【Elasticsearch篇】详解使用RestClient操作索引库的相关操作
文章目录

🍔什么是Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch是一个开源的分布式搜索和分析引擎,用于实时搜索、分析和存储大规模数据。它基于Apache Lucene库构建,提供了一个简单而强大的分布式搜索解决方案。
Elasticsearch具有以下特点:
- 分布式架构:Elasticsearch可以在多个节点上分布数据,并自动处理数据的复制、故障转移和负载均衡。
- 实时性能:Elasticsearch可以快速地进行实时搜索和分析,支持高并发查询。
- 多种数据类型支持:Elasticsearch支持各种类型的数据,包括结构化数据、无结构数据和地理位置数据等。
- 强大的查询功能:Elasticsearch提供了丰富而灵活的查询语言,可以进行全文搜索、过滤、聚合等操作。
- 可扩展性:Elasticsearch可以轻松地扩展到数百台甚至数千台服务器,以处理海量的数据和请求。
- 插件生态系统:Elasticsearch有一个活跃的插件生态系统,可以通过插件来扩展其功能,满足各种不同的需求。
由于其强大的功能和易于使用的特点,Elasticsearch被广泛应用于各种场景,包括企业搜索、日志分析、安全分析、商业智能等。
🌺什么是RestClient
在Java中,RestClient是一种用于与RESTful API进行通信的客户端库或框架,可以用来操作ES,这些客户端的本质就是组装DSL语句,通过http请求发给ES
🎆代码操作
相关代码我上传到网盘里面了
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1b6kMtGWL7FAK0f6R-3kyqA
提取码:lsyu
?初始化RestClient
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>7.12.1</version>
</dependency>
统一版本
在properties里面加上下面的代码
<elasticsearch.version>7.12.1</elasticsearch.version>
下面我们新创建一个单元测试类HotelIndexTest
写入下面的测试代码
package cn.itcast.hotel;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class HotelIndexTest {
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@Test
void testInit(){
System.out.println(client);
}
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
this.client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://192.168.125.131:9200")
));
}
//用完后销毁
@AfterEach
void tearDown() throws Exception {
this.client.close();
}
}
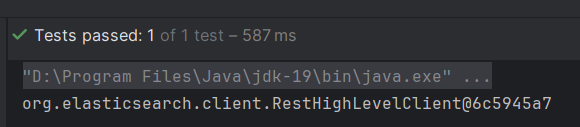
至此,初始化完成
?使用RestClient操作索引库
新建一个类,写入下面的代码,用来定义mapping映射的JSON字符串常量:
package cn.itcast.hotel.constants;
public class HotelConstants {
public static final String MAPPING_TEMPLATE = "{\n" +
" \"mappings\": {\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"id\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"name\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"address\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"index\": false\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"price\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"score\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"brand\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"city\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