Linux 文件:IO接口详解及实操
发布时间:2024年01月24日
一、C语言中的文件IO读写操作
在c语言文件中,创建、打开、读、写操作可以通过如下的代码进行:
1.1写文件
通过'w'指令对文件进行写入操作时,编译器会先将文件内容清空然后重新写入。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
FILE *fp = fopen("myfile", "w");
if(!fp){
printf("fopen error!\n");
}
const char *msg = "hello bit!\n";
int count = 5;
while(count--){
fwrite(msg, strlen(msg), 1, fp);
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}1.2读文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
FILE *fp = fopen("myfile", "r");
if(!fp){
printf("fopen error!\n");
}
char buf[1024];
const char *msg = "hello linux!\n";
while(1){
//注意返回值和参数,此处有坑,仔细查看man手册关于该函数的说明
ssize_t s = fread(buf, 1, strlen(msg), fp);
if(s > 0){
buf[s] = 0;
printf("%s", buf);
}
if(feof(fp)){
break;
}
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}1.3输出文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
const char *msg = "hello fwrite\n";
fwrite(msg, strlen(msg), 1, stdout);
printf("hello printf\n");
fprintf(stdout, "hello fprintf\n");
return 0;
}1.4stdin & stdout & stderr
C默认会打开三个输入输出流,分别是stdin, stdout, stderr。
仔细观察发现,这三个流的类型都是FILE*, fopen返回值类型,文件指针。
r Open text file for reading.
The stream is positioned at the beginning of the file.
r+ Open for reading and writing.
The stream is positioned at the beginning of the file.
w Truncate(缩短) file to zero length or create text file for writing.
The stream is positioned at the beginning of the file.
w+ Open for reading and writing.
The file is created if it does not exist, otherwise it is truncated.
The stream is positioned at the beginning of the file.
a Open for appending (writing at end of file).
The file is created if it does not exist.
The stream is positioned at the end of the file
a+ Open for reading and appending (writing at end of file).
The file is created if it does not exist. The initial file position
for reading is at the beginning of the file,
but output is always appended to the end of the file二、系统文件IO
操作文件,除了上述
C
接口(当然,
C++
也有接口,其他语言也有),我们还可以采用系统接口来进行文件访问,先来直接以代码的形式,实现和上面一模一样的代码:
2.1写文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
umask(0);
int fd = open("myfile", O_WRONLY|O_CREAT, 0644);
if(fd < 0){
perror("open");
return 1;
}
int count = 5;
const char *msg = "hello linux!\n";
int len = strlen(msg);
while(count--){
write(fd, msg, len);//fd:系统返回的文件描述符 , msg:缓冲区首地址, len: 本次读取,期望写入多少个字节的数
据。 返回值:实际写了多少字节数据
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}2.2读文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
int fd = open("myfile", O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0){
perror("open");
return 1;
}
const char *msg = "hello linux!\n";
char buf[1024];
while(1){
ssize_t s = read(fd, buf, strlen(msg));//类比write
if(s > 0){
printf("%s", buf);
}else{
break;
}
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}2.3接口功能介绍
open:
open 函数具体使用哪个,和具体应用场景相关,如目标文件不存在,需要open创建,则第三个参数表示创建文件的默认权限,否则,使用两个参数的open。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
pathname: 要打开或创建的目标文件
flags: 打开文件时,可以传入多个参数选项,用下面的一个或者多个常量进行“或”运算,构成flags。
参数:
O_RDONLY: 只读打开
O_WRONLY: 只写打开
O_RDWR : 读,写打开
这三个常量,必须指定一个且只能指定一个
O_CREAT : 若文件不存在,则创建它。需要使用mode选项,来指明新文件的访问权限
O_APPEND: 追加写
返回值:
成功:新打开的文件描述符
失败:-1
系统调用接口和库函数的关系,一目了然。
所以,可以认为,
f#
系列的函数,都是对系统调用的封装,方便二次开发。
2.4文件描述符fd
Linux进程默认情况下会有3个缺省打开的文件描述符,分别是标准输入0, 标准输出1, 标准错误2.
