SpringBoot读取配置文件中的内容
文章目录
配置文件application.yml:
server:
port: 8001
blog:
user:
name: xinliushijian
home: 徐州
work: 上海
marathonpb: 419
1. 读取配置文件application.yml中内容的方法
1.1 Environment
-
Environment 是 springboot 核心的环境配置接口,它提供了简单的方法来访问应用程序属性,包括系统属性、操作系统环境变量、命令行参数、和应用程序配置文件中定义的属性等等。
-
Springboot 程序启动加载流程里,会执行SpringApplication.run中的prepareEnvironment()方法进行配置的初始化
-
使用 Environment 方式来获取配置属性值非常简单,只要注入Environment类调用其方法getProperty(属性key)即可
示例代码:
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = XinJavaDemoApplication.class)
@Slf4j
public class EnvironmentTest {
@Resource
private Environment env;
@Test
public void test1() {
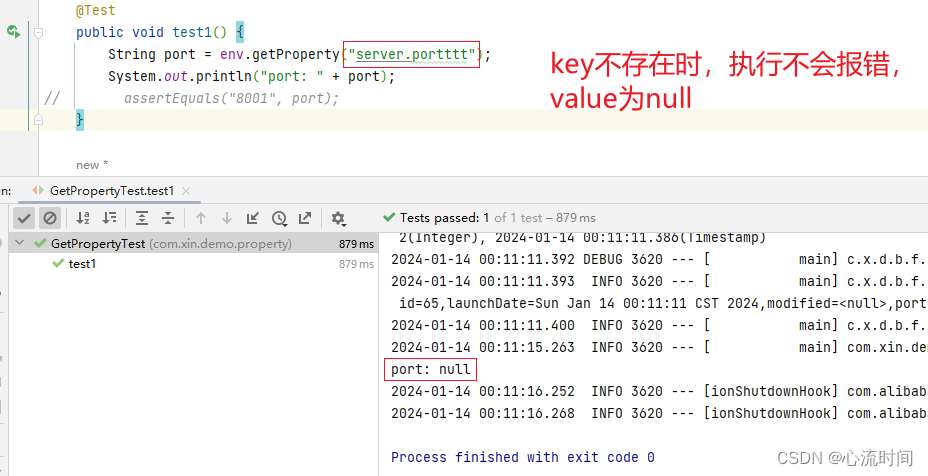
String port = env.getProperty("server.port");
System.out.println("port: " + port);
assertEquals(port, "8001");
}
@Test
public void test2() {
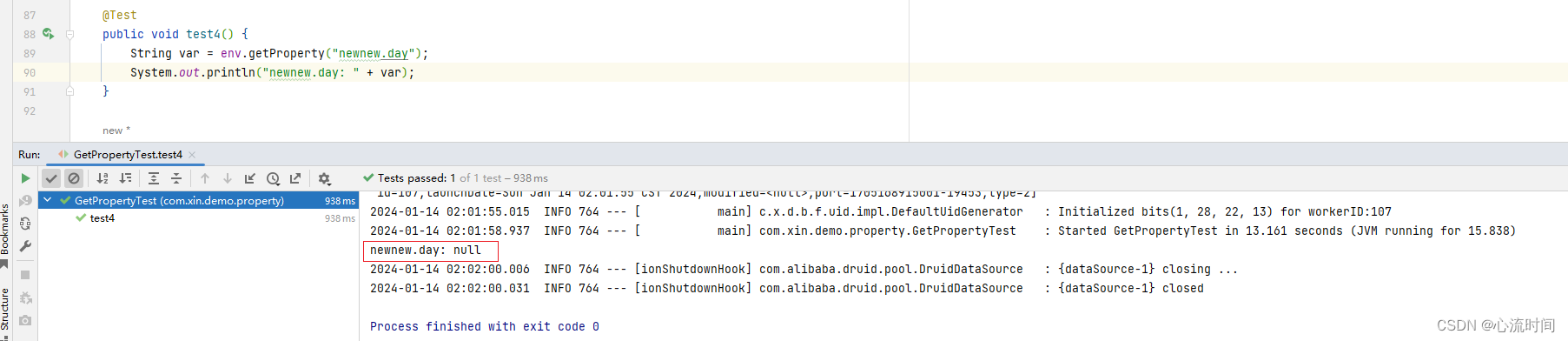
String home = env.getProperty("blog.user.home");
System.out.println("blog.user.home: " + home);
assertEquals(home, "徐州");
}
}
key不存在时,执行不会报错,value为null
1.2 @Value注解
-
@Value注解是Spring框架提供的用于注入配置属性值的注解,它可用于类的成员变量、方法参数和构造函数参数上,这个记住很重要!
