一文搞清楚Java BytesToAscii和AsciiToBytes
发布时间:2023年12月26日
BytesToAscii
@Test
public void convertBytesToAscii() {
byte[] bytes = new byte[] { 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34, 0x35 };
String asciiString = new String(bytes);
System.out.println("asciiString = " + asciiString);
}
asciiString = 12345
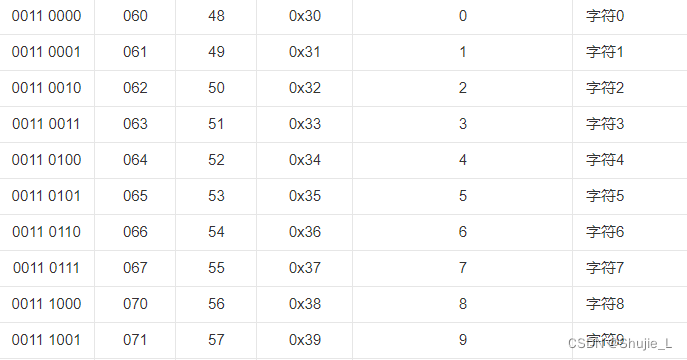
AsciiToBytes
@Test
public void convertAsciiToBytes() {
String asciiString = "12345";
byte[] result = new byte[asciiString.length()];
for (int i = 0; i < asciiString.length(); i++) {
result[i] = (byte) asciiString.charAt(i);
}
System.out.println("result = " + Arrays.toString(result));
}
result = [49, 50, 51, 52, 53]
由于 Arrays.toString()默认输出的是十进制,二前面我们输入的是十六进制,这样看起来不太顺眼。所以换一个输出:
public static String byteArrayToHexString(byte[] bytes) {
StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : bytes) {
hexString.append(String.format("%02X", b));
}
return hexString.toString();
}
result = 3132333435
10进制和16进制byte对比
public void compareBytes() {
byte b1 = 0x31;
byte b2 = 49;
System.out.println("b1 = " + b1);
System.out.println("b2 = " + b2);
System.out.println("compare b1 b2 = " + (b1 == b2));
byte[] bytes1 = new byte[] { 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34, 0x35 };
byte[] bytes2 = new byte[] { 49, 50, 51, 52, 53 };
System.out.println("bytes1 = " + Arrays.toString(bytes1));
System.out.println("bytes2 = " + Arrays.toString(bytes2));
System.out.println("compare bytes1 bytes2 = " + (bytes1 == bytes2));
}
b1 = 49
b2 = 49
compare b1 b2 = true
bytes1 = [49, 50, 51, 52, 53]
bytes2 = [49, 50, 51, 52, 53]
compare bytes1 bytes2 = false
bytes2HexString和hexStringToBytes
private static final byte[] HEX_ARRAY = "0123456789ABCDEF".getBytes(StandardCharsets.US_ASCII);
/**
* convert byte array to hex string
* 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34, 0x35, 0x36 -> "313233343536"
*/
public static String bytes2HexString(byte[] bytes) {
byte[] hexChars = new byte[bytes.length * 2];
for (int j = 0; j < bytes.length; j++) {
int v = bytes[j] & 0xFF;
hexChars[j * 2] = HEX_ARRAY[v >>> 4];
hexChars[j * 2 + 1] = HEX_ARRAY[v & 0x0F];
}
return new String(hexChars, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
/**
* convert byte array to hex string
* "313233343536" -> 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34, 0x35, 0x36
*/
public static byte[] hexStringToBytes(String hexstr) {
int len = (hexstr.length() / 2);
byte[] result = new byte[len];
char[] achar = hexstr.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int pos = i * 2;
result[i] = (byte) (((byte) "0123456789ABCDEF".indexOf(achar[pos])) << 4
| (((byte) "0123456789ABCDEF".indexOf(achar[pos + 1]))) & 0xff);
}
return result;
}
测试
@Test
public void bytes2Hex() {
byte[] bytes = new byte[] { 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34, 0x35 };
System.out.println("bytes = " + Arrays.toString(bytes));
String bytes2HexString = ConvertUtils.bytes2HexString(bytes);
System.out.println("bytes2HexString = " + bytes2HexString);
byte[] hexStringToBytes = ConvertUtils.hexStringToBytes(bytes2HexString);
System.out.println("hexStringToBytes = " + Arrays.toString(hexStringToBytes));
}
bytes = [49, 50, 51, 52, 53]
bytes2HexString = 3132333435
hexStringToBytes = [49, 50, 51, 52, 53]
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/Shujie_L/article/details/135230986
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【React系列】Hook(一)基本使用
- 每日汇评:尽管美元重新走强,但英镑仍有所上涨
- 408考研笔记合集
- Qlik Sense : Conditional Show/Hide Dimensions and Measures in a Chart
- laravel5.5 里面如果想要使用自定义的数据库连接器
- 2024年甘肃省职业院校技能大赛 高职学生组电子与信息大类信息安全管理与评估赛项样题卷①
- 了解 Vite 插件
- 对象属性的重命名
- 看图了解ODF光纤配线架,详细熔接过程学习
- 《SPSS统计学基础与实证研究应用精解》视频讲解:根据已存在的变量建立新变量