03-数据结构-栈与队列
发布时间:2023年12月20日
1.栈
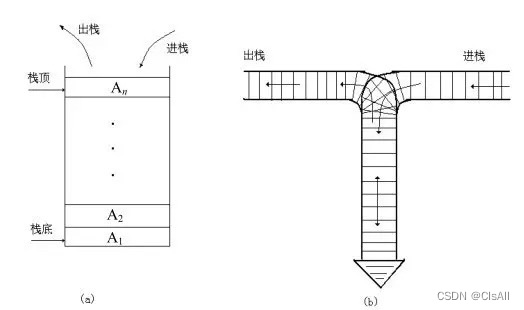
栈和队列是两种操作受限的线性表。如上图所示显示栈的结构
栈:先进后出,入栈(数据进入) 和出栈(数据出去)均在栈顶操作。
常见栈的应用场景包括括号问题的求解,表达式的转换和求值,函数调用和递归实现
1.1 栈的代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct node
{
STDataType x;
struct node* next;
}node;
typedef struct Stack
{
node* head;
int nums; // 长度
}Stack;
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->head = NULL;
ps->nums = 0;
}
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data)
{
assert(ps);
node* new_node = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
new_node->x = data;
new_node->next = ps->head;
ps->head = new_node;
ps->nums++;
}
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->nums == 0;
}
// 出栈
STDataType StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
STDataType ret = ps->head->x;
node* del = ps->head;
ps->head = ps->head->next;
free(del);
ps->nums--;
return ret;
}
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->nums;
}
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
node* tmp = ps->head;
while (tmp)
{
ps->head = ps->head->next;
free(tmp);
tmp = ps->head;
}
ps->head = NULL;
ps->nums = 0;
}
int main()
{
Stack sta;
StackInit(&sta);
StackPush(&sta, 1);
StackPush(&sta, 2);
StackPush(&sta, 3);
StackPush(&sta, 4);
StackPush(&sta, 5);
std::cout << StackSize(&sta) << std::endl;
while (!StackEmpty(&sta))
{
printf("%d\n", StackPop(&sta));
}
}
1.2 进制转化
#include <iostream>
#include <malloc.h>
using namespace std;
/**** 结 构 体 声 明 ****/
typedef struct scStack{
struct scStack *next;
int elem;
}scStack;
/*
余数入栈
*/
scStack *push(scStack *stack,int elem){
scStack *newStack = (scStack *)malloc(sizeof(scStack));
newStack->elem = elem;
newStack->next = stack;
stack = newStack;
return stack;
}
/*
进制转换
*/
scStack *sysConvert(int num,int system,scStack *sys){
while(num > 0){
sys = push(sys,num % system);
num /= system;
}
return sys; //返回栈顶
}
/*
余数出栈
*/
void pop(scStack *stack){
while(stack){
scStack *top = stack;
top->elem >= 10 ? printf("%c",top->elem + 'a' - 10) : printf("%d",top->elem);
stack = stack->next;
free(top);
}
cout<<endl<<"转换完毕!"<<endl;
}
/*
主函数
*/
int main(){
scStack *stack = NULL; //初始化栈
int num,system;
cout<<"请输入一个10进制数:";
cin>>num;
cout<<"请输入想要转换为多少进制:";
cin>>system;
stack = sysConvert(num,system,stack);
pop(stack);
return 0;
}
1.3 括号匹配
#include<stdio.h>
#define MaxSize 10
typedef struct { // 定义顺序栈
int data[MaxSize]; // 静态数组存放栈中元素
int top; // 栈顶指针:指向目前栈顶元素的位置
} SeqStack;
void InitStack(SeqStack &S) {
S.top = -1;
}
bool StackEmpty(SeqStack S) {
if(S.top == -1) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
bool Push(SeqStack &S, char x) {
if(S.top == MaxSize - 1) {
return false;
}
S.top = S.top + 1;
S.data[S.top] = x;
return true;
}
bool Pop(SeqStack &S, char &x) {
if(S.top == -1) {
return false;
}
x = S.data[S.top];
S.top = S.top - 1;
return true;
}
bool bracketCheck(char str[], int length) {
SeqStack S;
InitStack(S);
for(int i = 0;i < length;i++) {
if(str[i] == '(' || str[i] == '[' || str[i] == '{') {
Push(S, str[i]);
} else {
if(StackEmpty(S)) {
return false;
}
char topElem;
Pop(S, topElem);
if(str[i] == ')' && topElem != '(') {
return false;
}
if(str[i] == ']' && topElem != '[') {
return false;
}
if(str[i] == '}' && topElem != '{') {
return false;
}
}
}
return StackEmpty(S);
}
int main() {
char A[] = "[([][])]";
if(bracketCheck(A, 8)) {
printf("A The match is successful\n");