-
在应用程序启动时,使用 @Value 注解的 Bean 会被实例化。所有使用了 @Value 注解的 Bean 会被加入到 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 的后置处理器集合中。
-
当后置处理器开始执行时,它会读取 Bean 中所有 @Value 注解所标注的值,并通过反射将解析后的属性值赋值给标有 @Value 注解的成员变量、方法参数和构造函数参数。
-
需要注意,在使用 @Value 注解时需要确保注入的属性值已经加载到 Spring 容器中,否则会导致注入失败。
-
只有标注了@Component、@Service、@Controller、@Repository 或 @Configuration 等容器管理注解的类,由 Spring 管理的 bean 中使用 @Value注解才会生效。而对于普通的POJO类,则无法使用 @Value注解进行属性注入。
-
如果我们想要获取 TestService 类中的某个变量的属性值,需要使用依赖注入的方式,而不能使用 new 的方式。通过依赖注入的方式创建 TestService 对象,Spring 会在创建对象时将对象所需的属性值注入到其中。
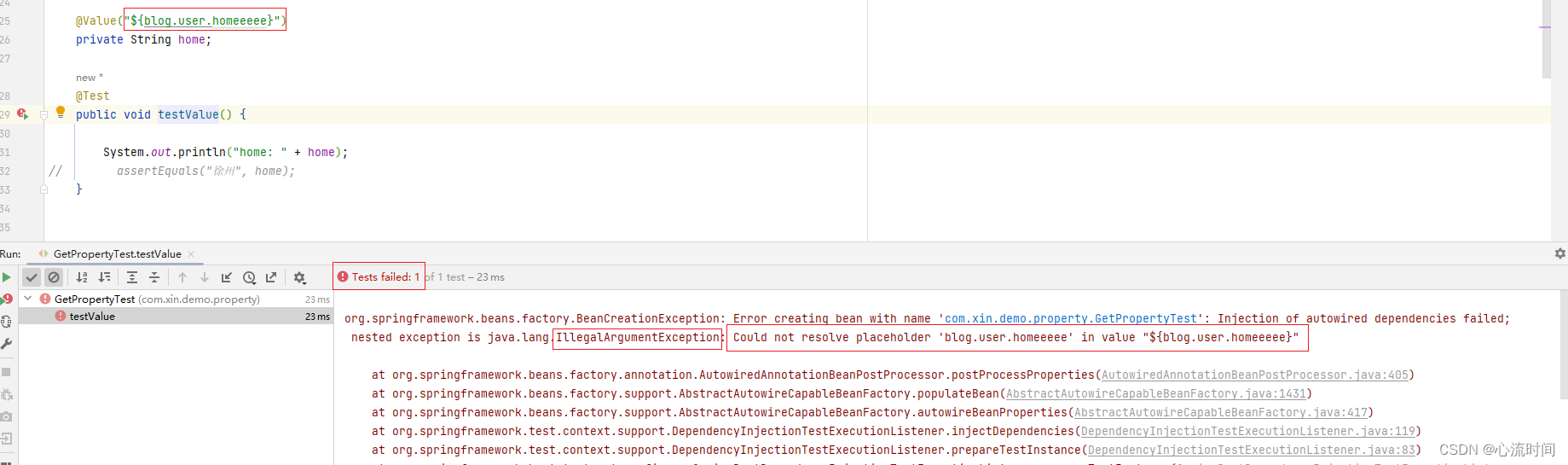
key不存在时,执行会报错:
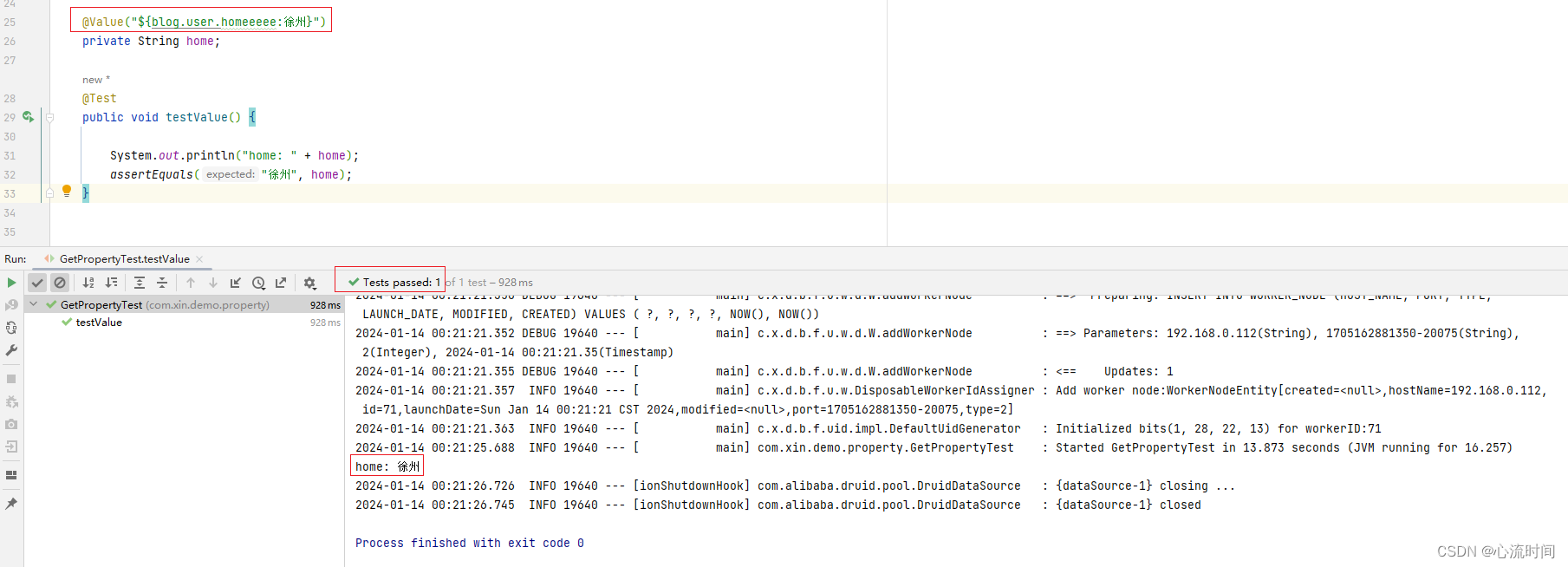
key不存在时,给出默认值,执行不会报错,结果就是取默认值:
示例代码:
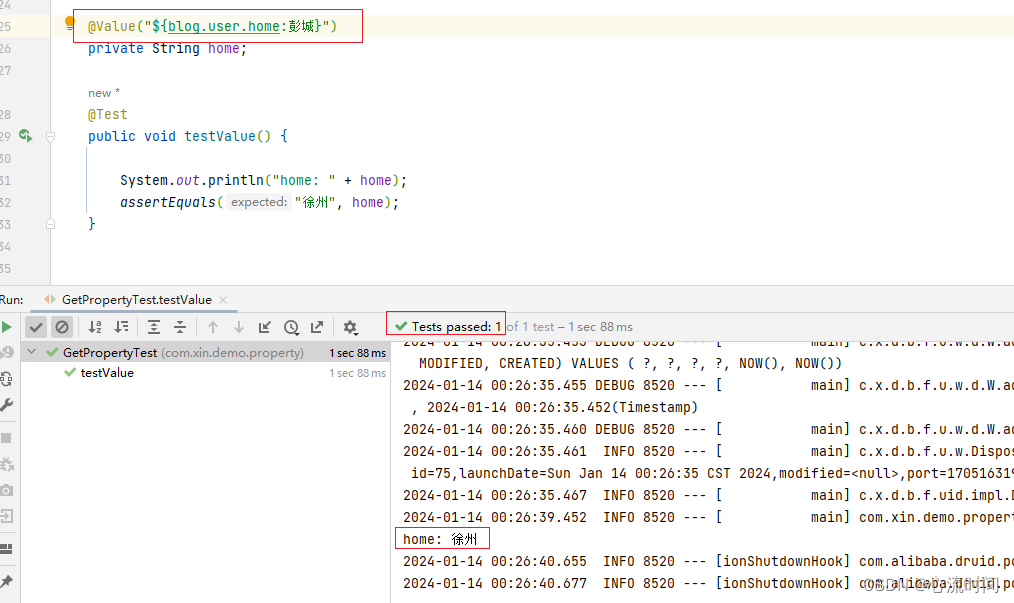
@Value("${blog.user.homeeeee:徐州}")
private String home;
@Test
public void testValue() {
System.out.println("home: " + home);
assertEquals("徐州", home);
}
正常取值:
1.3 @ConfigurationProperties 注解
@ConfigurationProperties注解是 SpringBoot 提供的一种更加便捷来处理配置文件中的属性值的方式,可以通过自动绑定和类型转换等机制,将指定前缀的属性集合自动绑定到一个Bean对象上
