Android codec2 视频框架之编码输出内存管理
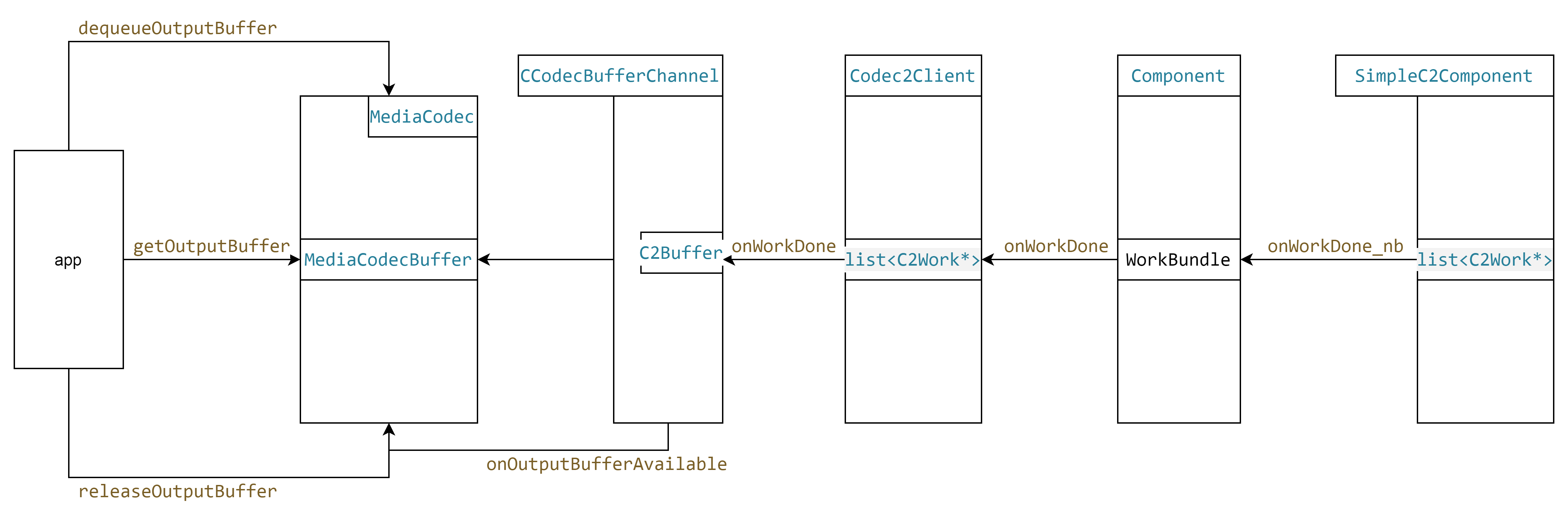
buffer在框架中的流动流程,从buffer的申请、填充数据到binder中传递、转换为应用层数据、从应用层释放。
围绕以下的方面:
-
buffer的申请
-
如何决定是哪个pool以及哪种类型的申请方式
-
pool的创建过程
-
pool中申请buffer、释放buffer的流程
-
-
buffer如何从c2的服务端传递到client端
- buffer生命周期
-
c2服务端的buffer类型转换为MediaCodec应用端的数据
- 应用端MediaCodecbuffer的申请
- buffer转换
- MediaCodecbuffer复用
pool的创建
-
fetchLinearBlock
以c2SoftHevcEnc 为例,在取编码数据之前首先通过fetchLinearBlock先从已经创建好的pool中获取buffer。
C2MemoryUsage usage = {C2MemoryUsage::CPU_READ, C2MemoryUsage::CPU_WRITE}; // TODO: error handling, proper usage, etc. c2_status_t err = pool->fetchLinearBlock(mOutBufferSize, usage, &mOutBlock); if (err == C2_OK) { mOutputBlockPool = std::make_shared<BlockingBlockPool>(blockPool); }-
GetCodec2BlockPool
上述的pool 是在simpleC2componet 中获取到并通过process(work, mOutputBlockPool);传递的。simpleC2componet的pool也是通过poolId 从已经创建的pool cache中获取。
C2BlockPool::local_id_t poolId =
outputFormat.value == C2BufferData::GRAPHIC
? C2BlockPool::BASIC_GRAPHIC
: C2BlockPool::BASIC_LINEAR;
if (params.size()) {
C2PortBlockPoolsTuning::output *outputPools =
C2PortBlockPoolsTuning::output::From(params[0].get());
if (outputPools && outputPools->flexCount() >= 1) {
poolId = outputPools->m.values[0];
}
}
std::shared_ptr<C2BlockPool> blockPool;
err = GetCodec2BlockPool(poolId, shared_from_this(), &blockPool);
process(work, mOutputBlockPool);
-
createBlockPool
simpleC2componet的poolId 是怎么获取的?总的来说是在CCodecBufferChannel 的start中根据componet组件中定义的参数来决定的(比如编码输出allocateId默认是ION(dmaheap),pool是linear一维类型),poolid在创建好pool后获取得到。得到后通过config 配置到组件中,这样在simplec2compoent就直接获取之前创建好的pool了。
err = mComponent->createBlockPool(
pools->outputAllocatorId, &pools->outputPoolId, &pools->outputPoolIntf);
std::unique_ptr<C2PortBlockPoolsTuning::output> poolIdsTuning =
C2PortBlockPoolsTuning::output::AllocUnique({ pools->outputPoolId });
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<C2SettingResult>> failures;
err = mComponent->config({ poolIdsTuning.get() }, C2_MAY_BLOCK, &failures);
-
C2PooledBlockPool
componet的createBlockPool会调用到c2store中的createBlockPool,根据之前决定的allocateId,走到ION的分支
在这个分支中 首先获取Allocator,并将Allocator传递到C2PooledBlockPool中。C2PooledBlockPool会创建bufferpool管理对象。在这个管理对象中实现对buffer的申请,回收,状态记录等等操作。
