使用Python的pygame库实现迷宫游戏
发布时间:2024年01月24日
使用Python的pygame库实现迷宫游戏
关于Python中pygame游戏模块的安装使用可见 https://blog.csdn.net/cnds123/article/details/119514520
先给出效果图:
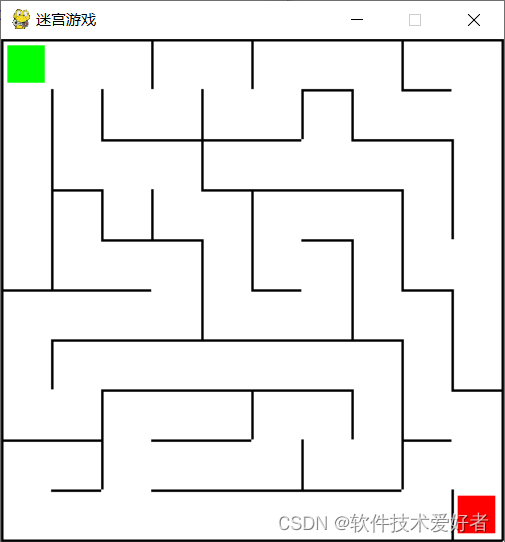
这个游戏能自动生成迷宫布局。
在这个游戏中,玩家将使用键盘箭头键来移动,并且目标是从迷宫的左上角移动到右下角。
源码如下:
import pygame
import random
import time # 导入time模块用于移动延迟
# 迷宫生成算法中使用的方向常量
UP = (0, -1)
DOWN = (0, 1)
LEFT = (-1, 0)
RIGHT = (1, 0)
# 初始化pygame
pygame.init()
# 设置迷宫的行数和列数
ROWS, COLS = 10, 10 #你可以根据需要调整迷宫的大小
# 设置每个单元格的大小
SIZE = 40
# 创建游戏窗口
WIN = pygame.display.set_mode((COLS * SIZE+2, ROWS * SIZE+2))
pygame.display.set_caption("迷宫游戏")
# 设置颜色常量
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
BLACK = (0, 0, 0)
GREEN = (0, 255, 0)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
# 定义单元格类
class Cell:
def __init__(self, row, col):
self.row = row
self.col = col
self.walls = {'top': True, 'right': True, 'bottom': True, 'left': True}
self.visited = False
def draw(self, win):
x = self.col * SIZE
y = self.row * SIZE
if self.visited:
pygame.draw.rect(win, WHITE, (x, y, SIZE, SIZE))
if self.walls['top']:
pygame.draw.line(win, BLACK, (x, y), (x + SIZE, y), 2)
if self.walls['right']:
pygame.draw.line(win, BLACK, (x + SIZE, y), (x + SIZE, y + SIZE), 2)
if self.walls['bottom']:
pygame.draw.line(win, BLACK, (x + SIZE, y + SIZE), (x, y + SIZE), 2)
if self.walls['left']:
pygame.draw.line(win, BLACK, (x, y + SIZE), (x, y), 2)
def remove_walls(self, next_cell):
dx = next_cell.col - self.col
dy = next_cell.row - self.row
if dx == 1:
self.walls['right'] = False
next_cell.walls['left'] = False
elif dx == -1:
self.walls['left'] = False
next_cell.walls['right'] = False
if dy == 1:
self.walls['bottom'] = False
next_cell.walls['top'] = False
elif dy == -1:
self.walls['top'] = False
next_cell.walls['bottom'] = False
# 迷宫生成算法
def generate_maze(rows, cols):
# 创建单元格网格
grid = [[Cell(row, col) for col in range(cols)] for row in range(rows)]
# 随机选择一个单元格作为当前单元格
current_cell = grid[random.randint(0, rows - 1)][random.randint(0, cols - 1)]
current_cell.visited = True
# 使用栈来跟踪单元格路径
stack = [current_cell]
while stack:
# 获取当前单元格的未访问邻居
neighbors = []
for direction in [UP, DOWN, LEFT, RIGHT]:
next_row = current_cell.row + direction[1]
next_col = current_cell.col + direction[0]
if (0 <= next_row < rows and
0 <= next_col < cols and
not grid[next_row][next_col].visited):
neighbors.append(grid[next_row][next_col])
if neighbors:
# 随机选择一个未访问的邻居
next_cell = random.choice(neighbors)
next_cell.visited = True
# 移除墙壁
current_cell.remove_walls(next_cell)