0,1,2对应的物理设备一般是:键盘,显示器,显示器
所以输入输出还可以采用如下方式
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char buf[1024];
ssize_t s = read(0, buf, sizeof(buf));
if(s > 0){
buf[s] = 0;
write(1, buf, strlen(buf));
write(2, buf, strlen(buf));
}
return 0;
}
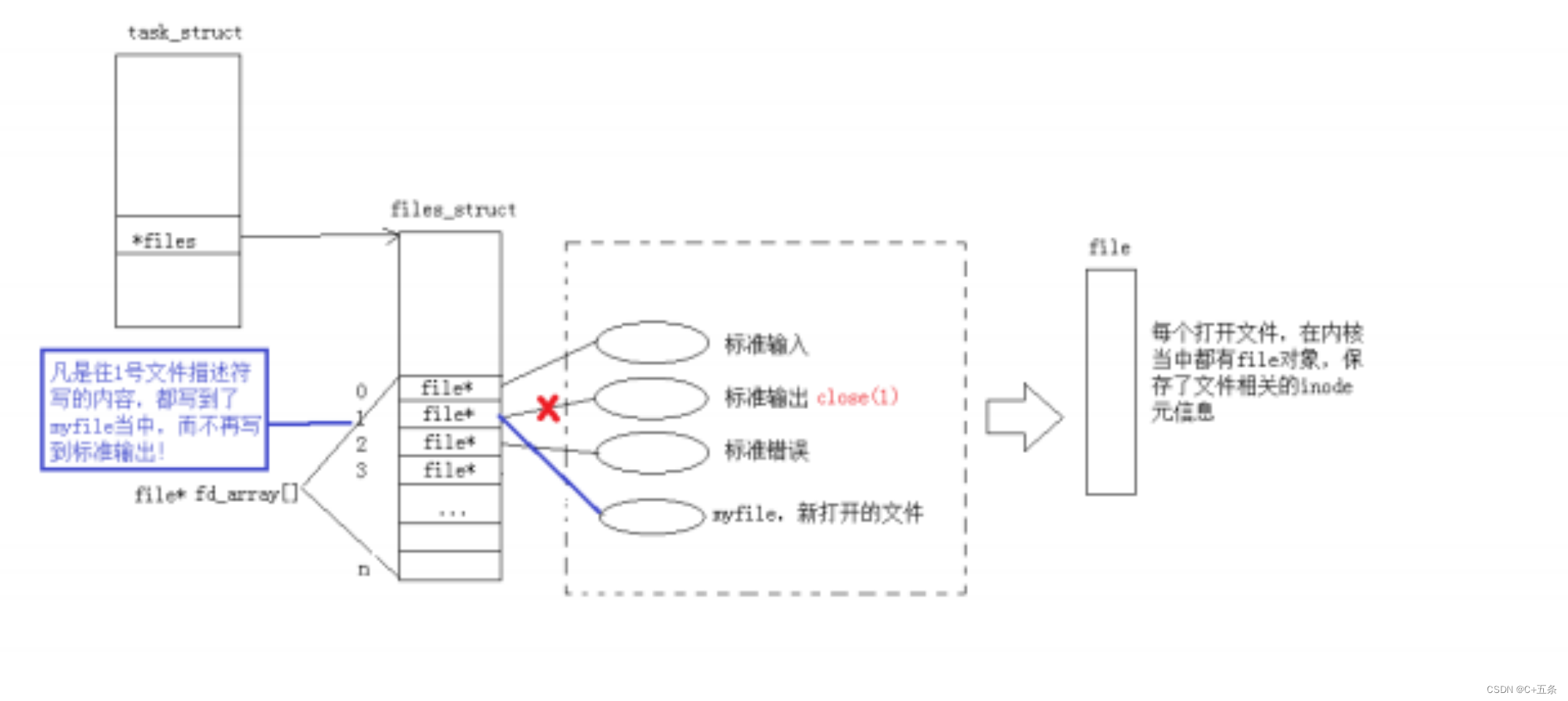
而现在知道,文件描述符就是从
0
开始的小整数。当我们打开文件时,操作系统在内存中要创建相应的数据结构来描述目标文件。于是就有了file
结构体。表示一个已经打开的文件对象。而进程执行
open
系统调用,所以必须让进程和文件关联起来。每个进程都有一个指针*files,
指向一张表
files_struct,
该表最重要的部分就是包涵一个指针数组,每个元素都是一个指向打开文件的指针!所以,本质上,文件描述符就是该数组的下标。所以,只要拿着文件描述符,就可以找到对应的文件。
三、文件描述符分配规则
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fd = open("myfile", O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0){
perror("open");
return 1;
}
printf("fd: %d\n", fd);
close(fd);
return 0;
}//结果为fd:3int main()
{
close(0);
//close(2);
int fd = open("myfile", O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0){
perror("open");
return 1;
}
printf("fd: %d\n", fd);
close(fd);
return 0;
}//结果为0
文件描述符的分配规则:在
files_struct
数组当中,找到当前没有被使用的最小的一个下标,作为新的文件描述符。
四、重定向
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
close(1);
int fd = open("myfile", O_WRONLY|O_CREAT, 00644);
if(fd < 0){
perror("open");
return 1;
}
printf("fd: %d\n", fd);
fflush(stdout);
close(fd);
exit(0);
}
此时,我们发现,本来应该输出到显示器上的内容,输出到了文件
myfile
当中,其中,
fd
=
1
。这种现象叫做输出重定向。当编译器去进行printf时会默认去打开fd=1的文件描述符所指向的,此时我们将myfile文件放到这个位置,那么编译器就会往myfile文件中进行写入。
五、使用dup2系统调用


#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main() {
int fd = open("log.txt", O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0666);
dup2(fd, 1);
printf("hello hahahaha\n");
return 0;
}
在理解重定向之后,我们直接使用close这种操作来实现重定向就显的较为暴力且存在很多不稳定因素,使用dup2就可以很好的解决这个问题,将oldfd拷贝到newfd,通过这种方式,我们就可以将内容printf到log.txt中。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2201_75880188/article/details/135767970
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!