加载原理:
-
在 Springboot 启动流程加载配置的 prepareEnvironment() 方法中,有一个重要的步骤方法 bindToSpringApplication(environment),它的作用是将配置文件中的属性值绑定到被 @ConfigurationProperties 注解标记的 Bean对象中。但此时这些对象还没有被 Spring 容器管理,因此无法完成属性的自动注入。
-
那么这些Bean对象又是什么时候被注册到 Spring 容器中的呢?
-
这就涉及到了 ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor 类,它是 Bean后置处理器,负责扫描容器中所有被 @ConfigurationProperties 注解所标记的 Bean对象。如果找到了,则会使用 Binder 组件将外部属性的值绑定到它们身上,从而实现自动注入。
创建配置类,prefix + 属性名 = 配置key
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Data
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "blog.user")
public class BlogUser {
private String name;
private String home;
private String work;
private String marathon;
private String nameeeee;
}
示例代码:
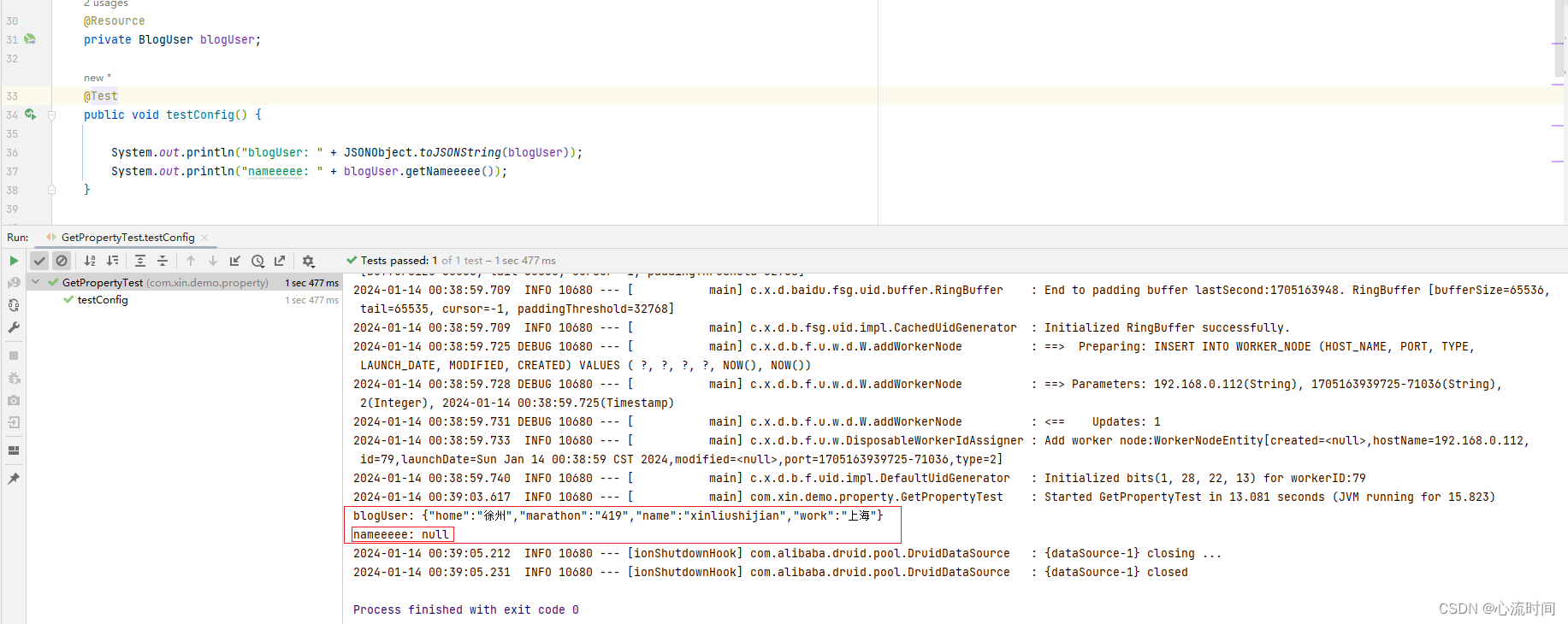
@Resource
private BlogUser blogUser;
@Test
public void testConfig() {
System.out.println("blogUser: " + JSONObject.toJSONString(blogUser));
System.out.println("nameeeee: " + blogUser.getNameeeee());
