简单rpc应用
发布时间:2024年01月16日
这里来介绍一个简单的rpc应用
首先我们安装需要的包
go install google.golang.org/protobuf/cmd/protoc-gen-go@v1.26
go install google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/protoc-gen-go-grpc@v1.1
创建消息文件实现代码如下
syntax = "proto3"; //声明语法为proto3语法,不声明的话默认的是proto2的语法
option go_package="./;pb";
package pb; //包名
//Greeter 微服务
service Greeter {
//sends a greeting
rpc SayHello(HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
}
//HelloRequest 请求数据格式
message HelloRequest {
string name=1; //这里1并不是说name的值为1,这里的1是一个唯一的编号
}
//HelloReply 响应数据格式
message HelloReply {
string message=1; //这里的1也不是值。是一个唯一的编号
}
然后需要编译生成相应文件
//前面路径./pb表示输出路径,后面的路径./pb/hello.proto表示当前需要编译的文件所在位置
protoc --go_out=./pb ./pb/hello.proto
//前面路径./pb表示输出路径,后面的路径./pb/hello.proto表示当前需要编译的文件所在位置
protoc --go-grpc_out=./pb ./pb/hello.proto
生成的hello.pb.go代码如下
// Code generated by protoc-gen-go. DO NOT EDIT.
// versions:
// protoc-gen-go v1.26.0
// protoc v4.25.0
// source: pb/hello.proto
package pb
import (
protoreflect "google.golang.org/protobuf/reflect/protoreflect"
protoimpl "google.golang.org/protobuf/runtime/protoimpl"
reflect "reflect"
sync "sync"
)
const (
// Verify that this generated code is sufficiently up-to-date.
_ = protoimpl.EnforceVersion(20 - protoimpl.MinVersion)
// Verify that runtime/protoimpl is sufficiently up-to-date.
_ = protoimpl.EnforceVersion(protoimpl.MaxVersion - 20)
)
// HelloRequest 请求数据格式
type HelloRequest struct {
state protoimpl.MessageState
sizeCache protoimpl.SizeCache
unknownFields protoimpl.UnknownFields
Name string `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=name,proto3" json:"name,omitempty"`
}
func (x *HelloRequest) Reset() {
*x = HelloRequest{}
if protoimpl.UnsafeEnabled {
mi := &file_pb_hello_proto_msgTypes[0]
ms := protoimpl.X.MessageStateOf(protoimpl.Pointer(x))
ms.StoreMessageInfo(mi)
}
}
func (x *HelloRequest) String() string {
return protoimpl.X.MessageStringOf(x)
}
func (*HelloRequest) ProtoMessage() {}
func (x *HelloRequest) ProtoReflect() protoreflect.Message {
mi := &file_pb_hello_proto_msgTypes[0]
if protoimpl.UnsafeEnabled && x != nil {
ms := protoimpl.X.MessageStateOf(protoimpl.Pointer(x))
if ms.LoadMessageInfo() == nil {
ms.StoreMessageInfo(mi)
}
return ms
}
return mi.MessageOf(x)
}
// Deprecated: Use HelloRequest.ProtoReflect.Descriptor instead.
func (*HelloRequest) Descriptor() ([]byte, []int) {
return file_pb_hello_proto_rawDescGZIP(), []int{0}
}
func (x *HelloRequest) GetName() string {
if x != nil {
return x.Name
}
return ""
}
// HelloReply 响应数据格式
type HelloReply struct {
state protoimpl.MessageState
sizeCache protoimpl.SizeCache
unknownFields protoimpl.UnknownFields
Message string `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=message,proto3" json:"message,omitempty"`
}
func (x *HelloReply) Reset() {
*x = HelloReply{}
if protoimpl.UnsafeEnabled {
mi := &file_pb_hello_proto_msgTypes[1]
ms := protoimpl.X.MessageStateOf(protoimpl.Pointer(x))
ms.StoreMessageInfo(mi)
}
}
func (x *HelloReply) String() string {
return protoimpl.X.MessageStringOf(x)
}
func (*HelloReply) ProtoMessage() {}
func (x *HelloReply) ProtoReflect() protoreflect.Message {
mi := &file_pb_hello_proto_msgTypes[1]
if protoimpl.UnsafeEnabled && x != nil {
ms := protoimpl.X.MessageStateOf(protoimpl.Pointer(x))
if ms.LoadMessageInfo() == nil {
ms.StoreMessageInfo(mi)
}
return ms
}
return mi.MessageOf(x)
}
// Deprecated: Use HelloReply.ProtoReflect.Descriptor instead.
