华清远见作业第二十四天——(第七天)
发布时间:2024年01月09日
思维导图:

使用消息队列完成两个进程之间相互通信
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <a.h>
//定义A消息结构体类型
struct msgbuf
{
long mtype; //消息类型
char mtext[1024]; //消息正文
};
//定义B消息结构体类型
struct msgbuf1
{
long mtype; //消息类型
int mtext1; //消息正文
};
//定义一个宏,表示正文大小
#define SIZE (sizeof(struct msgbuf) - sizeof(long))
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//定义变量存储进程号
pid_t pid=-1;
//创建一个子进程
pid=fork();
if(pid>0)
{
printf("这是A父进程,pid=%d\n",pid);
//1、创建key值
key_t key = 0;
if((key = ftok("/", 't')) == -1)
{
perror("fork error");
return -1;
}
printf("key = %#x\n", key);
//2、使用key值创建一个消息队列
int msqid = 0;
if((msqid=msgget(key, IPC_CREAT|0664)) == -1)
{
perror("msgget error");
return -1;
}
printf("msqid = %d\n", msqid);
//此时就已经在内核空间创建出消息队列了
//定义一个消息类型的容器
struct msgbuf buf = {.mtype=100};
//3、循环向消息队列中存放数据
while(1)
{
printf("请输入要存放的数据:");
scanf("%s", buf.mtext);
getchar(); //吸收回车
//将消息存放到消息队列中
msgsnd(msqid, &buf, SIZE, 0);
printf("发送成功\n");
if(strcmp(buf.mtext, "quit") == 0)
{
break;
}
}
}else if(pid==0)
{
printf("这是A子进程,pid=%d\n",pid);
//1、创建key值
key_t key = 0;
if((key = ftok("/", 't')) == -1)
{
perror("fork error");
return -1;
}
printf("key = %#x\n", key);
//2、使用key值创建一个消息队列
int msqid = 0;
if((msqid=msgget(key, IPC_CREAT|0664)) == -1)
{
perror("msgget error");
return -1;
}
printf("msqid = %d\n", msqid);
//此时就已经在内核空间创建出消息队列了
//定义一个消息类型的容器
struct msgbuf1 buf;
//3、循环向消息队列中存放数据
while(1)
{
//从消息队列中读取消息
msgrcv(msqid, &buf, SIZE, 0, 0);
//第一个0表示无视类型,每次都取第一个消息
//第二个0表示阻塞形式接收消息
printf("收到消息为:%d\n", buf.mtext1);
if(buf.mtext1 == 0007)
{
break;
}
}
}else
{
perror("fork error");
return -1;
}
printf("hello world再见\n");
return 0;
}?
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <a.h>
//定义A消息结构体类型
struct msgbuf
{
long mtype; //消息类型
char mtext[1024]; //消息正文
};
//定义B消息结构体类型
struct msgbuf1
{
long mtype; //消息类型
int mtext1; //消息正文
};
//定义一个宏,表示正文大小
#define SIZE (sizeof(struct msgbuf) - sizeof(long))
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//定义变量存储进程号
pid_t pid=-1;
pid =fork(); //创建一个子进程
if(pid>0)
{
printf("这是B父进程,pid=%d\n",pid);
//1、创建key值
key_t key = 0;
if((key = ftok("/", 't')) == -1)
{
perror("fork error");
return -1;
}
printf("key = %#x\n", key);
//2、使用key值创建一个消息队列
int msqid = 0;
if((msqid=msgget(key, IPC_CREAT|0664)) == -1)
{
perror("msgget error");
return -1;
}
printf("msqid = %d\n", msqid);
//此时就已经在内核空间创建出消息队列了
//定义一个消息类型的容器
struct msgbuf buf;
//3、循环向消息队列中存放数据
while(1)
{
//从消息队列中读取消息
msgrcv(msqid, &buf, SIZE, 0, 0);
//第一个0表示无视类型,每次都取第一个消息
//第二个0表示阻塞形式接收消息
printf("收到消息为:%s\n", buf.mtext);
if(strcmp(buf.mtext, "quit") == 0)
{
break;
}
}
}else if(pid==0)
{
printf("这是B子进程,pid=%d\n",pid);
//1、创建key值
key_t key = 0;
if((key = ftok("/", 't')) == -1)
{
perror("fork error");
return -1;
}
printf("key = %#x\n", key);
//2、使用key值创建一个消息队列
int msqid = 0;
if((msqid=msgget(key, IPC_CREAT|0664)) == -1)
{
perror("msgget error");
return -1;
}
printf("msqid = %d\n", msqid);
//此时就已经在内核空间创建出消息队列了
//定义一个消息类型的容器
struct msgbuf1 buf = {.mtype=100};
//3、循环向消息队列中存放数据
while(1)
{
printf("请输入要存放的数据:");
scanf("%d", &buf.mtext1);
getchar(); //吸收回车
//将消息存放到消息队列中
msgsnd(msqid, &buf, SIZE, 0);
printf("发送成功\n");
if(buf.mtext1== 0007)
{
break;
}
}
}
else
{
perror("fork error");
return -1;
}
printf("hello B再见\n");
return 0;
}运行效果:
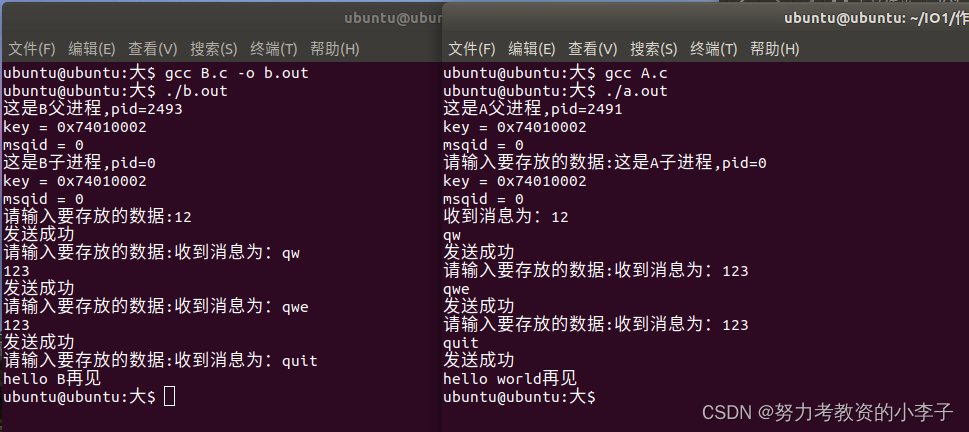
将信号通信相关代码重新实现一遍
代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <a.h>
//定义信号处理函数
void handler(int signo)
{
if(signo==SIGUSR1)
{
printf("逆子如何是好\n");
raise(SIGKILL); //自杀
}
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//定义进程号
pid_t pid=fork();
if(pid>0)
{
//父进程
//将SIGUSR1信号绑定
if(signal(SIGUSR1,handler)==SIG_ERR)
{
perror("signal error");
return -1;
}
while(1)
{
printf("我真的还想再活五百年\n");
sleep(1);
}
}else if(pid==0)
{
//子进程
printf("人生得意啊\n");
sleep(3);
printf("迷迷迷迷迷\n");
//向父进程发送信号
kill(getppid(),SIGUSR1);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); //退出进程
}else
{
perror("fork error");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}运行效果:

将共享内存相关代码重新实现一遍
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <a.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//1创建key值
key_t key=-1;
if((key=ftok("/",'t'))==-1)
{
perror("ftok error");
return -1;
}
printf("key=%#x\n",key);
//2将物理内存创建出共享内存段
int shmid=0;
if((shmid=shmget(key,PAGE_SIZE,IPC_CREAT|0664))==-1)
{
perror("shmget error");
return -1;
}
printf("shmid=%d\n",shmid);
//3将共享内存
//NULL表示让系统自动选项页分段
//0表示当前进程对共享内存具有读写功能
char *addr=(char *)shmat(shmid,NULL,0);
if(addr==(void*)-1)
{
perror("shmat error");
return -1;
}
printf("addr=%p\n",addr);
//4操作共享内存
while(1)
{
fgets(addr,PAGE_SIZE,stdin); //从终端输入数据
addr[strlen(addr)-1]='\0'; //将换行换成'\0'
if(strcmp(addr,"quit")==0)
{
break;
}
}
//5取消映射
while(1);
return 0;
}?
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <a.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//1创建key值
key_t key=-1;
if((key=ftok("/",'t'))==-1)
{
perror("ftok error");
return -1;
}
printf("key=%#x\n",key);
//2将物理内存创建出共享内存段
int shmid=0;
if((shmid=shmget(key,PAGE_SIZE,IPC_CREAT|0664))==-1)
{
perror("shmget error");
return -1;
}
printf("shmid=%d\n",shmid);
//3将共享内存
//NULL表示让系统自动选项页分段
//0表示当前进程对共享内存具有读写功能
char *addr=(char *)shmat(shmid,NULL,0);
if(addr==(void*)-1)
{
perror("shmat error");
return -1;
}
printf("addr=%p\n",addr);
//4操作共享内存
while(1)
{
printf("共享内存中的数据为:%s\n",addr);
sleep(1);
if(strcmp(addr,"quit")==0)
{
break;
}
}
//5取消映射
if(shmdt(addr)==-1)
{
perror("shmdt error");
return -1;
}
//删除共享内存
if(shmctl(shmid,IPC_RMID,NULL)==-1)
{
perror("shmctl error");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}运行效果:

文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_62462327/article/details/135489826
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章