"starName\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"business\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"location\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"geo_point\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"pic\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"index\": false\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"all\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";
}
我们继续使用上面的测试类,新建一个测试对象,代码如下
@Test
void createHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备请求的参数:DSL语句
request.source(MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON);
// 3.发送请求
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
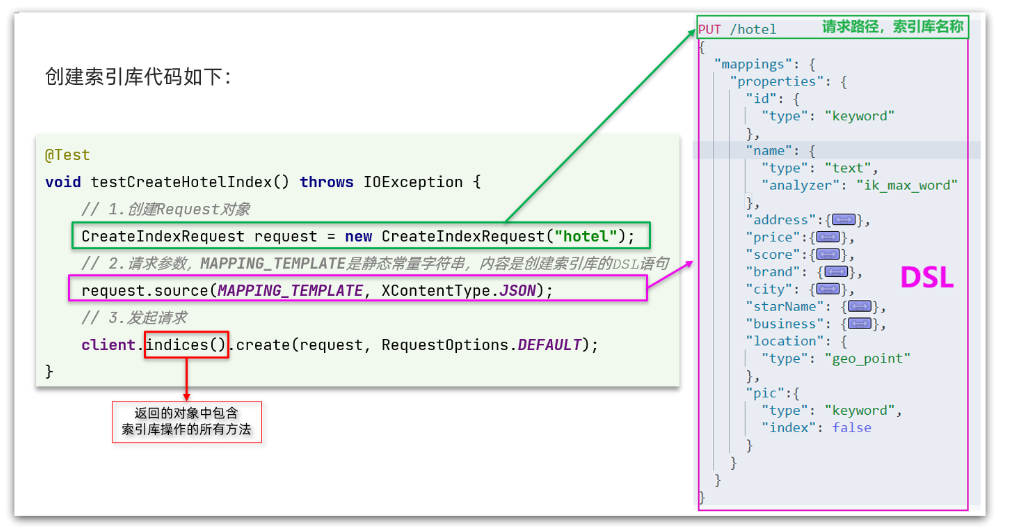 代码分为三步:
代码分为三步:
- 1)创建Request对象。因为是创建索引库的操作,因此Request是CreateIndexRequest。
- 2)添加请求参数,其实就是DSL的JSON参数部分。因为json字符串很长,这里是定义了静态字符串常量MAPPING_TEMPLATE,让代码看起来更加优雅。
- 3)发送请求,client.indices()方法的返回值是IndicesClient类型,封装了所有与索引库操作有关的方法。
我们运行一下上面的测试代码,然后去浏览器看一下效果
注意不要导错包了,我们测试类使用中的包是
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest;
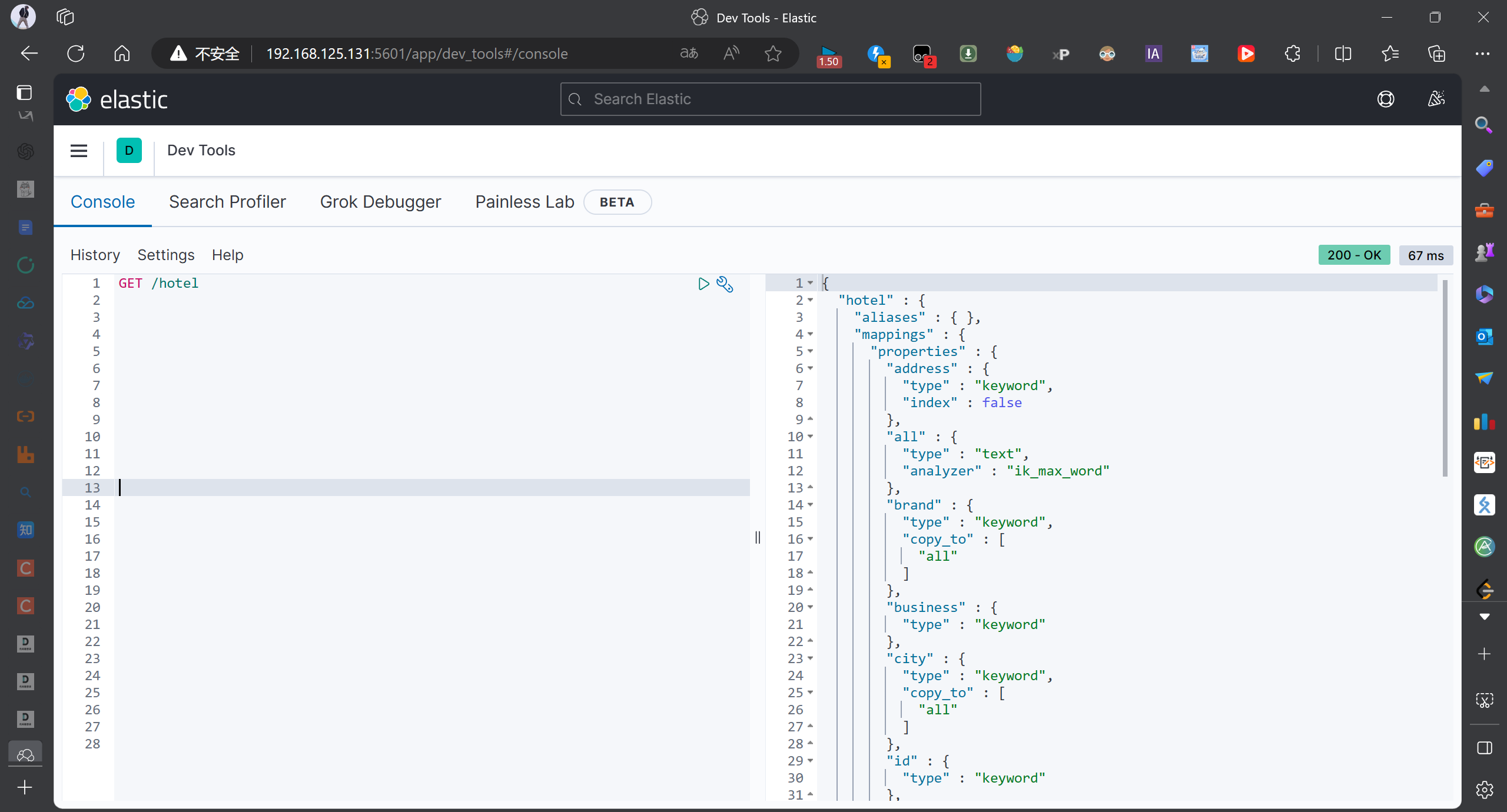
查询到了结果
?使用RestClient删除索引库
我们继续使用上面的测试类,加入下面的代码
- 1)创建Request对象。这次是DeleteIndexRequest对象
- 2)准备参数。这里是无参
- 3)发送请求。改用delete方法
@Test
void testDeleteHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.发送请求
client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
?使用RestClient判断索引库是否存在
我们继续使用上面的测试类,加入下面的代码
- 1)创建Request对象。这次是GetIndexRequest对象
- 2)准备参数。这里是无参
- 3)发送请求。改用exists方法
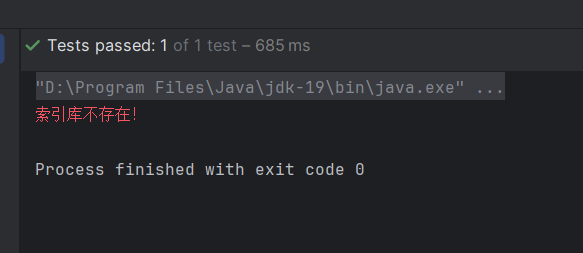
@Test
void testExistsHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.发送请求
boolean exists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 3.输出
System.err.println(exists ? "索引库已经存在!" : "索引库不存在!");
}
在技术的道路上,我们不断探索、不断前行,不断面对挑战、不断突破自我。科技的发展改变着世界,而我们作为技术人员,也在这个过程中书写着自己的篇章。让我们携手并进,共同努力,开创美好的未来!愿我们在科技的征途上不断奋进,创造出更加美好、更加智能的明天!

本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 清华裴丹|大模型时代的AIOps
- python怎么编写一个登录界面,python做用户登录界面
- 【分布式微服务专题】SpringSecurity OAuth2快速入门
- RK3568平台(网络篇) 有线网络基本概念及测试手法
- Windows10开启本地代理设置
- Java基础
- 【代码解析】代码解析之文件下载(1)
- OpenBMC hwmon内核子系统
- 【论文阅读笔记】ISINet: An Instance-Based Approach for Surgical Instrument Segmentation
- 九:day01_ 消息队列01