func (*HelloReply) Descriptor() ([]byte, []int) {
return file_pb_hello_proto_rawDescGZIP(), []int{1}
}
func (x *HelloReply) GetMessage() string {
if x != nil {
return x.Message
}
return ""
}
var File_pb_hello_proto protoreflect.FileDescriptor
var file_pb_hello_proto_rawDesc = []byte{
0x0a, 0x0e, 0x70, 0x62, 0x2f, 0x68, 0x65, 0x6c, 0x6c, 0x6f, 0x2e, 0x70, 0x72, 0x6f, 0x74, 0x6f,
0x12, 0x02, 0x70, 0x62, 0x22, 0x22, 0x0a, 0x0c, 0x48, 0x65, 0x6c, 0x6c, 0x6f, 0x52, 0x65, 0x71,
0x75, 0x65, 0x73, 0x74, 0x12, 0x12, 0x0a, 0x04, 0x6e, 0x61, 0x6d, 0x65, 0x18, 0x01, 0x20, 0x01,
0x28, 0x09, 0x52, 0x04, 0x6e, 0x61, 0x6d, 0x65, 0x22, 0x26, 0x0a, 0x0a, 0x48, 0x65, 0x6c, 0x6c,
0x6f, 0x52, 0x65, 0x70, 0x6c, 0x79, 0x12, 0x18, 0x0a, 0x07, 0x6d, 0x65, 0x73, 0x73, 0x61, 0x67,
0x65, 0x18, 0x01, 0x20, 0x01, 0x28, 0x09, 0x52, 0x07, 0x6d, 0x65, 0x73, 0x73, 0x61, 0x67, 0x65,
0x32, 0x39, 0x0a, 0x07, 0x47, 0x72, 0x65, 0x65, 0x74, 0x65, 0x72, 0x12, 0x2e, 0x0a, 0x08, 0x53,
0x61, 0x79, 0x48, 0x65, 0x6c, 0x6c, 0x6f, 0x12, 0x10, 0x2e, 0x70, 0x62, 0x2e, 0x48, 0x65, 0x6c,
0x6c, 0x6f, 0x52, 0x65, 0x71, 0x75, 0x65, 0x73, 0x74, 0x1a, 0x0e, 0x2e, 0x70, 0x62, 0x2e, 0x48,
0x65, 0x6c, 0x6c, 0x6f, 0x52, 0x65, 0x70, 0x6c, 0x79, 0x22, 0x00, 0x42, 0x07, 0x5a, 0x05, 0x2e,
0x2f, 0x3b, 0x70, 0x62, 0x62, 0x06, 0x70, 0x72, 0x6f, 0x74, 0x6f, 0x33,
}
var (
file_pb_hello_proto_rawDescOnce sync.Once
file_pb_hello_proto_rawDescData = file_pb_hello_proto_rawDesc
)
func file_pb_hello_proto_rawDescGZIP() []byte {
file_pb_hello_proto_rawDescOnce.Do(func() {
file_pb_hello_proto_rawDescData = protoimpl.X.CompressGZIP(file_pb_hello_proto_rawDescData)
})
return file_pb_hello_proto_rawDescData
}
var file_pb_hello_proto_msgTypes = make([]protoimpl.MessageInfo, 2)
var file_pb_hello_proto_goTypes = []interface{}{
(*HelloRequest)(nil), // 0: pb.HelloRequest
(*HelloReply)(nil), // 1: pb.HelloReply
}
var file_pb_hello_proto_depIdxs = []int32{
0, // 0: pb.Greeter.SayHello:input_type -> pb.HelloRequest
1, // 1: pb.Greeter.SayHello:output_type -> pb.HelloReply
1, // [1:2] is the sub-list for method output_type
0, // [0:1] is the sub-list for method input_type
0, // [0:0] is the sub-list for extension type_name
0, // [0:0] is the sub-list for extension extendee
0, // [0:0] is the sub-list for field type_name
}
func init() { file_pb_hello_proto_init() }
func file_pb_hello_proto_init() {
