基于蚁群算法的TSP问题建模求解(Python)
基于蚁群算法的TSP问题建模求解
一、蚁群优化算法(Ant Colony Optimization,ACO)
蚁群系统(Ant System或Ant Colony System(是由意大利学者Dorigo、Maniezzo等人于20世纪90年代(1992年)首先提出来的。他们在研究蚂蚁觅食的过程中,发现单个蚂蚁的行为比较简单,但是蚁群整体却可以体现一些智能的行为。例如蚁群可以在不同的环境下,寻找最短到达食物源的路径。这是因为蚁群内的蚂蚁可以通过某种信息机制实现信息的传递。后又经进一步研究发现,蚂蚁会在其经过的路径上释放一种可以称之为“信息素”的物质,蚁群内的蚂蚁对“信息素”具有感知能力,它们会沿着“信息素”浓度较高路径行走,而每只路过的蚂蚁都会在路上留下“信息素”,这就形成一种类似正反馈的机制,这样经过一段时间后,整个蚁群就会沿着最短路径到达食物源了。
1.1 蚁群算法的起源——“双桥实验”
双桥实验在研究蚂蚁觅食行为过程中,人们发现,尽管单只蚂蚁的能力十分有限,但整个蚁群却在觅食过程中可以发现从蚁巢到食物源的最短路径。在觅食过程中,蚂蚁通过“媒介质”来协调它们之间的行动。所谓“媒介质”指的是一种以环境的变化为媒介的间接通信方式。蚂蚁在寻找食物时,以其产生的被称为信息素的化学物质作为媒介而间接的传递信息。当蚂蚁从蚁穴走到食物源,从而形成了含有信息素的路径。
蚂蚁从A点出发,随机选择路线ABD或ACD。经过9个时间单位时:走ABD的蚂蚁到达终点,走ACD的蚂蚁刚好走到C点。
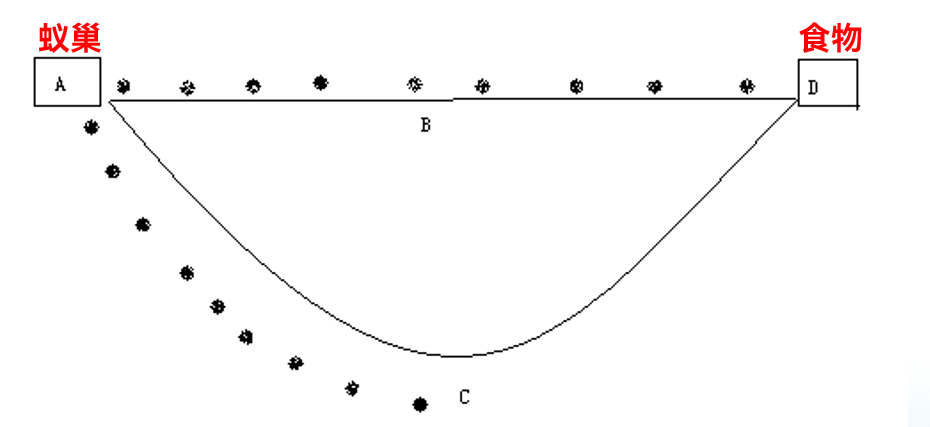
经过18个时间单位时:走ABD的蚂蚁到达终点后得到食物又返回了起点A,而走ACD的蚂蚁刚好走到D点。

最后的极限是所有的蚂蚁只选择ABD路线。(正反馈过程)

1.2 蚁群优化算法思想
蚁群优化算法思想:蚁群的自组织行为通过遗留在来往路径的信息素Pheromone)挥发的化学性物质来进行通信和协调。
- 蚁群算法是对自然界蚂蚁的寻径方式进行模似而得出的一种仿生优化算法:蚂蚁在运动过程中,能够在它所经过的路径上留下信息素(pheromone)的物质进行信息传递,而且蚂蚁在运动过程中能够感知这种物质,并以此指导自己的运动方向。
- 由大量蚂蚁组成的蚁群集体行为便表现出一种信息正反馈现象:某一路径上走过的蚂蚁越多,则后来者选择该路径的概率就越大。
1.3 蚁群算法应用于求解组合优化问题
将蚁群算法应用于解决优化问题的基本思路为:用蚂蚁的行走路径表示待优化问题的可行解,整个蚂蚁群体的所有路径构成待优化问题的解空间。路径较短的蚂蚁释放的信息素量较多,随着时间的推进,较短的路径上累积的信息素浓度逐渐增高,选择该路径的蚂蚁个数也愈来愈多。最终,整个蚂蚁会在正反馈的作用下集中到最佳的路径上,此时对应的便是待优化问题的最优解。
二、基于蚁群算法的TSP问题建模求解
2.1 旅行商问题(Travelling salesman problem,TSP)
刘兴禄 -《运筹优化常用模型、算法及案例实战:Python+Java实现》总结了TSP问题共有3种数学模型,本文采用DFJ模型,见 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43276566/article/details/134400764。
