Lagrange对偶法
这里写自定义目录标题
Lagrange dual
上海交通大学 CS257 Linear and Convex Optimization
南京大学 Duality (I) - NJU
the standard form (5.1)
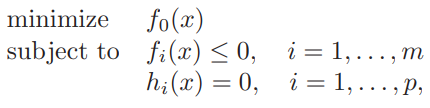
min
?
X
????
f
(
X
)
s
.
t
.
??
g
i
(
X
)
≤
0
,
?
i
=
1
,
…
,
m
,
\begin{array}{l} {\mathop {\min }_{\bf{X}} \;\;f\left( {\bf{X}} \right)}\\ {{\rm{s}}.{\rm{t}}.\;{g_i}\left( {\bf{X}} \right) \le 0,\forall i = 1, \ldots ,m,} \end{array}
minX?f(X)s.t.gi?(X)≤0,?i=1,…,m,?
5.1.1 The Lagrangian
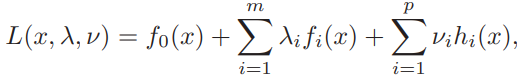
the dual variables or Lagrange multiplier vectors associated with the problem (5.1).
5.1.2 The Lagrange dual function
the minimum value of the Lagrangian
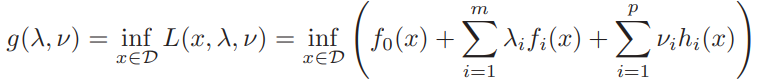
5.2 The Lagrange dual problem
the Lagrange dual problem associated with the problem (5.1).
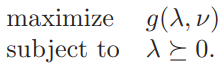
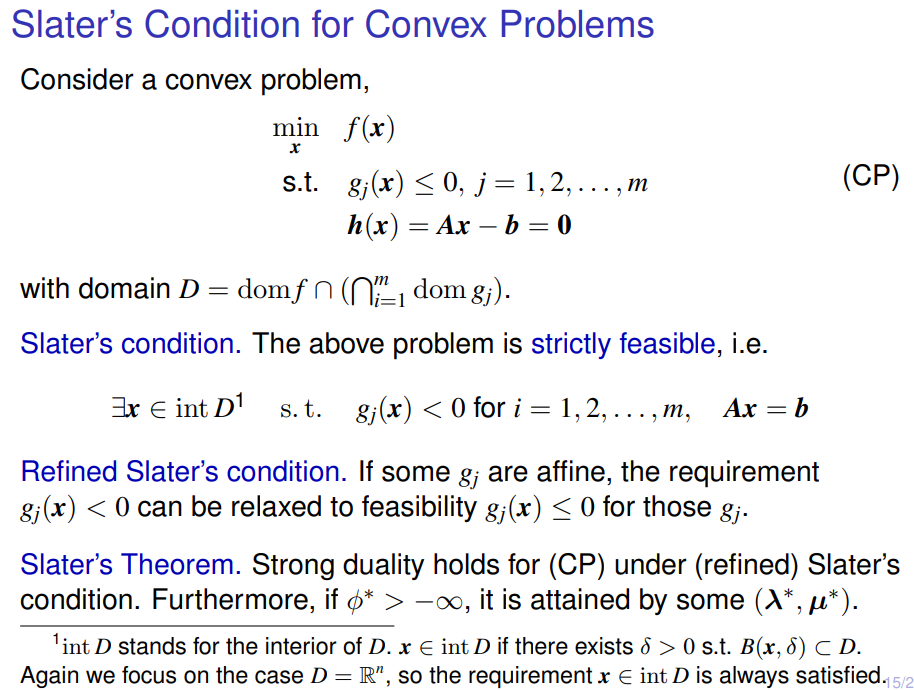
5.2.3 Strong duality and Slater’s constraint qualification

5.2.3 Strong duality and Slater’s constraint qualification
Slater’s theorem states that
strong duality holds, if Slater’s condition holds (and the problem is convex).
strong duality obtains, when the primal problem is convex and Slater’s condition holds
Slater’s Condition for Convex Problems
上海交通大学 CS257 Linear and Convex Optimization
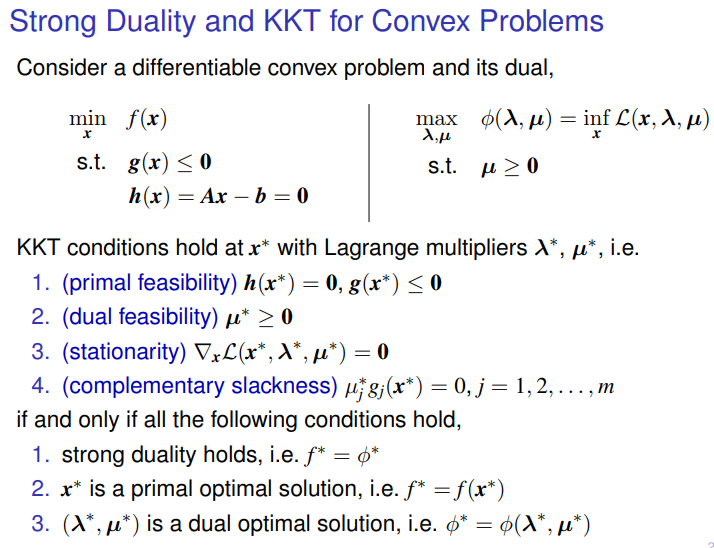
5.5.3 KKT optimality conditions
Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) conditions

for any optimization problem with differentiable objective and constraint functions for which strong duality obtains, any pair of primal and dual optimal points must satisfy the KKT conditions (5.49).
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- zabbix
- certmgr.msc
- Axure动态面板的使用
- im6ull学习总结(三-4)freetype显示单个字体
- java-使用代码获取classpath的路径
- 智能电子相册系统代码分析——图片上传和存储模块
- mtk 源码执行 development/tools/idegen/idegen.sh 卡住不动
- geemap学习笔记050:掩膜操作
- Navicat连接linux虚拟机上的MySQL
- P1563 [NOIP2016 提高组] 玩具谜题题解