,1在2的西边,两种固定方向。
内容:
1.相位相关匹配法
相位相关图像匹配(Phase Correlation Image Matching)是一种用于在图像中寻找相似区域的方法,特别适用于图像的平移、旋转和缩放等变换。其原理基于图像的频域表示和互相关运算。
以下是相位相关图像匹配的基本流程:
预处理:首先,对待匹配的两幅图像进行预处理。这包括灰度化、归一化、去噪或滤波等操作,以提高匹配的准确性。
傅里叶变换:对两幅预处理后的图像应用傅里叶变换,将它们转换到频域。傅里叶变换将图像从空域表示转换为频域表示,其中频率较高的部分对应图像中的边缘和纹理信息。
计算互相关谱:通过计算参考图像和待匹配图像的频域表示之间的互相关谱,得到一个复数矩阵。互相关谱反映了两幅图像之间的相似度信息。
计算幅度谱:从互相关谱中提取幅度谱,即取复数矩阵的模。幅度谱表示图像中的结构信息,可以用来检测图像的平移、旋转和缩放等变换。
计算逆傅里叶变换:对幅度谱进行逆傅里叶变换,将其转换回空域表示。得到的结果是一个实数矩阵,称为相位相关图像。
寻找峰值:在相位相关图像中寻找峰值点,即响应最强的位置。峰值点的位置表示了两幅图像之间的最佳匹配位置。
精细化匹配:在峰值点附近进行精细化匹配,可以使用插值等方法来获取更精确的匹配结果。
相位相关图像匹配的原理是基于相位信息的保持不变性,相位谱的峰值对应于最佳匹配位置。通过将图像转换到频域,利用频域的特性进行匹配,可以提高匹配的准确性和鲁棒性。
需要注意的是,相位相关图像匹配方法在处理包含大量变形的图像时可能存在一些局限性。在这种情况下,可能需要使用更高级的图像匹配方法来获得更好的结果。
详细的物理原理参考这篇博客,图像配准之相位配准-CSDN博客?,当然目前相关的论文已经发展到可以计算图像的场景旋转,但是在显微镜扫描的场景中默认是没有旋转,尺度变化,畸变变形等情况,仅存在xy平移,虽然目前的载物台精度已达到很高的精度,但也很难直接反馈得到准确的像素偏移。具体原因可以稍微分析一下,像与物体的大小可以认为是一一对应的关系,像的尺度表示就是相机的像元尺寸,一般为2~7微米,显微镜系统的放大倍率,高倍的话就是10,20,40倍,那么可以计算大概计算一下,一个像元,也就是一个像素代表多少。以7微米,40倍为例,7/40 = 0.175 um = 175 nm,当然只能大概这么算,事实上与波长尺度相关的计算需要考虑的东西很多,比如显微镜的口径,还有NA数值孔径。emmm,有点扯远了,总之就是大概介绍一下。意思就是目前的电动载物台可以达到100nm但是逐像素的精准移动,很难,所以还是需要计算。
好了接下来看代码(github感觉有点麻烦,后期会试试):
配置:VS2022 opencv 4.6.0?
