【JAVA】实验二 类与对象
发布时间:2024年01月02日
实验名称??? 实验二 类与对象
实验目的???
1. 深刻理解类的封装与继承;
2. 熟练掌握类的定义、包与路径、对象的创建、方法的调用、类的继承、方法的重写、运行时多态、访问权限修饰符的使用等;
3. 熟练运用JDK提供的常用类及API。??
实验内容(4学时)
1. 定义一个圆形类Circle,包括:
(1)属性:圆心、半径
(2)方法:求面积、周长;上下左右平移;缩放;绘图(虚拟表示)。
设计测试类CircleDemo,在测试类中测试上述方法。以后实验中均自行设计测试类。
class Circle {
??? private double centerX;
??? private double centerY;
??? private double radius;
??? public Circle(double centerX, double centerY, double radius) {
??????? this.centerX = centerX;
??????? this.centerY = centerY;
??????? this.radius = radius;
??? }
??? public double getArea() {
??????? return Math.PI * radius * radius;
??? }
??? public double getPerimeter() {
??????? return 2 * Math.PI * radius;
??? }
??? public void translate(double deltaX, double deltaY) {
??????? centerX += deltaX;
??????? centerY += deltaY;
??? }
??? public void scale(double factor) {
??????? radius *= factor;
??? }
??? public void draw() {
??????? System.out.println("Drawing a circle at (" + centerX + ", " + centerY + ") with radius " + radius);
??? }
}
public class CircleDemo {
??? public static void main(String[] args) {
??????? Circle circle = new Circle(0, 0, 5.0);
??????? System.out.println("Area: " + circle.getArea());
??????? System.out.println("Perimeter: " + circle.getPerimeter());
??????? circle.translate(2.0, 3.0);
??????? circle.scale(1.5);
??????? circle.draw();
??? }
}
2. 设计Bird类,包括:(1)属性:name;(2)方法:fly( ),fly方法以及后面提到的各种方法均以字符串输出来演示功能。
以Bird类为超类(父类),设计子类CarrierPigeon,
(1)为CarrierPigeon类新增方法:send(String address, String message)
(2)在CarrierPigeon 覆盖 Bird 的 fly() 方法
public class Bird {
??? private String name;
??? public Bird(String name) {
??????? this.name = name;
??? }
??? public String getName() {
??????? return name;
??? }
??? public void fly() {
??????? System.out.println(name + " is flying.");
??? }
}
public class CarrierPigeon extends Bird {
??? public CarrierPigeon(String name) {
??????? super(name);
??? }
??? public void send(String address, String message) {
??????? System.out.println(getName() + " is sending a message to " + address + ": " + message);
??? }
??? @Override
??? public void fly() {
??????? System.out.println(getName() + " is flying with a message.");
??? }
}
public class BirdDemo {
??? public static void main(String[] args) {
??????? Bird bird = new Bird("Sparrow");
??????? bird.fly();
??????? CarrierPigeon pigeon = new CarrierPigeon("Pigeon");
??????? pigeon.fly();
??????? pigeon.send("Recipient", "Important message");
??? }
}
3. Java编程实现:设计复数类Complex,类中实部和虚部都是实数,实现加法、减法、乘法和除法。
public class Complex {
??? private double real;
??? private double imaginary;
??? public Complex(double real, double imaginary) {
??????? this.real = real;
??????? this.imaginary = imaginary;
??? }
??? public Complex add(Complex other) {
??????? double newReal = this.real + other.real;
??????? double newImaginary = this.imaginary + other.imaginary;
??????? return new Complex(newReal, newImaginary);
??? }
??? public Complex subtract(Complex other) {