2.2 蚁群算法求解TSP问题思想、步骤、流程图
蚂蚁通过信息素指导寻优过程,每次迭代更新信息素,不断寻优。
蚂蚁在运动过程中,能够在它所经过的路径上留下信息素(pheromone)的物质进行信息传递,对应于求解TSP中
每只蚂蚁根据路径上的信息素和启发式信息(两城市间距离)独立地选择下一座城市,在时刻t,蚂蚁k从城市i转移到城市j的概率为:
p
i
j
k
(
t
)
=
{
[
τ
i
j
(
t
)
]
α
[
η
i
j
(
t
)
]
β
∑
s
∈
J
k
(
i
)
[
τ
i
s
(
t
)
]
α
[
η
i
s
(
t
)
]
β
,
j
∈
J
k
(
i
)
0
,
j
?
J
k
(
i
)
\begin{align} p_{i j}^{k}(t)=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} \frac{\left[\tau_{i j}(t)\right]^{\alpha}\left[\eta_{i j}(t)\right]^{\beta}}{\sum_{s \in J_{k}(i)}\left[\tau_{i s}(t)\right]^{\alpha}\left[\eta_{i s}(t)\right]^{\beta}}, & j \in J_{k}(i) \\ 0, & j \notin J_{k}(i) \end{array}\right.\end{align}
pijk?(t)={∑s∈Jk?(i)?[τis?(t)]α[ηis?(t)]β[τij?(t)]α[ηij?(t)]β?,0,?j∈Jk?(i)j∈/Jk?(i)???
其中:
- α \alpha α和 β \beta β分别表示信息素和启发式银子的相对重要程度。
- τ i j \tau_{ij} τij?表示城市i到j的信息素。
- η i j = 1 / d i j \eta_{ij}=1/d_{ij} ηij?=1/dij?, d i j d_{ij} dij?为城市间距离矩阵。
- J k ( i ) = { 1 , 2 , ? ? , n } ? t a b u k J_k(i)=\{1,2,\cdots,n\}- {tabu_k} Jk?(i)={1,2,?,n}?tabuk?, t a b u k {tabu_k} tabuk?是蚂蚁k已经访问过城市。
蚂蚁在运动过程中能够感知信息素,并以此指导自己的运动方向
当所有蚂蚁完成一次周游后,各路径上的信息素将进行更新:
τ
i
j
(
t
+
n
)
=
(
1
?
ρ
)
τ
i
j
+
Δ
τ
i
j
\begin{align} \tau_{ij}(t+n)=(1-\rho)\tau_{ij}+\Delta\tau_{ij}\end{align}
τij?(t+n)=(1?ρ)τij?+Δτij???
Δ
τ
i
j
=
∑
k
=
1
m
Δ
τ
i
j
k
\begin{align}\Delta\tau_{ij}=\sum_{k=1}^{m} \Delta\tau_{ij}^{k}\end{align}
Δτij?=k=1∑m?Δτijk???