if File_pb_hello_proto != nil {
return
}
if !protoimpl.UnsafeEnabled {
file_pb_hello_proto_msgTypes[0].Exporter = func(v interface{}, i int) interface{} {
switch v := v.(*HelloRequest); i {
case 0:
return &v.state
case 1:
return &v.sizeCache
case 2:
return &v.unknownFields
default:
return nil
}
}
file_pb_hello_proto_msgTypes[1].Exporter = func(v interface{}, i int) interface{} {
switch v := v.(*HelloReply); i {
case 0:
return &v.state
case 1:
return &v.sizeCache
case 2:
return &v.unknownFields
default:
return nil
}
}
}
type x struct{}
out := protoimpl.TypeBuilder{
File: protoimpl.DescBuilder{
GoPackagePath: reflect.TypeOf(x{}).PkgPath(),
RawDescriptor: file_pb_hello_proto_rawDesc,
NumEnums: 0,
NumMessages: 2,
NumExtensions: 0,
NumServices: 1,
},
GoTypes: file_pb_hello_proto_goTypes,
DependencyIndexes: file_pb_hello_proto_depIdxs,
MessageInfos: file_pb_hello_proto_msgTypes,
}.Build()
File_pb_hello_proto = out.File
file_pb_hello_proto_rawDesc = nil
file_pb_hello_proto_goTypes = nil
file_pb_hello_proto_depIdxs = nil
}
生成的hello_prpc.pb.go代码如下
// Code generated by protoc-gen-go-grpc. DO NOT EDIT.
package pb
import (
context "context"
grpc "google.golang.org/grpc"
codes "google.golang.org/grpc/codes"
status "google.golang.org/grpc/status"
)
// This is a compile-time assertion to ensure that this generated file
// is compatible with the grpc package it is being compiled against.
// Requires gRPC-Go v1.32.0 or later.
const _ = grpc.SupportPackageIsVersion7
// GreeterClient is the client API for Greeter service.
//
// For semantics around ctx use and closing/ending streaming RPCs, please refer to https://pkg.go.dev/google.golang.org/grpc/?tab=doc#ClientConn.NewStream.
type GreeterClient interface {
// sends a greeting
SayHello(ctx context.Context, in *HelloRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*HelloReply, error)
}
type greeterClient struct {
cc grpc.ClientConnInterface
}
func NewGreeterClient(cc grpc.ClientConnInterface) GreeterClient {
return &greeterClient{cc}
}
func (c *greeterClient) SayHello(ctx context.Context, in *HelloRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*HelloReply, error) {
out := new(HelloReply)
err := c.cc.Invoke(ctx, "/pb.Greeter/SayHello", in, out, opts...)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return out, nil
}
// GreeterServer is the server API for Greeter service.