# 将当前单元格压入栈
stack.append(current_cell)
# 将选择的邻居设置为当前单元格
current_cell = next_cell
else:
# 如果没有未访问的邻居,则回溯
current_cell = stack.pop()
return grid
# 游戏循环
def main():
clock = pygame.time.Clock()
grid = generate_maze(ROWS, COLS)
player_pos = [0, 0] # 玩家起始位置在左上角
end_pos = [COLS - 1, ROWS - 1] # 结束位置在右下角
move_delay = 0.2 # 移动延迟时间
last_move = time.time()
player_margin = 5 # 玩家边距
end_margin = 5 # 结束位置边距
# 游戏主循环
running = True
while running:
clock.tick(30)
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
running = False
keys = pygame.key.get_pressed()
current_cell = grid[player_pos[1]][player_pos[0]]
# 玩家移动逻辑
if time.time() - last_move > move_delay:
if keys[pygame.K_UP] and not current_cell.walls['top']:
player_pos[1] -= 1
last_move = time.time()
if keys[pygame.K_DOWN] and not current_cell.walls['bottom']:
player_pos[1] += 1
last_move = time.time()
if keys[pygame.K_LEFT] and not current_cell.walls['left']:
player_pos[0] -= 1
last_move = time.time()
if keys[pygame.K_RIGHT] and not current_cell.walls['right']:
player_pos[0] += 1
last_move = time.time()
# 游戏结束条件
if player_pos == end_pos:
print("恭喜你,成功到达终点!")
running = False
# 绘制迷宫和玩家
WIN.fill(WHITE)
for row in grid:
for cell in row:
cell.draw(WIN)
# 绘制玩家
#pygame.draw.rect(WIN, GREEN, (player_pos[0] * SIZE, player_pos[1] * SIZE, SIZE, SIZE))
pygame.draw.rect(WIN, GREEN, (player_pos[0] * SIZE + player_margin, player_pos[1] * SIZE + player_margin, SIZE - 2 * player_margin, SIZE - 2 * player_margin))
# 绘制结束位置
#pygame.draw.rect(WIN, RED, (end_pos[0] * SIZE, end_pos[1] * SIZE, SIZE, SIZE))
pygame.draw.rect(WIN, RED, (end_pos[0] * SIZE + end_margin, end_pos[1] * SIZE + end_margin, SIZE - 2 * end_margin, SIZE - 2 * end_margin))
pygame.display.update()
pygame.quit()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
这段代码首先定义了一个Cell类,用于表示迷宫中的单个单元格。迷宫生成算法使用了深度优先搜索算法来生成迷宫。每个单元格知道自己的位置以及哪些墙是存在的。generate_maze函数创建了一个单元格网格,并从一个随机单元格开始,追踪它的路径直到所有单元格都被访问过。最后,main函数包含了游戏的主循环,它不断地绘制迷宫并处理退出事件。
player_pos变量来跟踪玩家的位置,并在游戏循环中检查键盘输入来移动玩家。墙壁检查确保玩家不能穿过墙壁。游戏结束条件是当玩家到达迷宫的右下角结束位置时,会打印一条消息并退出游戏。
你可以根据需要调整迷宫的大小。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/cnds123/article/details/135813307
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- LabVIEW继电保护测试仪自动检测系统
- 使用 Apache POI XDGF 读取 vsdx 文件
- Flume基础知识(四):Flume实战之实时监控单个追加文件
- 前缀和详解,朴素前缀和,前缀和变形,二维前缀和
- python3:爬虫代理IP的使用+建立代理IP池
- CC工具箱使用指南:【添加图层名和路径到字段】
- 一篇文章讲清楚凸优化问题
- 喜讯!浪潮信息一体机破BWH Benchmark基准测试最高记录!
- 计算机中msvcr120.dll丢失怎样修复,这5个方法可以搞定
- 纯虚函数和抽象类(C++)