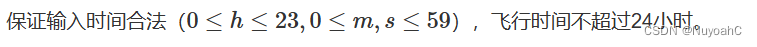AcWing1231-航班时间
发布时间:2024年01月08日
题目
输入格式
输出格式
数据范围
输入样例
3
17:48:19 21:57:24
11:05:18 15:14:23
17:21:07 00:31:46 (+1)
23:02:41 16:13:20 (+1)
10:19:19 20:41:24
22:19:04 16:41:09 (+1)
输出样例
04:09:05
12:10:39
14:22:05
思路
- scanf(“%d\n”,&n)去读取n;
- 读入字符串的时候要使用getline;
- sscanf的作用:
从一个字符串中读进于指定格式相符的数据。利用它可以从字符串中取出整数、浮点数和字符串;- s.back()!=’)'判断line中最后一个字符是不是);而s.end()返回的是最后一个字符的下一个位置;
- c_str()函数返回一个指向正规C字符串的指针常量, 内容与本string串相同s.c_str();
- 东半球飞向西半球加时差。
西半球飞向东半球减时差。
飞行的时间=到的时间-来的时间+时差。
飞行的时间=回去的时间-现在的时间-时差。
所以飞行的时间=[(end2-begin2)+(end1-begin1)] / 2;
代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n;
int gs(int h, int m, int s)//得到具体的秒数
{
return h * 60 * 60 + m * 60 + s;
}
int gt()//从字符串中读出时间
{
string s;
getline(cin, s);
if(s.back() != ')') //如果最后一位不是')',就意味时间没有横跨一天
s += "(+0)";//统一个数,方便下面sccanf读入数据
int h1, m1, s1, h2, m2, s2, d;
sscanf(s.c_str(), "%d:%d:%d %d:%d:%d (+%d)", &h1, &m1, &s1, &h2, &m2, &s2, &d);
return gs(h2, m2, s2) - gs(h1, m1, s1) + d * 24 * 60 * 60;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d\n", &n);//其中的\n是用来消化读入数据个数后面的回车的
while(n--)
{
int time = (gt() + gt()) / 2;
int h = time / 3600;
int m = time % 3600 / 60;
int s = time % 60;
printf("%02d:%02d:%02d\n", h, m, s);
}
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_74317866/article/details/135442441
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 从0开始界面设计师 Qt Designer
- python+ctypes:ctypes调用so库
- Jupyter Notebook又一地理数据可视化扩展!
- 性能测试:Jmeter压测过程中的短信验证码读取
- MySQL一行记录是怎么存储的?
- 【C#】当重复使用一段代码倒计时时,定义接口类和通过实现类继承接口方式进行封装方法和体现代码灵活性
- redis 从0到1完整学习 (十四):RedisObject 之 ZSet 类型
- 创业者必备:9大行之有效的客户参与策略与实践指南
- 如何使用cpolar+Inis在Ubuntu系统快速搭建本地博客网站公网可访问
- 哈希-力扣202快乐数