文件树:

?头文件,以及各类函数,还有主函数,第一次独立的写这种分文件类型的项目,写的拉跨还请包涵,以及当然可以转成类的形式,但感觉有点小麻烦,后期再修改吧。
1.PCIAM.h
#ifndef PCIAM_H
#define PCIAM_H
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/cuda.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <limits>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cuda;
struct PCC_type {
int x;
int y;
double value;
};
PCC_type initial(int x, int y, double value);
//图像显示
void showImg(Mat& Img, string windowname);
//图像预处理,数据转换,单通道
Mat Img_process(Mat& Img);
//计算PCM
Mat computePCM(Mat& I1, Mat& I2);
//峰值搜索
void peaksearch(Mat& PCM, int& num_peaks, vector<double>& max_value, vector<Point>& max_Loc);
//计算PCC
PCC_type computePCC(Mat& I1, Mat& I2, string& direction, Point& Loc);
//提取ROI
Mat grap_roi(Mat& Img, int x, int y);
//计算归一化互相关值
double computeNCC(Mat I1, Mat I2);
//加权融合
Mat awblending(const Mat& I1, const Mat& I2, int shiftx, int shifty);
//羽化融合
Mat featherblending(Mat& I1, Mat& I2, int& shiftx, int& shifty);
#endif // !PCIAM_H
?头文件,一些头文件,一些功能函数的声明,注释都有,所以就不详解了,所有函数,基本上都是使用opencv是实现的。
2.Img_process.cpp
#include "PCIAM.h"
Mat Img_process(Mat& Img) {
Mat Img_p;
extractChannel(Img, Img_p, 1); //提取绿色通道
Img_p.convertTo(Img_p, CV_64FC1);//转换数据类型 双精度浮点
Img_p = Img_p / sum(Img_p)[0];
//cout << Img_p.row(0) << endl;
//cout << "second" << endl;
//图像归一化
//double sum_Img = sum(Img_p)[0];
//sum(Img_p) 返回一个 Scalar 对象,这是一个包含四个元素的数组,
//对于单通道图像,只有第一个元素是有意义的,它代表所有像素值的总和。
//Img_p = Img_p / sum_Img;
return Img_p;
}这里是完全按照matlab代码来的,提取通道,一般绿色通道值更准确,然后转成double类型,再进行归一化,它这个归一化是除以所有像素点之和,而不是除以255之类的,需要注意。
3.computePCM函数
#include "PCIAM.h"
Mat computePCM(Mat& I1, Mat& I2) {
//傅里叶变换
Mat Img1_DFT, Img2_DFT;
dft(I1, Img1_DFT, DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT);
dft(I2, Img2_DFT, DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT);
//cout << Img1_DFT.row(0) << endl;
//Img2_DFT共轭变换后并相乘,
Mat FFT1;
mulSpectrums(Img1_DFT, Img2_DFT, FFT1, 0, true);
//替换零值
FFT1.forEach<Vec2d>([](Vec2d& value, const int* position) {
if (value[0] == 0 && value[1] == 0) {
value[0] = numeric_limits<double>::epsilon(); //当实部虚部都为0,只需要换实部即可
}
});
//计算模值
Mat channels[2];
split(FFT1, channels);
Mat abs;
magnitude(channels[0], channels[1], abs);
//计算互功率谱
Mat CPS;
Mat CPS_real = channels[0] / abs;
Mat CPS_imag = channels[1] / abs;
vector<Mat> channels2 = { CPS_real ,CPS_imag };
merge(channels2, CPS);
// 逆傅里叶变换
Mat PCM;
dft(CPS, PCM, DFT_INVERSE | DFT_REAL_OUTPUT | DFT_SCALE);
//先验经验,重叠部分不会在边缘,而PCIAM算法往往在边缘处的峰值高
//所以进行峰值过滤