??????? double newReal = this.real - other.real;
?????? ?double newImaginary = this.imaginary - other.imaginary;
??????? return new Complex(newReal, newImaginary);
??? }
??? public Complex multiply(Complex other) {
??????? double newReal = this.real * other.real - this.imaginary * other.imaginary;
??????? double newImaginary = this.real * other.imaginary + this.imaginary * other.real;
??????? return new Complex(newReal, newImaginary);
??? }
??? public Complex divide(Complex other) {
??????? double denominator = other.real * other.real + other.imaginary * other.imaginary;
??????? double newReal = (this.real * other.real + this.imaginary * other.imaginary) / denominator;
??????? double newImaginary = (this.imaginary * other.real - this.real * other.imaginary) / denominator;
??????? return new Complex(newReal, newImaginary);
??? }
??? @Override
??? public String toString() {
??????? return real + " + " + imaginary + "i";
??? }
}
public class ComplexDemo {
??? public static void main(String[] args) {
??????? Complex c1 = new Complex(2.0, 3.0);
??????? Complex c2 = new Complex(1.0, 1.0);
??????? Complex sum = c1.add(c2);
??????? Complex difference = c1.subtract(c2);
??????? Complex product = c1.multiply(c2);
??????? Complex quotient = c1.divide(c2);
??????? System.out.println("Sum: " + sum);
??????? System.out.println("Difference: " + difference);
??????? System.out.println("Product: " + product);
??????? System.out.println("Quotient: " + quotient);
??? }
}
4. Java编程实现:设计矩阵类Matrix,类中的方法能对矩阵进行加法、减法和乘法运算。在矩阵中再定义一个方法,生成如下的矩阵:

public class Matrix {
??? private int[][] data;
??? public Matrix(int[][] data) {
??????? this.data = data;
??? }
??? // 获取矩阵的行数
??? public int getRows() {
??????? return data.length;
??? }
??? // 获取矩阵的列数
??? public int getColumns() {
??????? return data[0].length;
??? }
??? // 矩阵加法
??? public Matrix add(Matrix other) {
??????? if (getRows() != other.getRows() || getColumns() != other.getColumns()) {
??????????? throw new IllegalArgumentException("矩阵维度不匹配");
??????? }
??????? int[][] result = new int[getRows()][getColumns()];
??????? for (int i = 0; i < getRows(); i++) {
??????????? for (int j = 0; j < getColumns(); j++) {
??????????????? result[i][j] = data[i][j] + other.data[i][j];
??????????? }
??????? }
??????? return new Matrix(result);
??? }
??? // 矩阵减法
??? public Matrix subtract(Matrix other) {
??????? if (getRows() != other.getRows() || getColumns() != other.getColumns()) {
??????????? throw new IllegalArgumentException("矩阵维度不匹配");
??????? }
??????? int[][] result = new int[getRows()][getColumns()];
??????? for (int i = 0; i < getRows(); i++) {
??????????? for (int j = 0; j < getColumns(); j++) {
??????????????? result[i][j] = data[i][j] - other.data[i][j];
??????????? }
??????? }
??????? return new Matrix(result);
??? }
??? // 矩阵乘法
??? public Matrix multiply(Matrix other) {
??????? if (getColumns() != other.getRows()) {
??????????? throw new IllegalArgumentException("矩阵维度不匹配");
??????? }
