构建强大应用的引擎:深度解析Spring Boot Starter机制
目录

引言
在当今互联网时代,构建高性能、可维护的应用已成为开发者的首要任务。Spring Boot Starter机制作为Spring Boot框架的一项强大功能,为开发者提供了简化配置、快速搭建项目的便捷工具。本文将深度解析Spring Boot Starter机制,揭示其背后的原理,同时通过综合案例展示其实际应用。
1. Spring Boot Starter机制
1.1 什么是Spring Boot Starter
SpringBoot中的starter是一种非常重要的机制(自动化配置),能够抛弃以前繁杂的配置,将其统一集成进starter,应用者只需要在maven中引入starter依赖,SpringBoot就能自动扫描到要加载的信息并启动相应的默认配置。starter让我们摆脱了各种依赖库的处理,需要配置各种信息的困扰。
SpringBoot会自动通过classpath路径下的类发现需要的Bean,并注册进IOC容器。SpringBoot提供了针对日常企业应用研发各种场景的spring-boot-starter依赖模块。
所有这些依赖模块都遵循着约定成俗的默认配置,并允许我们调整这些配置,即遵循“约定大于配置”的理念。
1.2 为什么要使用Spring Boot Starter
在我们的日常开发工作中,经常会有一些独立于业务之外的配置模块,我们经常将其放到一个特定的包下,然后如果另一个工程需要复用这块功能的时候,需要将代码硬拷贝到另一个工程,重新集成一遍,麻烦至极。如果我们将这些可独立于业务代码之外的功能配置模块封装成一个个starter,复用的时候只需要将其在pom中引用依赖即可, SpringBoot为我们完成自动装配,简直不要太爽。
对比分析:Starter与传统配置的优势
通过实际案例对比,分析使用Spring Boot Starter相对于传统配置方式的便捷性、可维护性等方面的优势。帮助开发者理解在何种场景下选择使用Spring Boot Starter更为合适。
1.3.应用场景
在我们的日常开发工作中,可能会需要开发一个通用模块,以供其它工程复用。SpringBoot就为我们提供这样的功能机制,我们可以把我们的通用模块封装成一个个starter,这样其它工程复用的时候只需要在pom中引用依赖即可,由SpringBoot为我们完成自动装配。
常见应用场景:
1)通用模块-短信发送模块
2)基于AOP技术实现日志切面
3)分布式雪花ID,Long转String,解决精度问题
4)微服务项目的数据库连接池配置
5)微服务项目的每个模块都要访问redis数据库,每个模块都要配置redisTemplate
1.4.自动加载核心注解说明
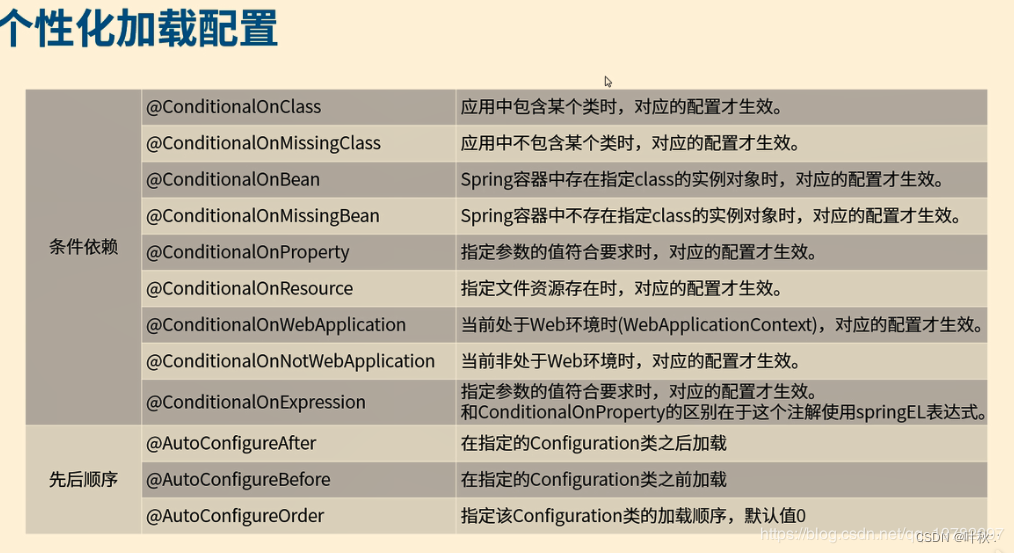
2. 综合案例
配置类制作
yml
sms:
key: 1001
secret: 1002
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
spring-boot-configuration-processor 是一个注解处理器,用于处理 Spring Boot 配置类的注解,并生成配置属性的元数据。它在开发过程中起到以下几个重要的作用:
- 生成配置属性的元数据: 当你使用
@ConfigurationProperties注解来声明配置类时,spring-boot-configuration-processor会解析该注解,并生成与配置属性相关的元数据。这些元数据包括属性的名称、类型、描述、默认值等信息。这些信息可以帮助 IDE 在开发过程中提供代码提示、自动补全和验证功能。 - 提供配置属性的编译时验证: 使用
@ConfigurationProperties注解时,你可以使用其他注解(如@Value、@Valid等)来描述配置属性的约束条件。spring-boot-configuration-processor可以处理这些注解,并在编译时进行验证。这样,你可以在开发阶段及早发现配置属性的错误或不一致,而不是在运行时才遇到问题。 - 简化配置类的编写: 通过使用