// All implementations must embed UnimplementedGreeterServer
// for forward compatibility
type GreeterServer interface {
// sends a greeting
SayHello(context.Context, *HelloRequest) (*HelloReply, error)
mustEmbedUnimplementedGreeterServer()
}
// UnimplementedGreeterServer must be embedded to have forward compatible implementations.
type UnimplementedGreeterServer struct {
}
func (UnimplementedGreeterServer) SayHello(context.Context, *HelloRequest) (*HelloReply, error) {
return nil, status.Errorf(codes.Unimplemented, "method SayHello not implemented")
}
func (UnimplementedGreeterServer) mustEmbedUnimplementedGreeterServer() {}
// UnsafeGreeterServer may be embedded to opt out of forward compatibility for this service.
// Use of this interface is not recommended, as added methods to GreeterServer will
// result in compilation errors.
type UnsafeGreeterServer interface {
mustEmbedUnimplementedGreeterServer()
}
func RegisterGreeterServer(s grpc.ServiceRegistrar, srv GreeterServer) {
s.RegisterService(&Greeter_ServiceDesc, srv)
}
func _Greeter_SayHello_Handler(srv interface{}, ctx context.Context, dec func(interface{}) error, interceptor grpc.UnaryServerInterceptor) (interface{}, error) {
in := new(HelloRequest)
if err := dec(in); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if interceptor == nil {
return srv.(GreeterServer).SayHello(ctx, in)
}
info := &grpc.UnaryServerInfo{
Server: srv,
FullMethod: "/pb.Greeter/SayHello",
}
handler := func(ctx context.Context, req interface{}) (interface{}, error) {
return srv.(GreeterServer).SayHello(ctx, req.(*HelloRequest))
}
return interceptor(ctx, in, info, handler)
}
// Greeter_ServiceDesc is the grpc.ServiceDesc for Greeter service.
// It's only intended for direct use with grpc.RegisterService,
// and not to be introspected or modified (even as a copy)
var Greeter_ServiceDesc = grpc.ServiceDesc{
ServiceName: "pb.Greeter",
HandlerType: (*GreeterServer)(nil),
Methods: []grpc.MethodDesc{
{
MethodName: "SayHello",
Handler: _Greeter_SayHello_Handler,
},
},
Streams: []grpc.StreamDesc{},
Metadata: "pb/hello.proto",
}
服务端程序main.go实现代码如下
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
pb "pro02/pb" //起别名
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"google.golang.org/grpc/reflection"
)
const (
port = ":50051" //定义一个端口常量
)
type server struct {
pb.UnimplementedGreeterServer
} //服务对象
// SayHello 实现服务的接口 在proto中定义的所有服务都是接口
// server实现了GreeterClient接口的SayHello方法,所以可以把server直接当成这个接口使用
func (s *server) SayHello(ctx context.Context, in *pb.HelloRequest) (*pb.HelloReply, error) {
return &pb.HelloReply{Message: "Hello " + in.Name}, nil
}
func main() {
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", port) //监听
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
s := grpc.NewServer() //起一个服务
//server实现了GreeterClient接口的SayHello方法,所以可以把server直接当成这个接口使用
pb.RegisterGreeterServer(s, &server{})
// 注册反射服务 这个服务是CLI使用的 跟服务本身没有关系
reflection.Register(s)
fmt.Println("开始启动服务")
if err := s.Serve(lis); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err)
}
}
客户端程序main.go实现代码如下
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"os"
"time"
pb "pro02/pb"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
const (
address = "localhost:50051" //ip地址端口号
defaultName = "world" //默认值,如果没有给定这个值,那么默认就是这个值
)
func main() {
//建立连接
conn, err := grpc.Dial(address, grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("did not connect: %v", err)
}
defer conn.Close()
c := pb.NewGreeterClient(conn) //新建一个客户端
// Contact the server and print out its response.
