11.1Linux串口应用程序开发
发布时间:2023年12月25日
UART简介
UART的全称是Universal Asynchronous Receiver and Transmitter,即异步发送和接收。
串口在嵌入式中用途非常的广泛,主要的用途有:
- 打印调试信息;
- 外接各种模块:GPS、蓝牙;
串口因为结构简单、稳定可靠(通过RXD 、TXD、GND三根线即可完成通信),广受欢迎。
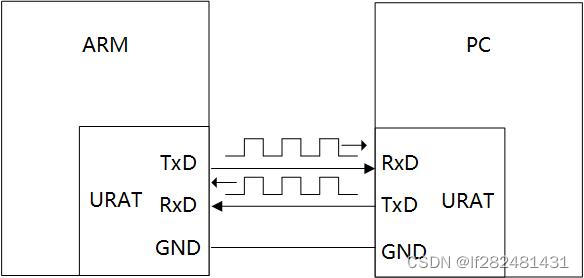
串口的参数
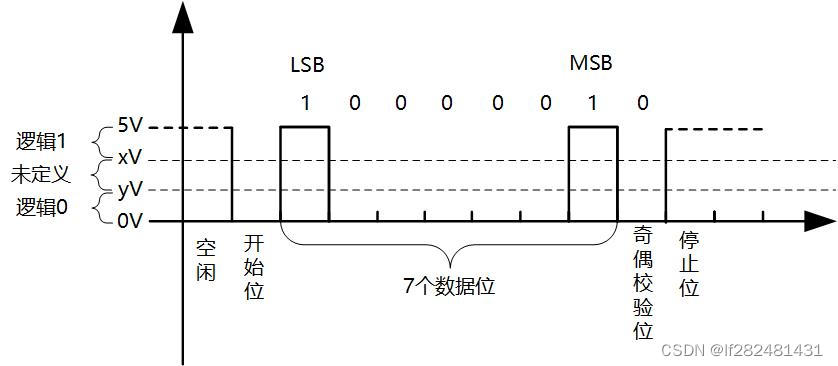
- 波特率:常用的有9600、19200、115200、230400、921600等,其实意思就是每秒传输这么多个比特位数(bit)
- 起始位:先发出一位或两位逻辑”0”的信号,表示传输数据的开始。
- 数据位:可以是5~8位逻辑”0”或”1”。如ASCII码(7位),扩展BCD码(8位)。
- 校验位:数据位加上这一位后,使得“1”的位数应为偶数(偶校验)或奇数(奇校验),以此来校验数据传送的正确性。
- 停止位:它是一个字符数据的结束标志,通常一位或两位逻辑”1”。
串口传输数据
- 双方约定好波特率(每一位占据的时间)。
- 双方约定好传输电平,即高电平是多少v,低电平是但是v。
- 双方约定好起始位位数。
- 双方约定好奇偶校验。
- 双方约定好停止位位数。
tty 设备节点命名规则
- /dev/ttyS0 、 /dev/ttySTM0 :串口终端。
- /dev/tty1 、 /dev/tty2 、 …… :虚拟终端设备。
- /dev/tty0 :当前正在使用的虚拟终端的别名。
- /dev/tty :本进程自己的终端。
- /dev/console :控制台,由内核的命令行参数确定,可以认为是一个拥有更高权限的终端,不管当前正在使用哪个终端,系统信息都会发送到控制台上。
串口编程
头文件
编写串口应用程序时需要先包含如下头文件:
#include <stdio.h> /* Standard input/output definitions */
#include <string.h> /* String function definitions */
#include <unistd.h> /* UNIX standard function definitions */
#include <fcntl.h> /* File control definitions */
#include <errno.h> /* Error number definitions */
#include <termios.h> /* POSIX terminal control definitions */
打开串口
int open_port(void)
{
int fd;
/* 打开串口
* "/dev/ttyf1" 串口文件名
* O_RDWR 以读写方式打开
* O_NOCTTY 不将此端口作为控制终端
* O_NDELAY 表示不关心 DCD 信号线的状态,同时它还将串口设置为非阻塞模式,在没有数据时进行读取返回0,
* 后面可以通过fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, 0)将其设置为阻塞式
**/
fd = open("/dev/ttyf1", O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY);
if (fd == -1)
{
/* 打开失败 */
perror("open_port: Unable to open /dev/ttyf1 - ");
}
else
{
/* 设置为阻塞式读取 */
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, 0);
}
return (fd);
}
读写串口
通过write函数写数据(发送数据),通过read函数都数据(接收数据)
关闭串口
通过close函数关闭串口设备
配置串口
可以通过如下来读取或配置串口参数:
/* tcgetattr 获取串口配置参数, tcsetattr 设置串口配置参数
- fd
- optional_actions 配置模式:
- TCSANOW 改变立即发生
- TCSADRAIN 改变在写入 fd 的数据都被传输后生效
- TCSAFLUSH 改变在写入 fd 的数据都被传输后生效,且已接收但未读取的数据全部丢弃
- termios_p 串口配置参数
**/
int tcgetattr(int fd, struct termios *termios_p)
int tcsetattr(int fd, int optional_actions, const struct termios *termios_p)
串口的配置参数保存在struct termios 结构体中,此结构体至少包含以下成员:
/* 输入控制标志 */
tcflag_t c_iflag;
/* 输出控制标志 */
tcflag_t c_oflag;
/* 控制模式标志 */
tcflag_t c_cflag;
/* 本地模式标志 */
tcflag_t c_lflag;
/* 行规程 */
cc_t c_cc[NCCS];
/* 输入波特率 */