Δ
τ
i
j
k
=
{
Q
L
k
,
?if?蚂蚁
k
?在本次周游中经过边?
i
j
0
,
?otherwise?
\begin{align} \Delta \tau_{i j}^{k}=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} \frac{Q}{L_{k}}, & \text { if 蚂蚁}k\text{ 在本次周游中经过边 } ij \\ 0, & \text { otherwise } \end{array}\right. \end{align}
Δτijk?={Lk?Q?,0,??if?蚂蚁k?在本次周游中经过边?ij?otherwise????
其中:
- ρ \rho ρ( 0 < ρ < 1 0<\rho<1 0<ρ<1)表示路径上信息素的蒸发系数;
- Q为正常数;
- L k L_k Lk?表示第k只蚂蚁在本次周游中所走过路径的长度。
蚁群算法求解TSP问题步骤如下:
- 初始化。问题相关参数(城市数量、城市间距离矩阵)、算法参数(蚂蚁数量、 α \alpha α、 β \beta β、 ρ \rho ρ、 Q Q Q、 m a x g e n maxgen maxgen)。
- 为每只蚂蚁构建路径。随机初始化蚂蚁路径的起点城市,根据式(1)计算每个城市的选择概率,通过轮盘赌选择下一个城市,直至路径蚂蚁路径形成一条TSP回路。
- 根据式(2)更新信息素矩阵。
- 检查终止条件
- 输出最优值
蚁群算法求解TSP问题算法流程图:

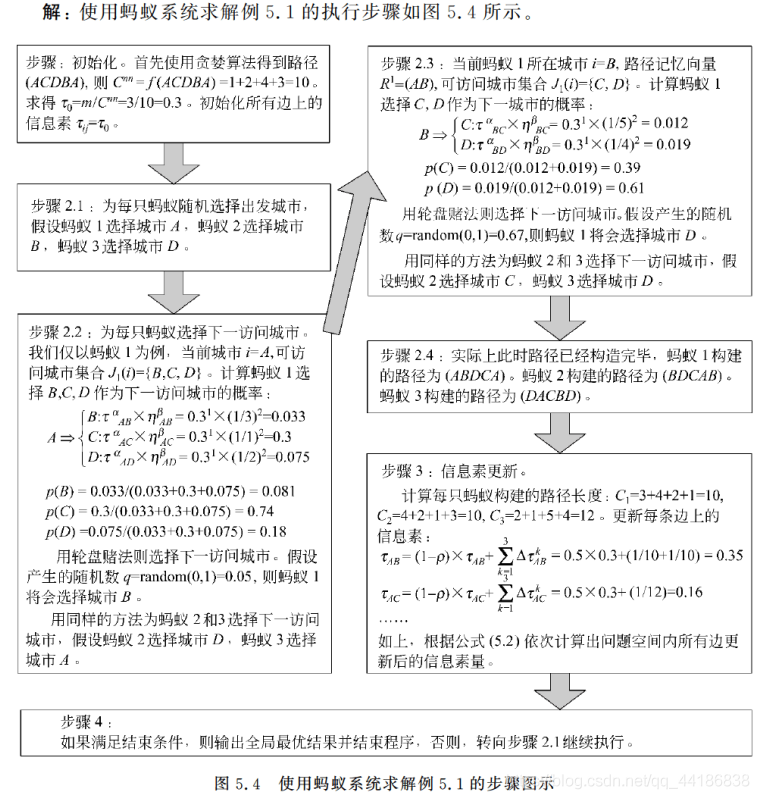
2.3 实例分析

2.4 完整代码
采用TSP问题标准测试函数att48,城市数量48进行测试,
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import itertools
import random
import copy
import numpy as np
from scipy.spatial import distance
from typing import List, Dict, Tuple
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from numpy import ndarray
np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf, linewidth=np.inf)
# 参数
'''
ALPHA:信息启发因子,值越大,则蚂蚁选择之前走过的路径可能性就越大,值越小,则蚁群搜索范围就会减少,容易陷入局部最优
BETA:Beta值越大,蚁群越就容易选择局部较短路径,这时算法收敛速度会加快,但是随机性不高,容易得到局部的相对最优
'''
# 城市距离和信息素
class AntColonyOpt:
def __init__(self, problem):
self.problem = problem
self.num_city = problem.num_city
self.city_coord = problem.city_coord
self.city_list = problem.city_list
self.distance = None
self.pheromone = None
self.num_ant = 48
self.alpha = 1.