name := defaultName //首先给一个默认值
if len(os.Args) > 1 { //判断Hello后面是否有值,有就将值改为这个后面的值
name = os.Args[1]
}
// 1秒的上下文
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second)
defer cancel()
r, err := c.SayHello(ctx, &pb.HelloRequest{Name: name})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("could not greet: %v", err)
}
//输出结果
log.Printf("Greeting: %s", r.Message)
}
项目左侧包结构如下
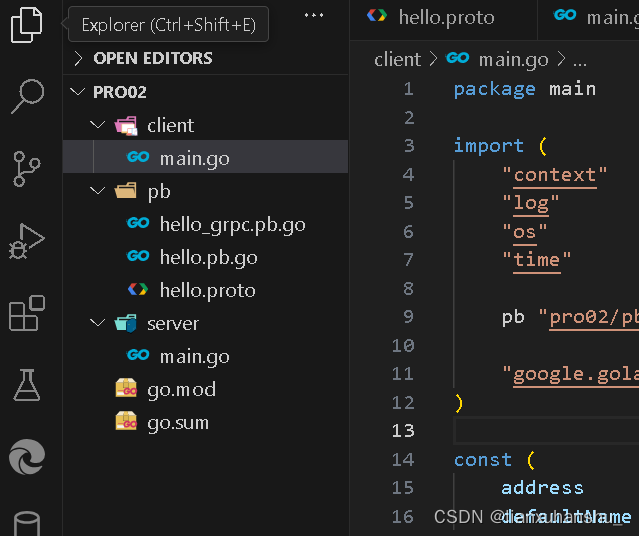 ?
?
详细操作步骤:
(1)首先初始化项目,会生成一个go.mod文件,这个是go的包管理工具
//pro02表示当前项目名称
go mod init pro02(2)然后新建pb包,然后在pb包下面新建hello.proto文件,然后实现消息文件hello.proto
(3)编译消息文件hello.proto.
//前面路径./pb表示输出路径,后面路径./pb/hello.proto表示当前需要编译的文件所在位置
protoc --go_out=./pb ./pb/hello.proto
//前面路径./pb表示输出路径,后面路径./pb/hello.proto表示当前需要编译的文件所在位置
protoc --go-grpc_out=./pb ./pb/hello.proto