c2_status_t CreateCodec2BlockPool(
C2PlatformAllocatorStore::id_t allocatorId,
const std::vector<std::shared_ptr<const C2Component>> &components,
std::shared_ptr<C2BlockPool> *pool) {
pool->reset();
return sBlockPoolCache->createBlockPool(allocatorId, components, pool);
}
c2_status_t createBlockPool(
C2PlatformAllocatorStore::id_t allocatorId,
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<const C2Component>> components,
C2BlockPool::local_id_t poolId,
std::shared_ptr<C2BlockPool> *pool) {
case C2PlatformAllocatorStore::ION: /* also ::DMABUFHEAP */
res = allocatorStore->fetchAllocator(
C2PlatformAllocatorStore::ION, &allocator);
if (res == C2_OK) {
std::shared_ptr<C2BlockPool> ptr(
new C2PooledBlockPool(allocator, poolId), deleter);
*pool = ptr;
mBlockPools[poolId] = ptr;
mComponents[poolId].insert(
mComponents[poolId].end(),
components.begin(), components.end());
}
pool 中申请内存
代码位置frameworks\av\media\codec2\vndk\C2Buffer.cpp.
从pool创建可知管理在C2PooledBlockPool类当中。C2PooledBlockPool Impl创建时传递两个参数 一个是allocator、一个是bufferPoolMananger。
class C2PooledBlockPool::Impl {
public:
Impl(const std::shared_ptr<C2Allocator> &allocator)
: mInit(C2_OK),
mBufferPoolManager(ClientManager::getInstance()),
mAllocator(std::make_shared<_C2BufferPoolAllocator>(allocator)) {
if (mAllocator && mBufferPoolManager) {
if (mBufferPoolManager->create(
mAllocator, &mConnectionId) == ResultStatus::OK) {
return;
}
}
mInit = C2_NO_INIT;
}
}
-
allocator
用系统的接口申请dma malloc 或者ion的内存。 在Android12 上面一般为dma的内存。
在createBlockPool的fetchAllocator获取分配器时创建了一个C2DmaBufAllocator并传递到Impl中。
这里同样有可能有多个分配的方式 基类是C2Allocator。-
C2DmaBufAllocator的alloc 调用到system 的libdmabufheap中Alloc进行真正的buffer 申请
frameworks\av\media\codec2\vndk\C2DmaBufAllocator.cpp C2DmaBufAllocation::C2DmaBufAllocation(BufferAllocator& alloc, size_t allocSize, size_t capacity, C2String heap_name, unsigned flags, C2Allocator::id_t id) : C2LinearAllocation(capacity), mHandle(-1, 0) { int bufferFd = -1; int ret = 0; bufferFd = alloc.Alloc(heap_name, allocSize, flags); } system\memory\libdmabufheap\BufferAllocator.cpp int BufferAllocator::Alloc(const std::string& heap_name, size_t len, unsigned int heap_flags, size_t legacy_align) { int fd = DmabufAlloc(heap_name, len); if (fd < 0) fd = IonAlloc(heap_name, len, heap_flags, legacy_align); return fd; }