}
else
{
printf("A The match is faild\n");
}
char B[] = "[([][]]";
if(bracketCheck(B, 8)) {
printf("B The match is successful\n");
}
else
{
printf("B The match is faild\n");
}
}
1.4 递归
//X有n个盘子,从上到下有从小到大的顺序,有三个柱子X,Y, Z,把n个盘子从X移到Z,
//Y为辅助,并在移动过程中有一个约束条件就是大盘永远不能在小盘上面。
//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef int ElemType;//盘子的结构
typedef struct//柱子(栈)的结构
{
char name;
ElemType* base;
ElemType* top;
}StackType;
int initstack(StackType* s,char name)
{
s->name=name;
s->base=(ElemType*)malloc(MAXSIZE*sizeof(ElemType));
if(s->base==NULL)
exit(0);
s->top=s->base;
return 1;
}
int push(StackType* s,ElemType e)
{
if(s->top-s->base>=MAXSIZE)
exit(0);
*(s->top)=e;
s->top++;
return 1;
}
ElemType pop(StackType* s)
{
if(s->top==s->base)
exit(0);
s->top--;
return *(s->top);
}
int main()
{
int all;
int i;
StackType X;
StackType Y;
StackType Z;
initstack(&X,'X');
initstack(&Y,'Y');
initstack(&Z,'Z');
while(1)
{
printf("请输入X柱子开始有多少个盘子\n");
scanf("%d",&all);
for(i=all;i>0;i--)
{
push(&X,i);
}
hannota(all,&X,&Y,&Z);
}
return 1;
}
int hannota(int n,StackType* x,StackType* y,StackType* z)
{
if(1==n)
{
move(x,z);
printf("from %c to %c\n",x->name,z->name);
return 1;
}
hannota(n-1,x,z,y);//先解决n-1个盘子移到辅助柱子Y的汉洛塔问题
move(x,z);//最后一个从x移到Z
printf("from %c to %c\n",x->name,z->name);
hannota(n-1,y,x,z);//解决n-1个盘子移到柱子z的汉洛塔问题
return 1;
}
int move(StackType* s1,StackType* s2)
{
ElemType temp;
temp=pop(s1);
push(s2,temp);
return 1;
}2.队列
队列的应用场景包括计算机系统中各种资源的管理,消息缓冲器的管理和广度优先搜索遍历等。

队列是先进先出,如上图所示,队列从队尾入队,从队头出队。队列有顺序队列,链队列和循环队列
2.1 链队列的代码实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct DataNode
{
ElemType data;
struct DataNode *next;
} DataNode; //链队数据结点类型
typedef struct
{
DataNode *front;
DataNode *rear;
} LinkQuNode; //链队类型
void InitQueue(LinkQuNode *&q)
{
q=(LinkQuNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkQuNode));
q->front=q->rear=NULL;
}
void DestroyQueue(LinkQuNode *&q)
{
DataNode *p=q->front,*r;//p指向队头数据结点
if (p!=NULL) //释放数据结点占用空间
{ r=p->next;
while (r!=NULL)
{ free(p);
p=r;r=p->next;
}
}
free(p);
free(q); //释放链队结点占用空间
}
bool QueueEmpty(LinkQuNode *q)
{
return(q->rear==NULL);
}
void enQueue(LinkQuNode *&q,ElemType e)
{ DataNode *p;
p=(DataNode *)malloc(sizeof(DataNode));
p->data=e;
p->next=NULL;
if (q->rear==NULL) //若链队为空,则新结点是队首结点又是队尾结点
q->front=q->rear=p;
else
{ q->rear->next=p; //将p结点链到队尾,并将rear指向它
q->rear=p;
}
}
bool deQueue(LinkQuNode *&q,ElemType &e)
{ DataNode *t;
if (q->rear==NULL) //队列为空
return false;
t=q->front; //t指向第一个数据结点
if (q->front==q->rear) //队列中只有一个结点时
q->front=q->rear=NULL;
else //队列中有多个结点时
q->front=q->front->next;
e=t->data;
free(t);
return true;
}
int main()
{
LinkQuNode *q; //创建队列q
ElemType e;
InitQueue(q); //初始化队
enQueue(q,'a');
enQueue(q,'b');
enQueue(q,'c'); //依次进队a,b,c
deQueue(q,e);
printf("%c\n",e); //出队元素a
deQueue(q,e);
printf("%c\n",e); //出队元素b
deQueue(q,e);
printf("%c\n",e); //出队元素c
DestroyQueue(q); //销毁队
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/sishen4199/article/details/132839102
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 美易官方:新年伊始美企狂发450多亿美元债券
- 10分钟让你彻底搞懂Java泛型!!
- Git - 强制替换覆盖 master 分支解决方案
- 【K12】练习使用Python数学函数解物理中的电功率变化的问题
- 基于多反应堆的高并发服务器【C/C++/Reactor】(中)EventLoop初始化
- java获取访间者IP
- linux内核initcall放置在各个section中函数执行流程
- Leetcode160 两个链表是否相交
- ssh: connect to host github.com port 22: Connection refused
- uniapp中uview组件库的NoticeBar 滚动通知 使用方法