C++学习笔记(二十七):c++ 动态数组vector及优化
发布时间:2024年01月08日
- c++的动态数组vector是STL的内容,关于STL,有兴趣可自行网上搜索资料。本节主要介绍vector的基本内容以及vector的简单优化。
- vector当超过数组最大范围,需要往里面添加新的元素时,会在内存中创建一个比上一个更大的数组,将上一个数组中的所有元素复制过来,然后删除旧的数组。
-
#include <iostream> #include <vector> struct Vertex { float x, y, z; Vertex(float x,float y, float z) { this->x = x; this->y = y; this->z = z; } }; std::ostream& operator<< (std::ostream& stream, const Vertex& vertex) { stream << vertex.x << vertex.y << vertex.z; return stream; } int main() { std::vector<Vertex> vertices; vertices.push_back(Vertex(1.3f, 2.1f, 4.4f)); vertices.push_back({ 2,3,4 }); //两种方式便利vertor //for (int i = 0; i < vertices.size(); i++) //{ //std::cout << vertices[i] << std::endl; //} for (Vertex &ver:vertices) //传入引用的原因时为了尽量减少复制,如果不是引用,则会将每个vertices复制到for循环中,影响性能 { std::cout << ver << std::endl; } vertices.erase(vertices.begin() + 1); //删除vertices中的第二个元素。因为erase中的参数时一个iterator vertices.clear(); //清空整个vertices中的元素 std::cin.get(); return 0; }下面简单对vector进行优化
-
vector影响性能的主要原因是当插入新的元素是,原来的vector分配的剩余内存不够时,需要复制原来vector中存在的所有元素,重新分配内存,从而影响程序的性能。
-
#include <iostream> #include <vector> struct Vertex { float x, y, z; Vertex(float x,float y, float z) { this->x = x; this->y = y; this->z = z; } //新增一个拷贝构造函数,查看复制操作的产生时机 Vertex(const Vertex& ver) :x(ver.x),y(ver.y),z(ver.z) { std::cout << "进行一次复制操作!!!" << std::endl; } }; std::ostream& operator<< (std::ostream& stream, const Vertex& vertex) { stream << vertex.x << ", " << vertex.y<< ", " << vertex.z; return stream; } int main() { std::vector<Vertex> vertices; vertices.push_back(Vertex(1.3f, 2.1f, 4.4f)); vertices.push_back({ 2,3,4 }); //这个状态下执行三次复制操作 std::cin.get(); return 0; }运行结果
-
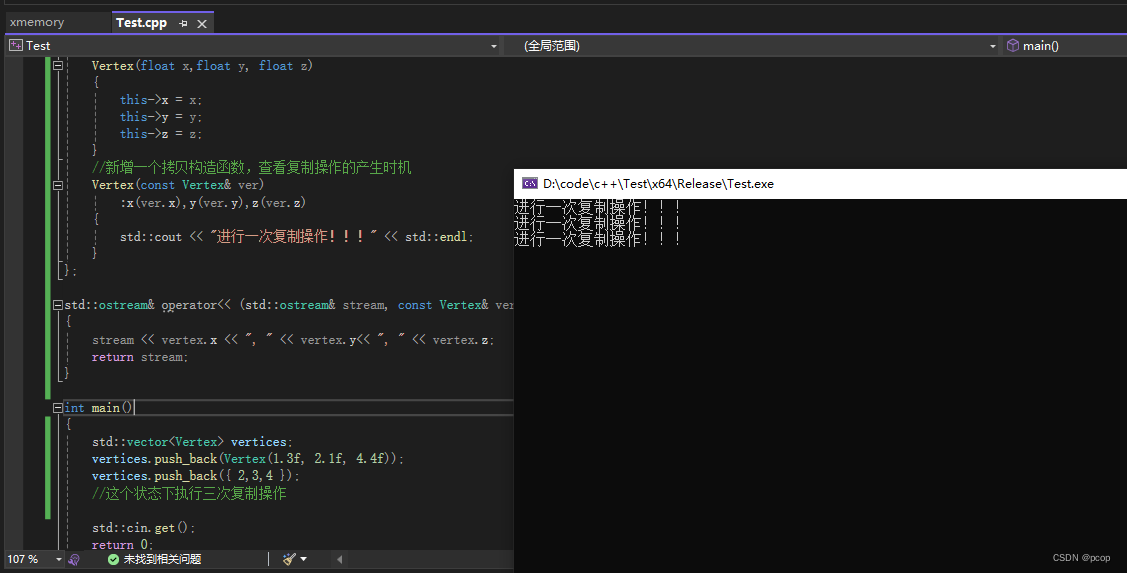 ???????
??????? -
#include <iostream> #include <vector> struct Vertex { float x, y, z; Vertex(float x,float y, float z) { this->x = x; this->y = y; this->z = z; } //新增一个拷贝构造函数,查看复制操作的产生时机 Vertex(const Vertex& ver) :x(ver.x),y(ver.y),z(ver.z) { std::cout << "进行一次复制操作!!!" << std::endl; } }; std::ostream& operator<< (std::ostream& stream, const Vertex& vertex) { stream << vertex.x << ", " << vertex.y<< ", " << vertex.z; return stream; } int main() { std::vector<Vertex> vertices; vertices.reserve(3); //vertices.push_back(Vertex(1.3f, 2.1f, 4.4f)); //vertices.push_back({ 2,3,4 }); //vertices.push_back(Vertex(3, 4, 5)); //提前reserve后,这个状态下执行三次复制操作,是因为push_back操作,每次先在main函数的栈帧创建一个Vertex,然后再将main中创建好的Vertex复制到vertices分配好的内存中 vertices.emplace_back(1.3f, 2.1f, 4.4f); vertices.emplace_back( 2,3,4 ); vertices.emplace_back(3, 4, 5); //使用emplace_back替换push_back,这个状态下不会执行复制操作,因为push_back是用参数的数据在vertices分配好的内存中创建Vertex对象,不需要再去复制 std::cin.get(); return 0; }
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_16701727/article/details/135411752
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- freesurfer-reconall后批量提取TIV(颅内总体积)
- 关于图像分割项目的可视化脚本
- 14、Citrix 云桌面HDX协议之TCP和UDP
- 西门子WINCC常用C脚本1
- 如何用编程代码来庆祝春节?
- 司铭宇老师:门店销售人员培训:门店销售的素质要求:打造高绩效销售团队的秘诀
- 【算法专题】二叉树中的深搜(DFS)
- setup 语法糖
- Pot-开源划词翻译软件
- 向量数据库:usearch的简单使用+实现图片检索应用