}
属性名在配置文件中不存在时,获取此属性值的时候,执行不会报错,结果为null
1.4 @PropertySources 注解,获取自定义配置文件中的内容,yml文件需要自行实现适配器
-
除了系统默认的 application.yml 或者 application.properties 文件外,我们还可能需要使用自定义的配置文件来实现更加灵活和个性化的配置。与默认的配置文件不同的是,自定义的配置文件无法被应用自动加载,需要我们手动指定加载。
-
@PropertySources 注解的实现原理相对简单,应用程序启动时扫描所有被该注解标注的类,获取到注解中指定自定义配置文件的路径,将指定路径下的配置文件内容加载到 Environment 中,这样可以通过 @Value 注解或 Environment.getProperty() 方法来获取其中定义的属性值了。
-
当加载.yaml文件时,启动项目居然报错了,经过一番摸索我发现,@PropertySources 注解只内置了PropertySourceFactory适配器。也就是说它只能加载.properties文件。
-
如果想要加载一个.yaml类型文件,则需要自行实现yaml的适配器 YamlPropertySourceFactory
-
而在加载配置时要显示的指定使用 YamlPropertySourceFactory适配器,这样就完成了@PropertySource注解加载 yaml 文件。
支持.properties文件,若是.yml文件则自行实现yaml的适配器,否则识别不了,@Value注解中没给默认值启动时就会报错
增加自定义配置文件
xinliushijian.properties:
blog.user.name=心流时间
blog.user.home=徐州
blog.user.work=上海
blog.user.marathon: 419
xinliu.yml:
new:
year: 2024
month: 01
day: 04
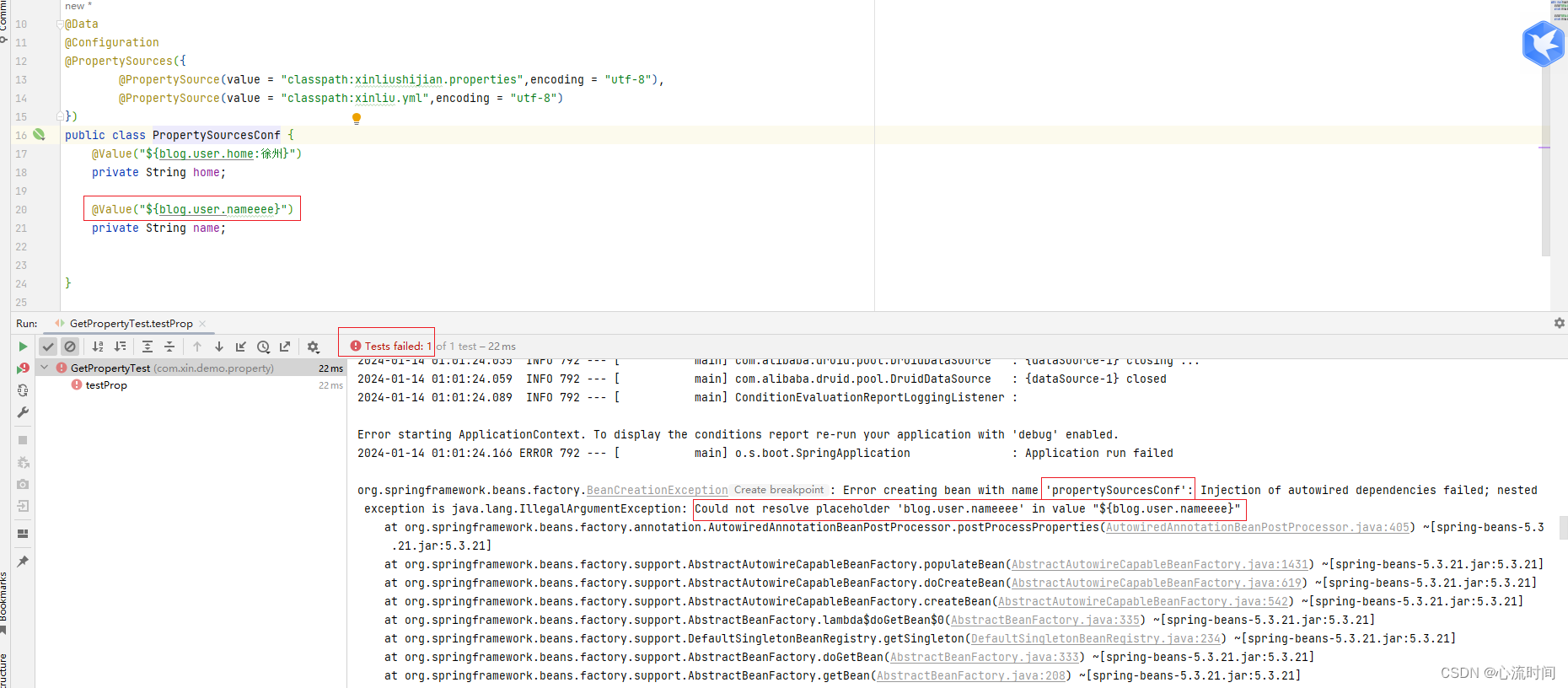
其中用到的@Value注解,在key不存在时报错(启动时)
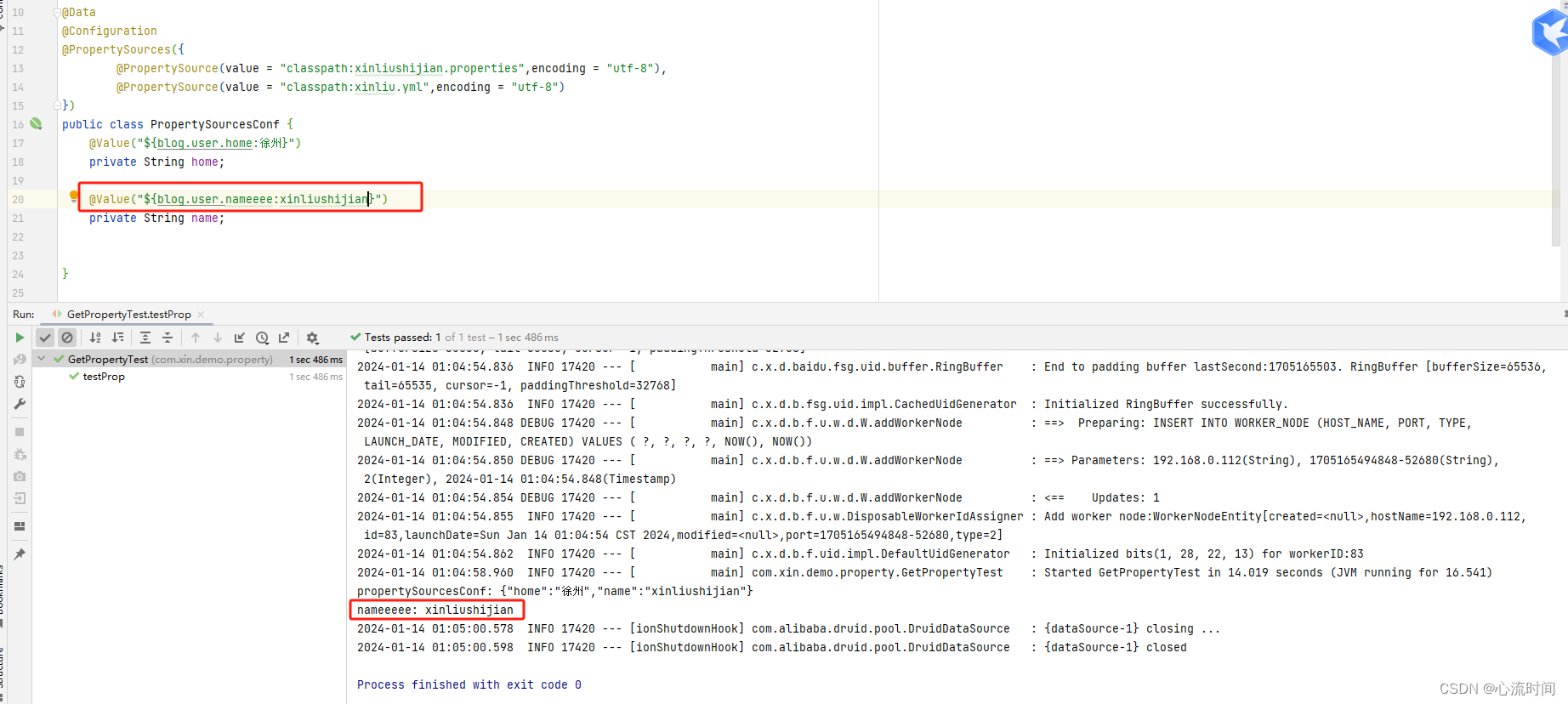