-
-
bufferPoolManager:
获取ClientManager类。C2PooledBlockPool的操作都是通过调用bufferPoolManager来实现的。mBufferPoolManager 是通过创建
BufferPoolClient来进行管理的。创建出来的client会存储在mActive.mClients中。 -
ClientManager类: 创建Accessor 并将allocator传递的里面。真正申请内存是在Access类当中。
-
BufferPoolClient类:创建的时候会传递Accessor 并调用accessor的connect 进行连接
Access 类: 创建BufferPool 结构体mBufferPool 进行管理, 这边才是真正的pool实现的地方。 -
BufferPool: 管理bufferpool的状态信息,管理buffer的申请和轮转。 同时也可以管理不同buffer pool 客户端buffer的转换。
-
AccessorImpl:通过bufferId来进行bufferpool的管理。 存储的是bufferId 和 native_handle_t的对应关系。相关的接口
- allocate: 从pool中free的buffer 取出一个,没有的话进行申请。申请之后将bufferpool 中对应buffer的引用加一。并加入到mUsingBuffers中
- transfer: To From是记录将buffer 从HIDL 服务端传递到客户端的信息。对于buffer的处理记录transaction的次数。
首先是TO 然后From 最后result。 - release 和allocte的操作对应, 是找到bufferID的buffer,然后重新返回到pool。
pool中申请内存:fetchLinearBlock根据前面的层级关系, 这个alloc会一路调用到AccessorImpl中。在AccessorImpl, 会先从mBufferPool中看一下能不能获取到freebuffer 获取不到在创建新的,新的内存从dmabuffer中申请出来 并将新的buffer加入到bufferpool中。
buffer 从service传递到client
-
buffer 从服务端到客户端
从pool中取到一个dmabuffer, 这个buffer将硬件或软件编码后的数据拷贝到这里面。通过copomnet onworkDone传递到client端。传递过程需要进行两次的结构体的转换
-
为什么需要转换
使用了HIDL,是将服务端的数据结构体传递出来 给到客户端的时候,先要转换为HIDL的结构体。
然后从HIDL的结构体转换为客户端的。 -
具体如何实现的
首先在创建compont的时候会注册compont的listener到simpleC2componet。同时clinet也会注册listener到component.
Return<void> ComponentStore::createComponent(
const hidl_string& name,
const sp<IComponentListener>& listener,
const sp<IClientManager>& pool,
createComponent_cb _hidl_cb) {
component->initListener(component);
}
void Component::initListener(const sp<Component>& self) {
std::shared_ptr<C2Component::Listener> c2listener =
std::make_shared<Listener>(self);
c2_status_t res = mComponent->setListener_vb(c2listener, C2_DONT_BLOCK);
if (res != C2_OK) {
mInit = res;
}
}
struct Component::Listener : public C2Component::Listener {
virtual void onWorkDone_nb(
std::weak_ptr<C2Component> /* c2component */,
std::list<std::unique_ptr<C2Work>> c2workItems) override {
sp<IComponentListener> listener = mListener.promote();
if (!objcpy(&workBundle, c2workItems, strongComponent ?