PCM.row(0).setTo(Scalar(0.0));
PCM.row(PCM.rows - 1).setTo(Scalar(0.0));
PCM.col(0).setTo(Scalar(0));
PCM.col(PCM.cols - 1).setTo(Scalar(0.0));
return PCM;
}这一段就是PCIAM算法的核心了,计算两幅图像的峰值相关矩阵,也是完全按照matlab移植过来的,但是后面几行,是为了筛选一些不可能存在的情况,比如边缘处的完全重合,或者只有一行,或者一列重合等等情况,由于PCIAM算法在边缘处的响应值高,所以在一些场景下可能是一种干扰,所以进行了剔除,当然可以不剔除,就是对后期的峰值选取会有影响。

4.peaksearch
#include "PCIAM.h"
void peaksearch(Mat& PCM, int& num_peaks, vector<double>& max_value, vector<Point>& max_Loc) {
for (int i = 0; i < num_peaks; i++) {
double minValue, maxValue;
Point minLoc, maxLoc;
minMaxLoc(PCM, &minValue, &maxValue, &minLoc, &maxLoc);
max_value.push_back(maxValue);
max_Loc.push_back(maxLoc);
// 将找到的最大值置为一个较小的值,以便继续查找下一个最大值
PCM.at<double>(maxLoc) = -numeric_limits<double>::max();
}
}这步就是从峰值相关矩阵中,选择峰值点,由于存在噪声点,所以选取多个峰值点位置,这个看自己情况,一般10个。
5. compute_PCC
#include "PCIAM.h"
PCC_type computePCC(Mat& I1, Mat& I2, string& direction, Point& Loc) {
int h = I1.rows;
int w = I1.cols;
int x = Loc.x;
int y = Loc.y;
vector<int>m;
vector<int>n;
PCC_type PCC;
PCC = initial(0, 0, 0.0);
//8种可能的平移解释
if (direction == "north") {
m = { y,y,h - y,h - y,y,y,h - y,h - y };
n = { x,w - x,x,w - x,-x,x - w,-x,x - w };
}
else if (direction == "west") {
m = { y,y,h - y,h - y,-y,-y,y - h,y - h };
n = { x,w - x,x,w - x,x,w - x,x,w - x };
}
else {
cerr << "direction is wrong,please retry follow the ture direction" << endl;
return PCC;
}
vector<double>value;//ncc值
Point position;//最佳位置
for (int i = 0; i < m.size(); i++) {
Mat I1_roi = grap_roi(I1, n[i], m[i]);
Mat I2_roi = grap_roi(I2, -n[i], -m[i]);
//roi大小不一样,roi没有长或者框,直接返回n[i],m[i],-1
if (I1_roi.size() != I2_roi.size()) {
//cerr << "Error: Image sizes do not match." << endl;
PCC = initial(n[i], m[i], -1);
value.push_back(PCC.value);
}
else if (I1_roi.rows == 0 || I1_roi.cols == 0 || I2_roi.rows == 0 || I2_roi.cols == 0) {
//cerr << "roi is empty " << endl;
PCC = initial(n[i], m[i], -1);
value.push_back(PCC.value);
}
else {
value.push_back(computeNCC(I1_roi, I2_roi));
}
}
auto max_iter = max_element(value.begin(), value.end()); //max_element,返回的是最大位置处的迭代器
int idx = distance(value.begin(), max_iter); //得到最大值坐标
PCC = initial(n[idx], m[idx], value[idx]); //返回PCC内容
return PCC;
}由于选出来多个峰值点位置,都有可能是对的匹配位置,又因为傅里叶变换的周期性,每个峰值点位置,又存在多种变化(这部分解释可以看mist的说明文件),所以需要在原图上截取重叠部分计算NCC归一化互相关矩阵,来确定最优的位置。
6.featherblending 羽化融合
#include "PCIAM.h"
Mat featherblending(Mat& I1, Mat& I2, int& shiftx, int& shifty) {
//转成双精度浮点
I1.convertTo(I1, CV_64FC3);
I2.convertTo(I2, CV_64FC3);
