Response 实现重定向
发布时间:2023年12月27日
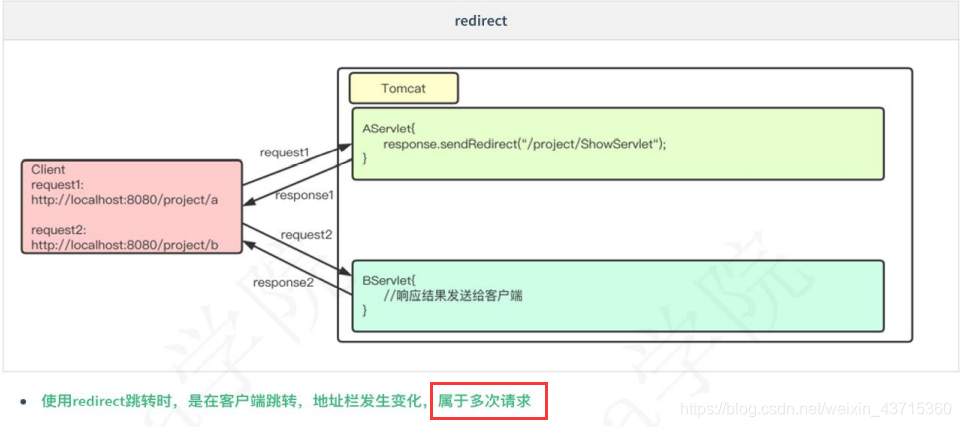
1.重定向:
重定向作用在客户端,客户端将请求发送给服务器后,服务器响应给客户端一个新的请求地址,客户端重新发送新请求。
重定向数据传递:
重定向特点:
- 重定向是客户端行为。
- 重定向是浏览器做了至少两次的访问请求。
- 重定向浏览器地址改变。
- 重定向两次跳转之间传输的信息会丢失(request范围)。
- 重定向可以
指向任何的资源,包括当前应用程序中的其他资源、同一个站点上的其他应用程序中的资源、其他站点的资源。
重定向特点:
当两个Servlet需要传递数据在同一个站点上的其他应用程序中的资源时,选择forward转发。不建议使用sendRedirect进行传递
2.示例代码(A重定向到B):
AServlet:
@WebServlet(value = "/a")
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//重定向及传递数据
resp.sendRedirect("/WebProject_war_exploded/b?username=tom");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req,resp);
}
}
12345678910111213
BServlet:
@WebServlet(value = "/b")
public class BServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//重定向通过请求方式获取数据
String username=req.getParameter("username");
System.out.println(username);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req,resp);
}
}
1234567891011121314
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43985303/article/details/135235929
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- deeplabv3模型的关键点
- 人工智能未来发展前景怎么样?
- scrapy框架核心知识Spider,Middleware,Item Pipeline,scrapy项目创建与启动,Scrapy-redis与分布式
- 在黑马程序员大学的2023年终总结
- HDFS入门基础
- 顺序结构复习
- 【C++】开源:cpp-httplib HTTP协议库配置与使用
- CMake在Ubuntu中找不到GoogleTest所需的库
- 网上购物推荐系统的设计与实现(JSP+java+springmvc+mysql+MyBatis)
- 电脑屏幕横过来了怎么恢复?这4个方法好用又简单!