spring-boot-configuration-processor,你可以更轻松地编写配置类。它会自动处理@ConfigurationProperties注解及其相关注解,生成属性的 getter、setter 方法,并提供默认的配置文件映射规则。这样,你可以专注于定义配置属性的结构和业务逻辑,而不需要手动编写重复的代码。 - 提升开发体验:
spring-boot-configuration-processor增强了开发工具的功能,例如在 IDE 中提供配置属性的智能提示、文档、类型检查等功能。这可以减少开发过程中的错误,并提高代码的可读性和可维护性。
package com.yuan.smsspringbootstart;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 叶秋
* @site
* @company 卓京公司
* @create 2023-12-15 14:03
*/
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "sms")
public class SmsProperties {
//应用标识
private String key;
//应用密钥
private String secret;
}
package com.yuan.smsspringbootstart;
import com.yuan.smsspringbootstart.service.ISmsService;
import com.yuan.smsspringbootstart.service.SmsServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
/**
* @author 叶秋
* @site
* @company 卓京公司
* @create 2023-12-15 14:28
*/
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties({SmsProperties.class})
public class SmsConfig {
@Autowired
private SmsProperties smsProperties;
@Bean
public ISmsService smsService(){
return new SmsServiceImpl(smsProperties);
}
}
package com.yuan.smsspringbootstart.service;
public interface ISmsService {
/**
* 发送短信
*
* @param phone 要发送的手机号
* @param data 要发送的内容
*/
void send(String phone, String data);
}
package com.yuan.smsspringbootstart.service;
import com.yuan.smsspringbootstart.SmsProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
public class SmsServiceImpl implements ISmsService {
private SmsProperties smsProperties; //null
public SmsServiceImpl(SmsProperties smsProperties) {
this.smsProperties=smsProperties;
}
@Override
public void send(String phone, String data) {
String key = smsProperties.getKey();
String secret = smsProperties.getSecret();
System.out.println("接入短信系统,Key=" + key + ",Secret=" + secret);
System.out.println("短信发送,phone=" + phone + "data=" + data);