??????? int[][] result = new int[getRows()][other.getColumns()];
??????? for (int i = 0; i < getRows(); i++) {
??????????? for (int j = 0; j < other.getColumns(); j++) {
??????????????? int sum = 0;
??????????????? for (int k = 0; k < getColumns(); k++) {
??????????????????? sum += data[i][k] * other.data[k][j];
??????????????? }
??????????????? result[i][j] = sum;
??????????? }
??????? }
??????? return new Matrix(result);
??? }
??? // 生成指定的矩阵
??? public static Matrix createMatrixE() {
??????? int[][] eMatrixData = {
??????????????? {1, 3, 8, 7, 5, 6},
??????????????? {3, 8, 7, 5, 6, 1},
??????????????? {8, 7, 5, 6, 1, 3},
??????????????? {7, 5, 6, 1, 3, 8},
??????????????? {5, 6, 1, 3, 8, 7},
??????????????? {6, 1, 3, 8, 7, 5}
??????? };
??????? return new Matrix(eMatrixData);
??? }
??? // 打印矩阵
??? public void printMatrix() {
??????? for (int i = 0; i < getRows(); i++) {
??????????? for (int j = 0; j < getColumns(); j++) {
??????????????? System.out.print(data[i][j] + " ");
??????????? }
??????????? System.out.println();
??????? }
??? }
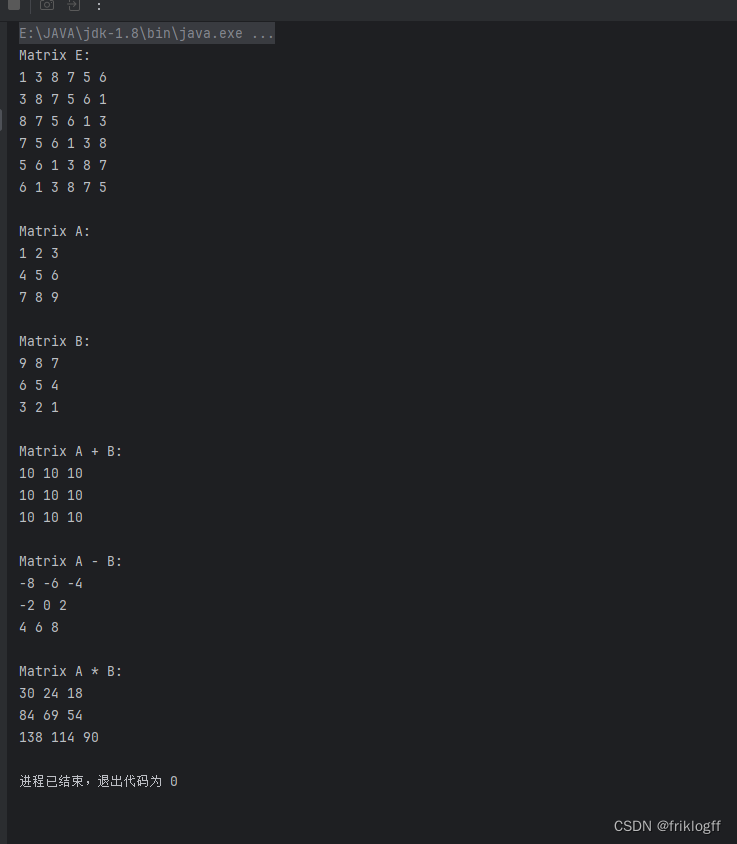
??? public static void main(String[] args) {
??????? Matrix matrixE = createMatrixE();
??????? System.out.println("Matrix E:");
??????? matrixE.printMatrix();
??????? Matrix matrixA = new Matrix(new int[][] {
??????????????? {1, 2, 3},
??????????????? {4, 5, 6},
??????????????? {7, 8, 9}
??????? });
??????? Matrix matrixB = new Matrix(new int[][] {
??????????????? {9, 8, 7},
??????????????? {6, 5, 4},
??????????????? {3, 2, 1}
??????? });
??????? System.out.println("\nMatrix A:");
??????? matrixA.printMatrix();
??????? System.out.println("\nMatrix B:");
??????? matrixB.printMatrix();
??????? Matrix matrixSum = matrixA.add(matrixB);
??????? System.out.println("\nMatrix A + B:");
??????? matrixSum.printMatrix();
??????? Matrix matrixDifference = matrixA.subtract(matrixB);
??????? System.out.println("\nMatrix A - B:");
??????? matrixDifference.printMatrix();
??????? Matrix matrixProduct = matrixA.multiply(matrixB);
??????? System.out.println("\nMatrix A * B:");
??????? matrixProduct.printMatrix();
??? }
}
实验程序及结果(附录)
思考
以C为代表的结构化编程语言和以Java为代表的面向对象编程语言有哪些本质不同?
关于结构化编程语言(以C为代表)和面向对象编程语言(以Java为代表)的本质不同:
- 抽象与封装:面向对象编程强调对象的抽象和封装,允许将数据和操作封装在对象内部,提供更好的信息隐藏和模块化。结构化编程相对较少使用对象,更多地依赖于函数和数据的分离。
- 继承与多态:面向对象编程支持继承和多态,允许创建层次结构的类,重用代码并实现多态性。结构化编程通常较少使用这些概念,更注重逻辑流程和模块化设计。
- 对象:面向对象编程以对象为中心,将数据和操作封装在对象中。结构化编程更倾向于使用数据结构和函数。
- 设计模式:面向对象编程强调设计模式,例如单例模式、工厂模式等,以提供更好的可维护性和可扩展性。结构化编程通常较少使用这些模式。
- 类型系统:面向对象编程通常有更强的类型系统,支持多态和动态绑定。结构化编程的类型系统通常较为简单。
总之,面向对象编程更注重数据和操作的封装、继承、多态等概念,而结构化编程更注重逻辑流程和分离数据和函数。不同编程范式适用于不同类型的问题和项目。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42531954/article/details/135344126
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 荷兰公司注册优势 注册荷兰公司所需条件 荷兰公司年审
- Linux环境变量、export命令、env命令、$符号
- 代码随想录训练营第一天| 704.二分查找、27.移除元素
- Spring Boot 中实现文件上传、下载、删除功能
- Vue 进阶面试题
- canvas设置图形图案、文字图案
- 数据库系统概念 第七版 中文答案 第3章 SQL介绍
- 基于ssm的物业管理系统论文
- keras with pytorch backend : GPU版
- 小白编程题:组合数问题