在@Value注解中加上默认值,执行就不报错了
不通过bean,通过new 构造器的方法得到对象获得属性值,执行不报错,结果为null
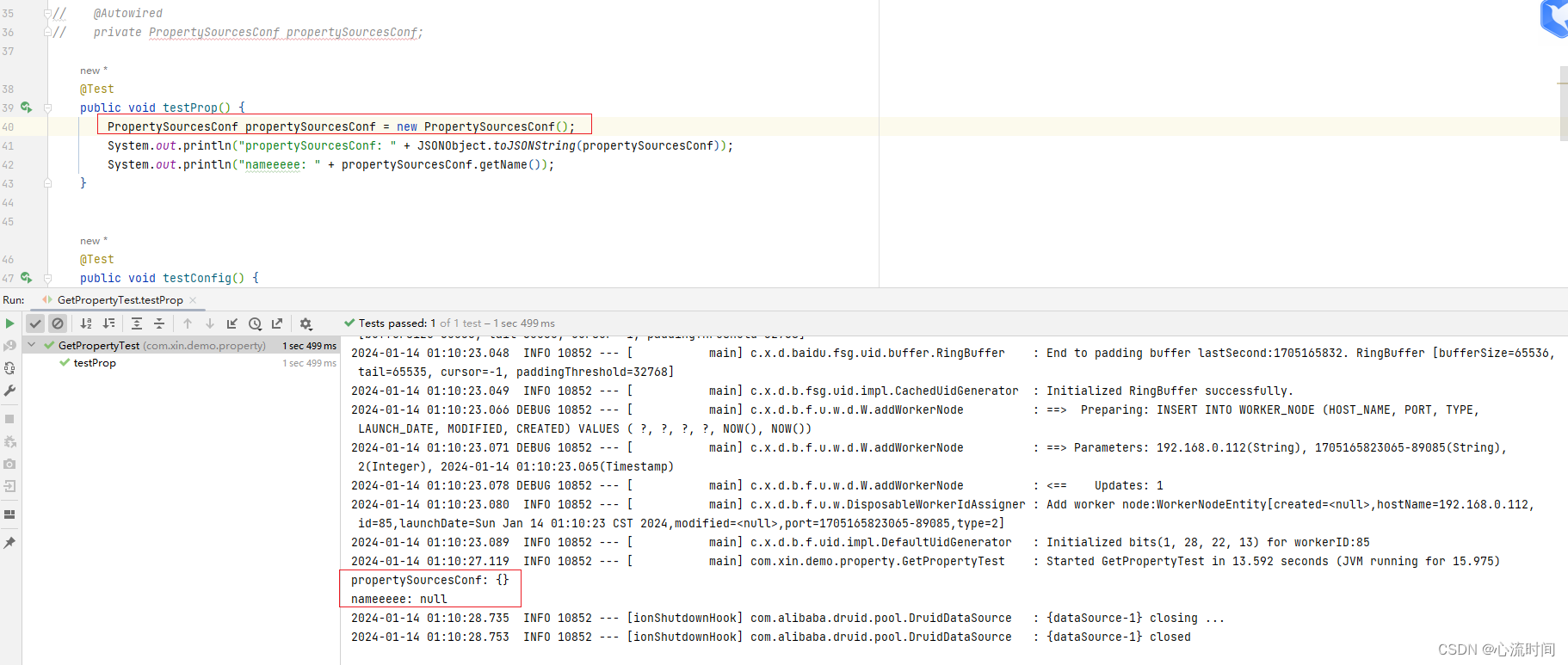
xinliu.yml文件中的内容识别不到,启动时就会报错,需要自行实现yaml的适配器
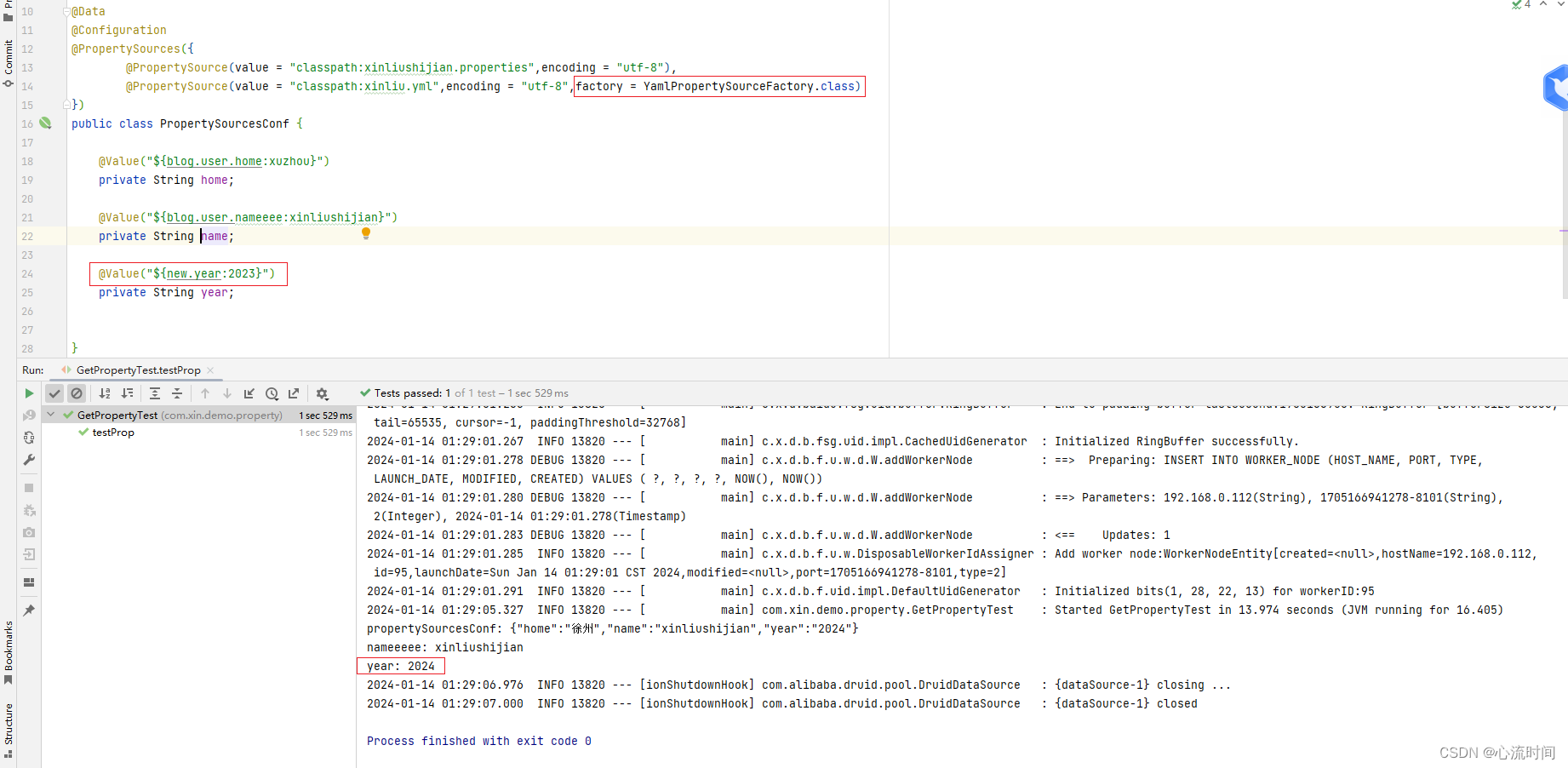
配置类示例代码
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySources;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
@Data
@Configuration
@PropertySources({
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:xinliushijian.properties",encoding = "utf-8"),
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:xinliu.yml",encoding = "utf-8",factory = YamlPropertySourceFactory.class)
})
public class PropertySourcesConf {
@Value("${blog.user.home:xuzhou}")
private String home;
@Value("${blog.user.nameeee:xinliushijian}")
private String name;
@Value("${new.year:2023}")
private String year;
}
yaml适配器示例代码:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.YamlPropertiesFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertiesPropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.EncodedResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PropertySourceFactory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class YamlPropertySourceFactory implements PropertySourceFactory {
@Override
public PropertySource<?> createPropertySource(String name, EncodedResource encodedResource) throws IOException {
YamlPropertiesFactoryBean factory = new YamlPropertiesFactoryBean();
factory.setResources(encodedResource.getResource());
Properties properties = factory.getObject();
return new PropertiesPropertySource(encodedResource.getResource().getFilename(), properties);
}
}
测试类示例代码:
@Autowired
private PropertySourcesConf propertySourcesConf;
@Test
public void testProp() {
System.out.println("propertySourcesConf: " + JSONObject.toJSONString(propertySourcesConf));
System.out.println("nameeeee: " + propertySourcesConf.getName());
System.out.println("year: " + propertySourcesConf.getYear());
}
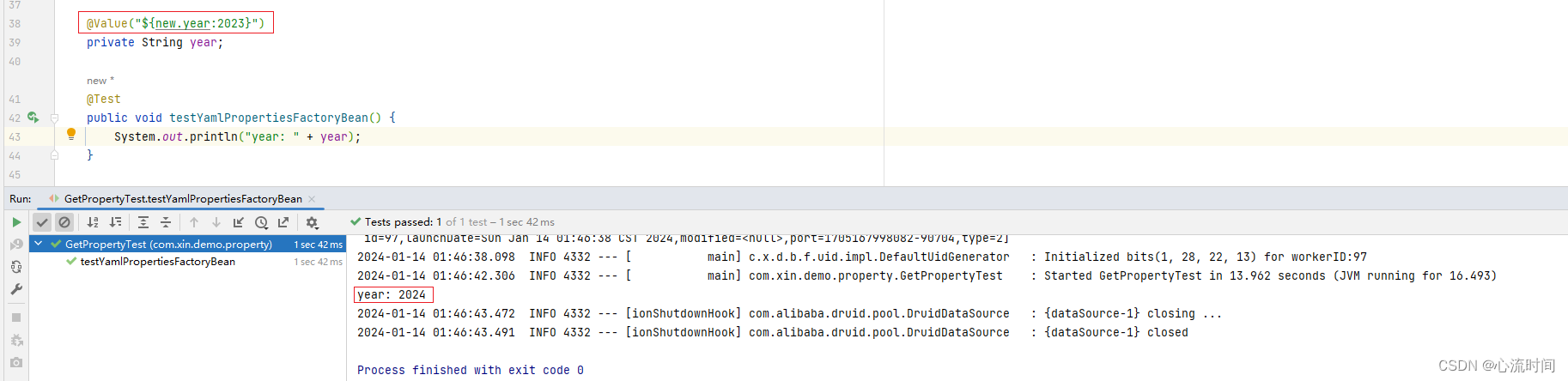