//拼接后图像尺寸
int fusionW = abs(shiftx) + I1.cols;
int fusionH = abs(shifty) + I1.rows;
//创建一个画布
Mat fusionImg = Mat::zeros(fusionH, fusionW, I1.type());
//I1,I2起始位置的确定
int x1_st, y1_st, x2_st, y2_st;
if (shiftx >= 0) {
x1_st = 0;
x2_st = shiftx;
}
else {
x1_st = abs(shiftx);
x2_st = 0;
}
if (shifty >= 0) {
y1_st = 0;
y2_st = shifty;
}
else {
y1_st = abs(shifty);
y2_st = 0;
}
//先把I1放上去
I1.copyTo(fusionImg(Rect(x1_st, y1_st, I1.cols, I1.rows)));
//分别提取I1,I2的重叠区域
Mat roi1 = grap_roi(I1, shiftx, shifty);
Mat roi2 = grap_roi(I2, -shiftx, -shifty);
//创建掩码矩阵,这里是生成I1大小的羽化矩阵采用
float featherAmount = 1.5;//羽化量
Mat mask = Mat::zeros(I1.size(), CV_64FC3);
Mat hang = Mat::zeros(1, I1.cols, CV_64F);
Mat lie = Mat::zeros(I1.rows, 1, CV_64F);
for (int i = 1; i < hang.cols + 1; i++) {
hang.at<double>(0, i - 1) = min(i, hang.cols - i + 1);
}
for (int j = 1; j < lie.rows + 1; j++) {
lie.at<double>(j - 1, 0) = min(j, lie.rows - j + 1);
}
Mat channels[3];
channels[0] = lie * hang;
channels[1] = lie * hang;
channels[2] = lie * hang;
merge(channels, 3, mask);
//截取I1,I2重叠区域mask
Mat I1mask = grap_roi(mask, shiftx, shifty);
Mat I2mask = grap_roi(mask, -shiftx, -shifty);
I1mask.convertTo(I1mask, roi1.depth());
//融合计算
multiply(roi1, I1mask, roi1);
multiply(roi2, I2mask, roi2);
Mat blending = (roi1 + roi2) / (I1mask + I2mask);
cout << blending.size() << " " << blending.channels() << endl;
//计算I2中重叠部分的位置
// 计算子区域的起始和结束坐标
int x_st = max(0, -shiftx);
int y_st = max(0, -shifty);
int x_end = min(I2.cols, I2.cols + -shiftx);
int y_end = min(I2.rows, I2.rows + -shifty);
//将blending放入I2中
blending.copyTo(I2(Rect(x_st, y_st, x_end - x_st, y_end - y_st)));
//再将I2放入fusionImg中。
I2.copyTo(fusionImg(Rect(x2_st, y2_st, I2.cols, I2.rows)));
//将fusion转为CV_8UC3
fusionImg.convertTo(fusionImg, CV_8UC3);
return fusionImg;
}在确定出最佳位置后,根据二者位置,进行融合,融合方法采用羽化融合,可以自行百度,这里不详细解释。原理就是生成随中心距离变化的mask矩阵,对重叠部分进行羽化融合。
其余的工具文件。
1.grap_roi?
功能,给定一个图像,一个坐标点,从图像中提取出区域,x,y是起点。如果为负,则相反。
#include "PCIAM.h"
Mat grap_roi(Mat& Img, int x, int y) {
// 计算图像的宽度和高度
int w = Img.cols;
int h = Img.rows;
// 计算子区域的起始和结束坐标
int x_st = max(0, x);
int y_st = max(0, y);
int x_end = min(w, w + x);
int y_end = min(h, h + y);
// 计算宽度和高度
int width = x_end - x_st;
int height = y_end - y_st;
// 如果计算出的宽度或高度小于1,则返回空Mat
if (width < 1 || height < 1) {
return cv::Mat();
}
// 使用cv::Rect来裁剪子区域
cv::Rect region_of_interest(x_st, y_st, width, height);
return Img(region_of_interest).clone(); // 返回子区域的深拷贝
}PCC_type