self.beta = 2.
self.rho = .5 # 信息素的蒸发率
self.Q = 100.
self.tau = np.ones(shape=(self.num_city, self.num_city)) # 信息素
self.eta = None
self.ant_list = []
self.best_ant = None
self.gen = 0 # 初始化迭代次数
self.max_gen = 1e3
self.initialize()
# 初始化
def initialize(self):
# 初始化城市之间的距离
city_coord = np.asarray(list(self.city_coord.values()))
self.distance = distance.cdist(city_coord, city_coord, 'euclidean')
self.eta = 1 / self.distance
# 初始城市之间的信息素
self.pheromone = np.ones(shape=(self.num_city, self.num_city), dtype=np.float64)
# self.pheromone = [[1.0 for col in range(num_city)] for raw in range(num_city)]
for i in range(self.num_ant):
ant = {
"id": i,
"path": [i],
"path_length": 1 << 31,
"tabu": {i},
"allow": [True if city != i else False for city in self.city_list],
"move_count": 0
}
self.ant_list.append(ant)
self.best_ant = {
"id": -1,
"path": [0],
"path_length": 1 << 31,
"tabu": set(),
"allow": [True] * self.num_city,
"move_count": 0
} # 初始最优解
def build_path(self, ant):
while ant["move_count"] < self.num_city - 1:
# 移动到下一个城市
next_city = self.select(ant)
self.move(ant, next_city)
def select(self, ant):
# 计算选择概率: i 当前城市, j 遍历allow中j城市
ant_path = ant["path"]
i = ant_path[-1] # 当前城市
numerator = np.array([(self.tau[i][j] ** self.alpha) * (self.eta[i][j] ** self.beta) if ant["allow"][j] is True else 0 for j in self.city_list])
denominator = np.sum(numerator)
p_select = numerator / denominator
p_cum = np.cumsum(p_select)
# 轮盘赌选择
select = None
r = np.random.uniform(0, 1)
for city in self.city_list:
if ant["allow"][city] is True:
if r < p_cum[city]:
select = city
break
return select
# 移动操作
def move(self, ant, next_city):
ant["path"].append(next_city)
ant["allow"][next_city] = False
ant["tabu"].add(next_city)
ant["move_count"] += 1
def clear(self):
self.ant_list = []
random_city = np.random.randint(low=0, high=self.num_city)
for i in range(self.num_ant):
ant = {
"id": random_city,
"path": [random_city],
"path_length": 1 << 31,
"tabu": {random_city},
"allow": [True if city != random_city else False for city in self.city_list],
"move_count": 0
}
self.ant_list.append(ant)
# 运行蚁群优化算法
def run(self):
trace = []
while self.gen <= self.max_gen:
# 遍历每一只蚂蚁
for ant in self.ant_list:
# 搜索一条路径
self.build_path(ant)
ant["path_length"] = self.calc_path_length(ant["path"])
# 与当前最优蚂蚁比较, 更新最优解
if ant["path_length"] < self.best_ant["path_length"]:
self.best_ant = copy.deepcopy(ant)
# print(ant)
# 更新信息素
self.update_pheromone()
print(u"迭代次数:", self.gen, u"最佳路径总距离:", int(self.best_ant["path_length"]))
self.gen += 1
trace.append((self.best_ant['path'], self.best_ant['path_length']))
self.clear()
self.draw([(self.best_ant["path"], self.best_ant["path_length"])])
# 计算路径总距离
def calc_path_length(self, path):
total_distance = 0.