}
}
控制功能实现
在新的项目中加入配置
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.yuan</groupId>
<artifactId>sms-spring-boot-start</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
yml
sms:
key: 1001
secret: 1002
enable: true
package com.yuan.smsspringbootstart;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 叶秋
* @site
* @company 卓京公司
* @create 2023-12-15 14:03
*/
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "sms")
public class SmsProperties {
//应用标识
private String key;
//应用密钥
private String secret;
private String enable;
}
package com.yuan.smsspringbootstart;
import com.yuan.smsspringbootstart.service.ISmsService;
import com.yuan.smsspringbootstart.service.SmsServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
/**
* @author 叶秋
* @site
* @company 卓京公司
* @create 2023-12-15 14:28
*/
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties({SmsProperties.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "sms",name = "enable",havingValue = "true")
public class SmsConfig {
@Autowired
private SmsProperties smsProperties;
@Bean
public ISmsService smsService(){
return new SmsServiceImpl(smsProperties);
}
}
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.yuan.smsspringbootstart.SmsConfig
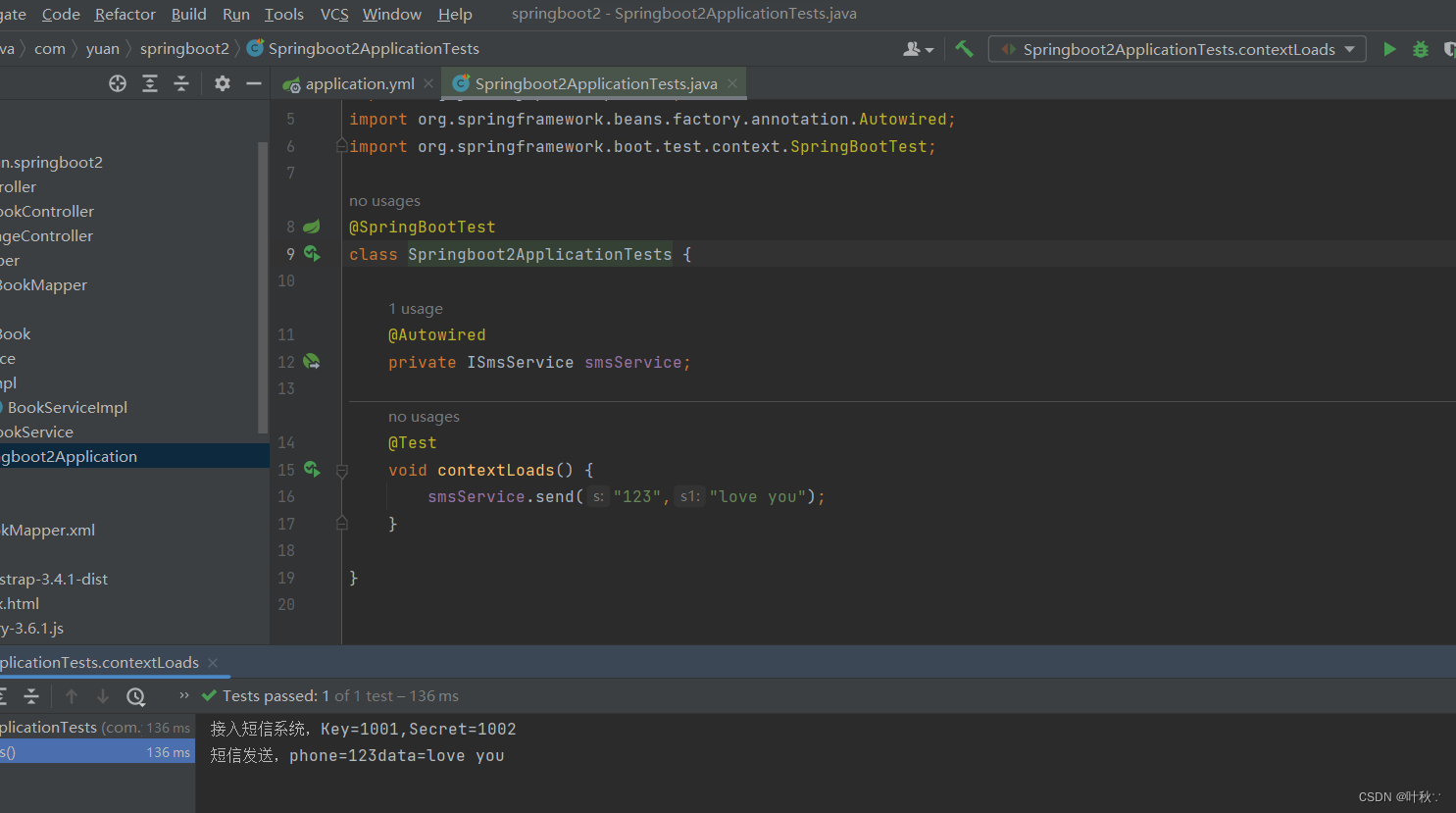
测试效果
总结
Spring Boot Starter机制作为Spring Boot框架的一项核心功能,为开发者提供了更便捷、高效的开发体验。通过深入解析Starter的结构、优势以及自动加载机制,本文旨在帮助开发者更好地理解和应用Spring Boot Starter,从而构建出更为强大、可维护的应用。希望读者在阅读完本文后,能够对Spring Boot Starter有更深入的认识,并在实际项目中充分发挥其优势。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 跟着cherno手搓游戏引擎【7】Input轮询
- 工业排放废水氨氮超标怎么处理
- XUbuntu22.04之免费开源DesktopNaotu脑图(二百零七)
- 第一章 函数及其特性基础考研练习题
- oh no!mysql数据丢失了
- 人工智能在老年痴呆症治疗中的影响与展望
- 2024年顶级编程语言趋势——Python 的受欢迎程度持续存在
- 蓝牙音箱如何实现USB-C接口pd协议快充?
- 【avue-crud】---- 实现表格的单选
- git打标签,tag常见命令及说明