&strongComponent->mBufferPoolSender : nullptr)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Component::Listener::onWorkDone_nb -- "
<< "received corrupted work items.";
endTransferBufferQueueBlocks(c2workItems, false, true);
return;
}
Return<void> transStatus = listener->onWorkDone(workBundle);
}
}
这样simpleC2compont 处理完一帧后会回调到componet 中
componet中调用objcpy将C2Work转换为HIDL的workBundle,转换后回调到clinet中
client 再次将HIDL的workBundle转换为非HIDL的C2Work,返回给ccodecbufferChannel。
struct Codec2Client::Component::HidlListener : public IComponentListener {
std::weak_ptr<Component> component;
std::weak_ptr<Listener> base;
virtual Return<void> onWorkDone(const WorkBundle& workBundle) override {
std::list<std::unique_ptr<C2Work>> workItems;
if (!objcpy(&workItems, workBundle)) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "onWorkDone -- received corrupted WorkBundle.";
return Void();
}
// release input buffers potentially held by the component from queue
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Component> strongComponent =
component.lock();
if (strongComponent) {
strongComponent->handleOnWorkDone(workItems);
}
if (std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Listener> listener = base.lock()) {
listener->onWorkDone(component, workItems);
} else {
LOG(DEBUG) << "onWorkDone -- listener died.";
}
return Void();
}
}
C2buffer转换为MediaCodecBuffer
根据前面的信息client的onWorkDone 首先回调到CCodec, CCodec回调到CCodecBufferChannel
-
CCodecBufferChannel onWorkDone
- 根据work的信息进行 一系列的处理, 如输出帧的情况,传递的参数是不是发生了变化等等。
- 处理完成之后 就要将C2buffer转换为MediaCodecBuffer。转换流程是先push 到一个pending的双向队列,先push到队列尾,然后里面就从队列头取出来。
- 如果是编码输出的,将这个buffer拷贝到初始化时申请的output->buffers中。(linaer 拷贝c2buffer内容到MediaCodecbuffer、gralloc共享这块内存到MediaCodecbuffer)
- 转换完成之后从队列中将C2buffer pop出来 并调用C2buffer的析构函数,析构会调用release 将buffer push回pool中
-
应用端MediaCodecbuffer的申请(output->buffers的申请)
- 当为编码时申请的是linearOutputBuffers。linearOutputBuffers是使用的malloc的方式进行申请的。
最开始申请的size为constexpr size_t kLinearBufferSize = 1048576;
申请到的buffer push到mBuffers 进行管理。
- 当为编码时申请的是linearOutputBuffers。linearOutputBuffers是使用的malloc的方式进行申请的。
output->buffers.reset(new LinearOutputBuffers(mName));
class LinearOutputBuffers : public FlexOutputBuffers {
public:
LinearOutputBuffers(const char *componentName, const char *name = "1D-Output")
: FlexOutputBuffers(componentName, name) { }
if (oStreamFormat.value == C2BufferData::LINEAR) {
if (buffersBoundToCodec) {
// WORKAROUND: if we're using early CSD workaround we convert to
// array mode, to appease apps assuming the output
// buffers to be of the same size.
output->buffers = output->buffers->toArrayMode(numOutputSlots);
}
}
std::unique_ptr<OutputBuffersArray> FlexOutputBuffers::toArrayMode(size_t size) {
std::unique_ptr<OutputBuffersArray> array(new OutputBuffersArray(mComponentName.c_str()));
array->transferFrom(this);
std::function<sp<Codec2Buffer>()> alloc = getAlloc();
array->initialize(mImpl, size, alloc);
return array;
}
std::function<sp<Codec2Buffer>()> LinearOutputBuffers::getAlloc() {
return [format = mFormat]{
// TODO: proper max output size
return new LocalLinearBuffer(format, new ABuffer(kLinearBufferSize));
};
ABuffer::ABuffer(size_t capacity)
: mRangeOffset(0),
mInt32Data(0),
mOwnsData(true) {
mData = malloc(capacity);
if (mData == NULL) {
mCapacity = 0;
mRangeLength = 0;
} else {
mCapacity = capacity;
mRangeLength = capacity;
}
}
- buffer转换
是从申请的mBuffer中取出一个可用的MediaCodecbuffer 返回出去。
OutputBuffersArray::registerBuffer
status_t err = mImpl.grabBuffer(
index,
&c2Buffer,
[buffer](const sp<Codec2Buffer> &clientBuffer) {
return clientBuffer->canCopy(buffer);
});
if (!c2Buffer->copy(buffer)) {
ALOGD("[%s] copy buffer failed", mName);
return WOULD_BLOCK;
}
status_t BuffersArrayImpl::grabBuffer(
size_t *index,
sp<Codec2Buffer> *buffer,
std::function<bool(const sp<Codec2Buffer> &)> match) {
// allBuffersDontMatch remains true if all buffers are available but
// match() returns false for every buffer.