一个结构体,含义最后每个点计算出的结果,一个该点的坐标。
#include "PCIAM.h"
PCC_type initial(int x, int y, double value) {
PCC_type p;
p.x = x;
p.y = y;
p.value = value;
return p;
}3.showImg
显示图片,自定义大小窗口
#include "PCIAM.h"
void showImg(Mat& Img, string windowname) {
namedWindow(windowname, WINDOW_NORMAL); //启动窗口
resizeWindow(windowname, 800, 600); //调整窗口大小
imshow(windowname, Img); //show图
}最后看下主函数:
main.cpp
#include "PCIAM.h"
int main() {
string Img1_fliepath = "D:/ManualWSI/C14_Liver fatty Degeneration/Liver_15.tif";
string Img2_fliepath = "D:/ManualWSI/C14_Liver fatty Degeneration/Liver_16.tif";
string direction = "north"; //west 或者north I1 在 I2的上面或者左边
//初始化opencv的cuda支持
cuda::setDevice(0);
//读图
Mat Img1 = imread(Img1_fliepath);
Mat Img2 = imread(Img2_fliepath);
double start = static_cast<double>(getTickCount()); //计时
//创建Img1,Img2的gpu副本
//GpuMat d_I1,d_I2;
//d_I1.upload(Img1);
//d_I2.upload(Img2);
//图像预处理,提取绿色通道,并归一化
Mat I1p = Img_process(Img1);
Mat I2p = Img_process(Img2);
//计算峰值相关矩阵
Mat PCM = computePCM(I1p, I2p);
//搜索峰值及其位置
int numPeaks = 1; //峰值搜索个数
vector<double> max_value;
vector<Point> max_Loc;
peaksearch(PCM, numPeaks, max_value, max_Loc);
//互相关筛选
int idx = 0;
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
double ncc_value = numeric_limits<double>::lowest();//最小值
for (int i = 0; i < numPeaks; i++) {
PCC_type ePCC = computePCC(I1p, I2p, direction, max_Loc[i]);
if (ePCC.value > ncc_value) {
x = ePCC.x;
y = ePCC.y;
ncc_value = ePCC.value;
}
}
cout << "匹配位置 x:" << x << " y:" << y << " value:" << ncc_value << endl;
Mat fusionImg1 = featherblending(Img1, Img2, x, y);
double end = static_cast<double>(getTickCount());
double totalTime = (end - start) / getTickFrequency();
cout << "Code executed in " << totalTime << " seconds." << endl; //计时结束
showImg(fusionImg1, "fusion_img1");
// Mat fusionImg2 = awblending(Img1, Img2, x, y);
// showImg(fusionImg2, "fusion_img2");
imwrite("liver.tif", fusionImg1);
waitKey();
return 0;
}以上就是全部文件,流程与步骤大致与mist,PCIAM算法相同。后续结果,
原图:
?结果:

还有一个竖直方向的拼接结果:
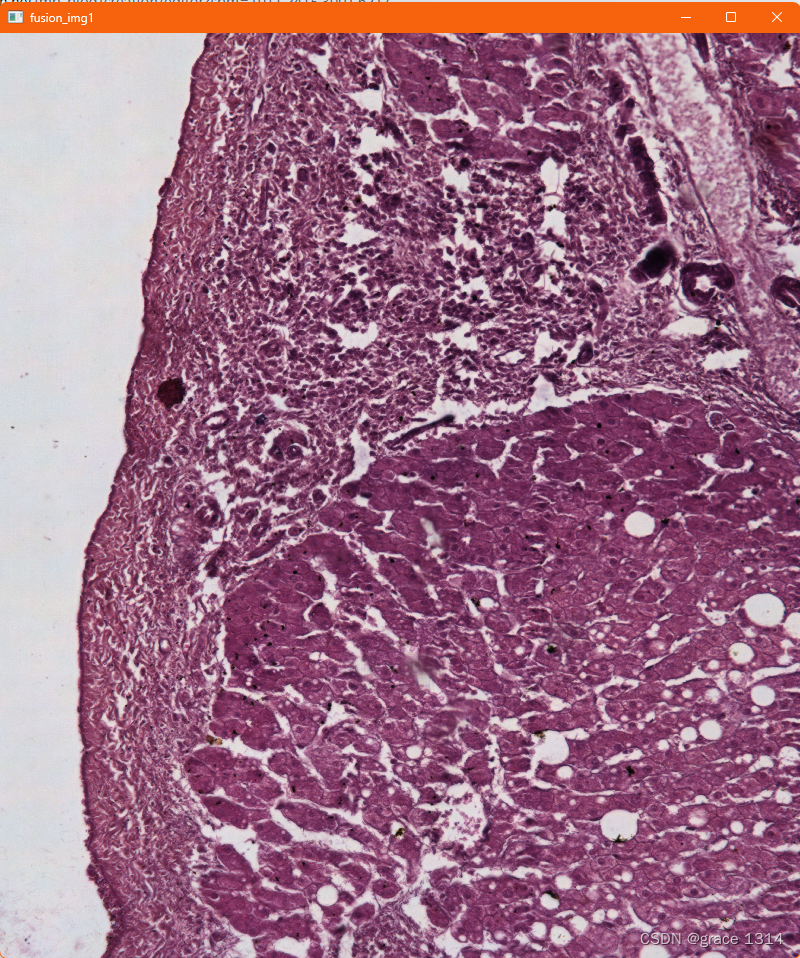
?效果还不错的。在剔除后,峰值搜索数只选一个也能实现拼接。当然实际工程中还是要将numPeaks设置为合理值才行。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 3D点云分割之SAGA(cvpr2023) 配置及使用
- Logistic回归实战
- 感染了后缀为.[sqlback@memeware.net].2700勒索病毒如何应对?数据能够恢复吗?
- ssm/php/node/python大学生心理咨询系统【计算机毕设】
- pytohn的with/as语句
- 2023 前端实战面试题
- java版微信小程序商城 免 费 搭 建 java版直播商城平台规划及常见的营销模式有哪些?电商源码/小程序/三级分销
- WebGL开发的行业应用
- 划片机,国内权威品牌博捷芯引领行业风向标
- 并发编程:线程同步基础:3.2、使用两个线程模拟生产者和消费者执行任务。