1.5 YamlPropertiesFactoryBean 加载 YAML 文件
我们可以使用 YamlPropertiesFactoryBean 类将 YAML 配置文件中的属性值注入到 Bean 中。
配置类
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.YamlPropertiesFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import java.util.Objects;
@Configuration
public class MyYamlConfig {
@Bean
public static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer yamlConfigurer() {
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer configurer = new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
YamlPropertiesFactoryBean yaml = new YamlPropertiesFactoryBean();
yaml.setResources(new ClassPathResource("xinliu.yml"));
configurer.setProperties(Objects.requireNonNull(yaml.getObject()));
return configurer;
}
}
可以通过 @Value 注解或 Environment.getProperty() 方法来获取其中定义的属性值。
1.6 各种方式总结
-
我们可以通过 @Value 注解、Environment 类、@ConfigurationProperties 注解、@PropertySource 注解等方式来获取配置信息。
-
其中,@Value 注解适用于单个值的注入,而其他几种方式适用于批量配置的注入。不同的方式在效率、灵活性、易用性等方面存在差异,在选择配置获取方式时,还需要考虑个人编程习惯和业务需求。
-
如果重视代码的可读性和可维护性,则可以选择使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解;如果更注重运行效率,则可以选择使用 Environment 类。总之,不同的场景需要选择不同的方式,以达到最优的效果。
2. 自定义的配置文件,如果不使用配置类加载,即使放在resources目录下也是获取不到内容的
自定义文件:xinliushijianhaha.yml
newnew:
year: 2024
month: 01
day: 04
测试结果:
3. 如果两个文件的key重复了,以默认配置文件application.yml中的内容为准
application.yml中的配置:
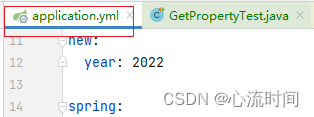
自定义配置文件(有用配置类自动加载)xinliu.yml:
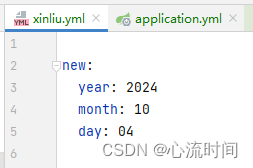
测试结果:
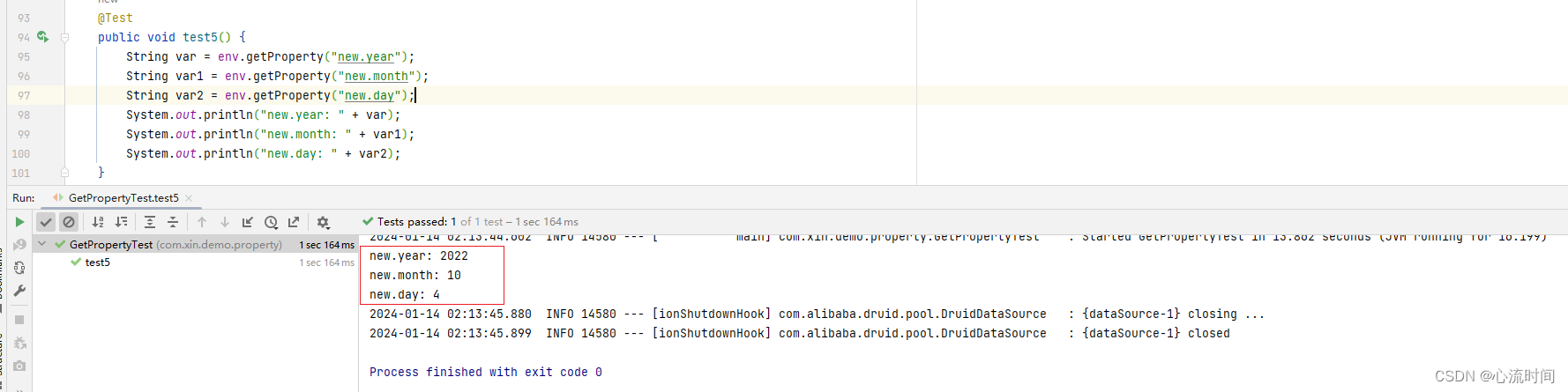
结果分析:
- application.yml这种默认的配置文件中的key和自定义配置文件中的key相等时,以application.yml中的内容为准
- 当配置内容是数字时,前面的0会消失(value是04,得到的结果是4,自动减去了0)
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 深入理解Spring Security授权机制原理
- 系统蓝屏检查工具bluescreenview和WinDbg对比
- 理解编译选项-no_unaligned_access
- Hands-On 基于加特兰 CAL77S244-AB 的短距雷达方案SOC 简介
- 关于 log4net 日志功能使用方法
- clip安装使用教程
- Python:最新Windows及Mac开发环境搭建(最详细版,附安装包)
- 在线直线度测量仪确保了出厂圆棒无不合格品
- 【运维】如何恢复默认的~/.bashrc
- 【课程-笔记】Vue3+React18+TS4入门到实战系统学习3大热门技术