for i, j in itertools.pairwise(path):
total_distance += self.distance[i][j]
i = path[-1]
j = path[0]
total_distance += self.distance[i][j]
return total_distance
def draw(self, trace: List[Tuple[List, float]]) -> None:
"""
最优路径可视化
:param trace:每次迭代过程中最优路径及路径长度,trace是一个list,len(trace)=max_gen
:return:
"""
iteration = np.arange(len(trace))
obj_value = [trace[i][1] for i in range(len(trace))]
plt.plot(iteration, obj_value)
plt.show()
final_solution, final_obj_value = trace[-1]
x = []
y = []
for city in final_solution:
city_x, city_y = self.city_coord[city]
x.append(city_x)
y.append(city_y)
city_x, city_y = self.city_coord[final_solution[0]]
x.append(city_x)
y.append(city_y)
plt.plot(x, y, 'o-', alpha=1, linewidth=2)
plt.savefig("ACO-TSP.png", bbox_inches="tight")
def update_pheromone(self):
"""
更新信息素
:return:
"""
delta_tau = np.zeros(shape=(self.num_city, self.num_city))
for ant in self.ant_list:
for i in range(1, self.num_city):
start, end = ant["path"][i - 1], ant["path"][i]
# 在路径上的每两个相邻城市间留下信息素,与路径总距离反比
delta_tau[start][end] += self.Q / ant["path_length"]
delta_tau[end][start] = delta_tau[start][end]
for i in range(self.num_city):
for j in range(self.num_city):
self.tau[i][j] = (1 - self.rho) * self.tau[i][j] + delta_tau[i][j]
class TSP(object):
num_city: int = None # 城市数量
city_coord: Dict[int, Tuple[int, int]] = None # 城市标号及对应坐标,示例 1:(23,312)
distance: ndarray = None # 城市间距离矩阵
pheromone: List = None
def __init__(self, city_coord):
self.num_city = len(city_coord)
self.city_coord = city_coord
self.city_list = city_coord.keys()
self.distance = np.empty(shape=(self.num_city, self.num_city), dtype=np.float64)
if __name__ == '__main__':
city_coord_att48 = {
0: (6734, 1453),
1: (2233, 10),
2: (5530, 1424),
3: (401, 841),
4: (3082, 1644),
5: (7608, 4458),
6: (7573, 3716),
7: (7265, 1268),
8: (6898, 1885),
9: (1112, 2049),
10: (5468, 2606),
11: (5989, 2873),
12: (4706, 2674),
13: (4612, 2035),
14: (6347, 2683),
15: (6107, 669),
16: (7611, 5184),
17: (7462, 3590),
18: (7732, 4723),
19: (5900, 3561),
20: (4483, 3369),
21: (6101, 1110),
22: (5199, 2182),
23: (1633, 2809),
24: (4307, 2322),
25: (675, 1006),
26: (7555, 4819),
27: (7541, 3981),
28: (3177, 756),
29: (7352, 4506),
30: (7545, 2801),
31: (3245, 3305),
32: (6426, 3173),
33: (4608, 1198),
34: (23, 2216),
35: (7248, 3779),
36: (7762, 4595),
37: (7392, 2244),
38: (3484, 2829),
39: (6271, 2135),
40: (4985, 140),
41: (1916, 1569),
42: (7280, 4899),
43: (7509, 3239),
44: (10, 2676),
45: (6807, 2993),
46: (5185, 3258),
47: (3023, 1942),
}
problem = TSP(city_coord_att48)
aco = AntColonyOpt(problem)
aco.run()
2.5 运行结果
采用TSP问题标准测试函数att48,城市数量48,最优解为33523)本文迭代次数:1000最佳路径总距离:35408,其他文章基于禁忌搜索的TSP问题建模求解(Java)结果为34974.67245297696。本文求解结果如下图:

参考:
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 啊哈c语言——4.5逻辑挑战4(60秒倒计时)
- 第十一部分 隐含规则(三)
- openGauss学习笔记-201 openGauss 数据库运维-常见故障定位案例-执行修改表分区操作时报错
- HNOI2014 米特运输
- 字符流的输入输出,以及序列化与反序列化的基础知识
- 用VS Code修改源代码的编码格式
- 课程表 II
- QT5.15.2在Debug模式下QT+mysql打包程序本地连接mysql成功,别的主机连接数据库失败(driver not loaded)的解决方案
- 使用Microsoft托管密钥的Azure信息保护云退出
- NLP论文阅读记录 - | 文本生成的动量校准