bool allBuffersDontMatch = true;
for (size_t i = 0; i < mBuffers.size(); ++i) {
if (!mBuffers[i].ownedByClient && mBuffers[i].compBuffer.expired()) {
if (match(mBuffers[i].clientBuffer)) {
mBuffers[i].ownedByClient = true;
*buffer = mBuffers[i].clientBuffer;
(*buffer)->meta()->clear();
(*buffer)->setRange(0, (*buffer)->capacity());
*index = i;
return OK;
}
} else {
allBuffersDontMatch = false;
}
}
return allBuffersDontMatch ? NO_MEMORY : WOULD_BLOCK;
}
- MediaCodec
将这个buffer放到外部的mPortBuffers中,返回给应用。
case kWhatDrainThisBuffer:
{
/* size_t index = */updateBuffers(kPortIndexOutput, msg);
}
- 内存不够的处理
内存不够按照下面的规则进行申请内存的扩展。
constexpr size_t kMaxLinearBufferSize = 7680 * 4320 * 2;
uint32_t size = kLinearBufferSize;
const std::vector<C2ConstLinearBlock> &linear_blocks = c2buffer->data().linearBlocks();
const uint32_t block_size = linear_blocks.front().size();
if (block_size < kMaxLinearBufferSize / 2) {
size = block_size * 2;
} else {
size = kMaxLinearBufferSize;
}
mAlloc = [format = mFormat, size] {
return new LocalLinearBuffer(format, new ABuffer(size));
};
- MediaCodec 中buffer 的轮转
编码 默认会申请出4个outputBuffer。 所有从服务端回来的buffer 都会先转换到这四个buffer里面。如果这4个buffer都被占用的话,那么编码的数据会源源不断的缓冲在内部的队列中。
MediaCodec 管理的输入输出buffer 的结构体为
List<size_t> mAvailPortBuffers[2];
std::vector<BufferInfo> mPortBuffers[2];
外部dequeueInputBuffer 和 dequeueOutputBuffer的时候 设置为mOwnedByClient为true
当buffer release回来的时候,mOwnedByClient就为false。能够被重新使用。
ssize_t MediaCodec::dequeuePortBuffer(int32_t portIndex) {
CHECK(portIndex == kPortIndexInput || portIndex == kPortIndexOutput);
BufferInfo *info = peekNextPortBuffer(portIndex);
if (!info) {
return -EAGAIN;
}
List<size_t> *availBuffers = &mAvailPortBuffers[portIndex];
size_t index = *availBuffers->begin();
CHECK_EQ(info, &mPortBuffers[portIndex][index]);
availBuffers->erase(availBuffers->begin());
CHECK(!info->mOwnedByClient);
{
Mutex::Autolock al(mBufferLock);
info->mOwnedByClient = true;
}
编码 输出C2buffer的生命周期
-
从dmabuf 中申请出来
在componet 中从c2BufferPool 申请 最后会调用到系统的dmabuf申请出dmabufferHeap。 申请后同时加入到bufferPoolManager进行管理。 是在bufferPoolClient 中进行处理的。 -
componet 中进行buffer的转换
主要转换budle 和 work 之间的相互转换。 转换过程会通过bufferpoolclinet 进行cache 的存储。
通过post 和 receive 来操作的。
post加buffer添加到pool。recerive buffer 从pool中取出来。 -
ccodec ccodecbufferchannel mediacodec
回到上面的是componet中传递work。 在上层就通过work取出c2buffer。c2buffer 转化为mediacodecbuffer。
这个过程是拷贝的,拷贝完成之后 c2buffer就释放了。MediaCodecBuffer 是malloc出来的 固定的几个。 拷贝完成 给到外部。 外部在释放会内部。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 边框渐变色+圆角
- 对象存储COS是什么?如何接入SCDN
- 骨传导耳机不踩坑推荐指南,南卡/韶音/墨觉实测告诉你答案!
- 机场数据治理系列介绍(3):从数据到资产认定过程要搞懂的一些概念
- 用React给XXL-JOB开发一个新皮肤(三):实现登录页和Layout骨架
- 【Docker】概述与安装
- 从临床预测模型到临床实践的三个问题探讨
- 我的512天创作者纪念日,记录数字的不平凡
- linux-XFS类型文件备份和恢复
- 大数据人工智能在线实习项目:某实习网站招聘信息采集与分析