编译成功之后会在输出路径下生成一个hello.pb.go文件和一个hello_grpc.pb.go文件,如下图所示
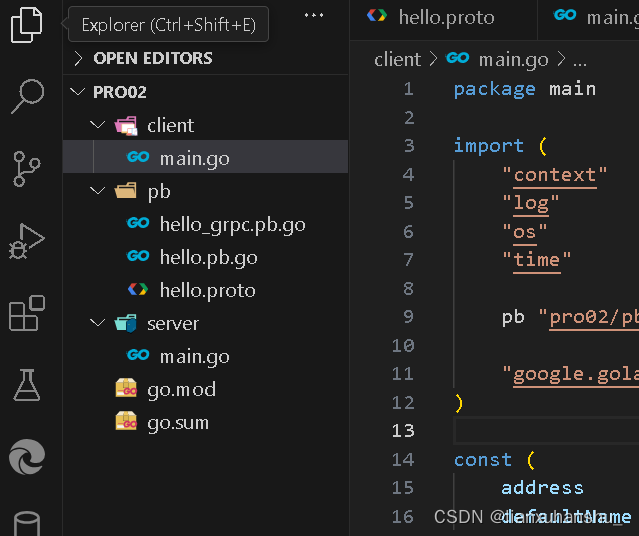
(4)进入server包,运行server包下面的main.go文件
cd server
go run main.go由于我在server的main.go程序中写了一个打印"开始启动服务",所以我们可以在终端看到“开始启动服务”,如果看到了说明服务启动成功,否则说明启动失败,如下图所示就表示成功了。
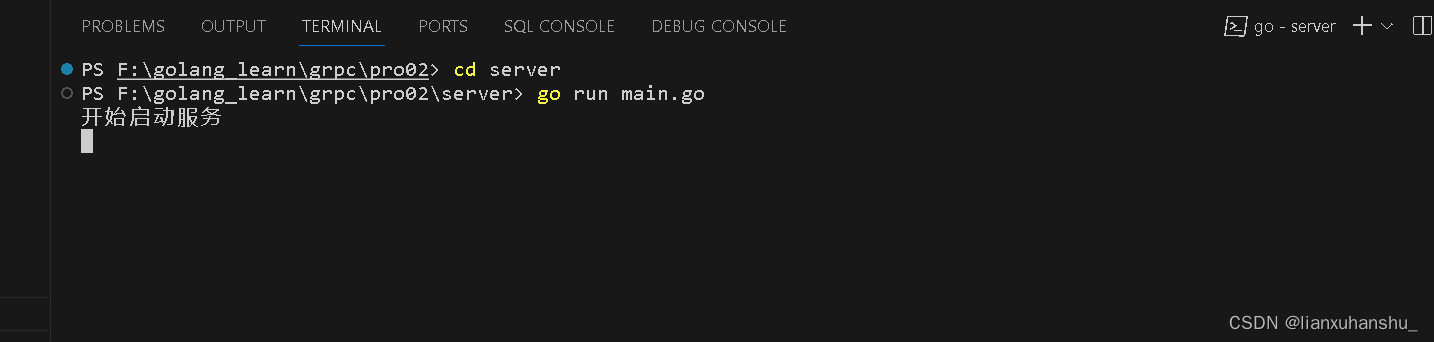 ?
?
(5)上面启动了一个终端,这里需要打开一个新的终端,进入client包,在客户端程序中进行测试,
测试:
cd client
go run .\main.go 你好呀?上述的go run .\main.go 命令后面输入你好呀那就会在控制台上面打印Hello 你好呀,也就是说在这个命令后面输入什么就会打印什么内容,如果后面没有带任何内容,就会输出我们程序中给定的默认值Hello world。当然我们可以通过改动程序代码实现我们其他需要打印出来的内容。
如果程序执行结果如下图所示,表示程序代码实现是正确的,并且操作过程也是正确的。
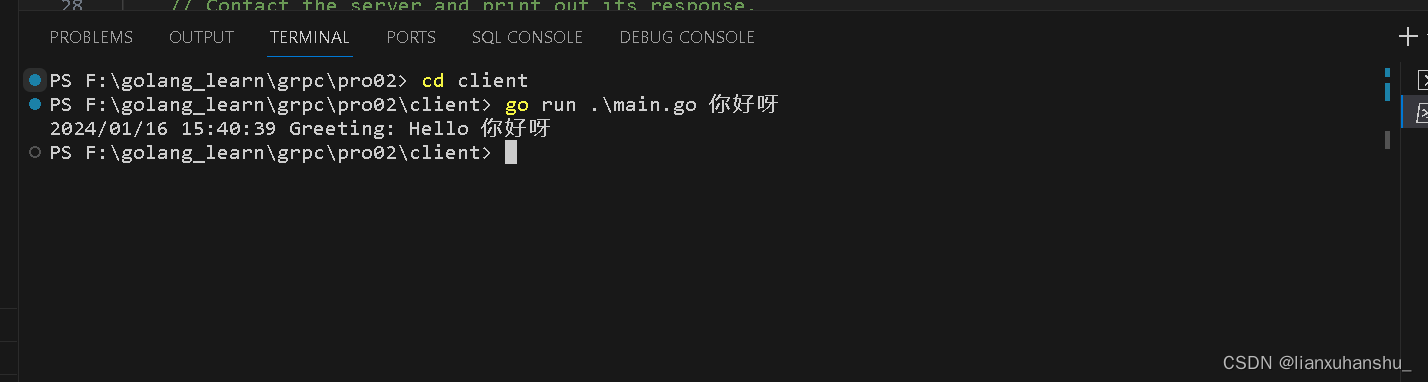
到这里就实现了一个简单的rpc应用了。?
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/lianxuhanshu_/article/details/135625678
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!