int c_ispeed;
/* 输出波特率 */
int c_ospeed;
- 输入控制标志选项(c_iflag)
INPCK :启用输入奇偶校验
IGNPAR :忽略奇偶校验错误
PARMRK :标记奇偶校验错误
ISTRIP :去掉奇偶校验位
IXON :启用输出的 XON/XOFF 流控制
IXOFF :启用输入的 XON/XOFF 流控制
IXANY :允许任何字符来重新开始输出
IGNBRK :忽略输入中的 BREAK 状态
BRKINT :检测到中断条件时发送 SIGINT
INLCR :将换行映射到回车
IGNCR :忽略回车
ICRNL :将回车映射到换行
IUCLC :将大写映射到小写
启用输入奇偶校验并剥离奇偶校验位:
c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP)
启用软件流控制:
c_iflag |= (IXON | IXOFF | IXANY);
禁用软件流控:
c_iflag &= ~(IXON | IXOFF | IXANY);
- 输出控制标志选项(c_oflag)
OPOST :启用输出处理(未设置 = 原始输出)
OLCUC :将小写映射到大写
ONLCR :将换行映射到回车+换行
OCRNL :将回车映射到换行
NOCR :不在第 0 列输出回车
ONLRET :将换行映射到回车
OFILL :发送填充字符作为延时,而不是使用定时来延时
OFDEL :填充字符为 DEL
NLDLY :新行延时掩码
NL0 :新行没有延迟
NL1 :换行后延迟100ms
CRDLY :回车延时掩码
CR0 :回车没有延迟
CR1 :回车后的延迟取决于当前列位置
CR2 :回车后延迟 100 毫秒
CR3 :回车后延迟 150 毫秒
TABDLY :tab延时掩码
TAB0 :TAB 没有延迟
TAB1 :TAB 后的延迟取决于当前列位置
TAB2 :发送 TAB 后延迟 100 毫秒
TAB3 :将 TAB 字符扩展为空格
BSDLY :回退延时掩码
BS0 :回退没有延迟
BS1 :回退后延迟 50 毫秒
VTDLY :竖直跳格延时掩码
VT0 :竖直跳格无延迟
VT1 :竖直跳格后延迟 2 秒
FFDLY :进表延时掩码
FF0 :进表没有延迟
FF1 :进表后延迟 2 秒
选择原始输出:
/* 禁用OPOST选项时,将忽略 c_oflag中的所有其他选项位 */
c_oflag &= ~OPOST;
- 控制模式标志(c_cflag)
CSIZE :字符长度掩码
CS5 :5 个数据位
CS6 :6 个数据位
CS7 :7 个数据位
CS8 :8 个数据位
CSTOPB :2 个停止位(否则为 1 个)
CREAD :启用接收器
PARENB :启用奇偶校验位
PARODD :使用奇校验而不是偶校验
HUPCL :关闭时挂断 moden
CLOCAL :忽略 modem 控制线
CRTSCTS :启用硬件流控制
设置字符大小:
c_cflag &= ~CSIZE; /* 屏蔽字符大小位 */
c_cflag |= CS8; /* 选择 8 个数据位 */
设置奇偶校验:
/*无奇偶校验 (8N1) */
c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
c_cflag |= CS8;
/* 偶校验(7E1) */
c_cflag |= PARENB;
c_cflag &= ~PARODD;
c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
c_cflag |= CS7;
/* 奇校验(7O1) */
c_cflag |= PARENB;
c_cflag |= PARODD;
c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
c_cflag |= CS7;
设置硬件流控制:
c_cflag |= CRTSCTS;
禁用硬件流控制:
c_cflag &= ~CRTSCTS;
- 本地模式标志(c_lflag)
ISIG :启用 SIGINTR、SIGSUSP、SIGDSUSP 和 SIGQUIT 信号
ICANON :使能规范输入,这使 EOF 、 EOL 、 EOL2 、 ERASE 、 KILL 、 REPRINT 、 STATUS 、 WERASE 字符起作用,输入字符被装配成行
XCASE :如果同时设置了 ICANON ,则输入被转换为小写(除有前缀 / 的字符以外),输出一个大写字符也在其前加一个 /
ECHO :回显输入字符
ECHOE :如果同时设置了 ICANON ,字符 ERASE 擦除前一个输入字符, WERASE 擦除前一个词
ECHOK :如果同时设置了 ICANON,字符 KILL 删除当前行
ECHONL :如果同时设置了 ICANON,回显字符 NL,即使没有设置 ECHO
NOFLSH :禁止在产生 SIGINT, SIGQUIT 和 SIGSUSP 信号时刷新输入和输出队列
IEXTEN :启用扩展字符处理,这个标志必须与 ICANON 同时使用才能解释特殊字符 EOL2 、 LNEXT 、 REPRINT 、 WERASE, IUCLC 标志才有效
ECHOCTL :如果同时设置了 ECHO,除了 TAB, NL, START, 和 STOP 之外的 ASCII 控制字符被回显为 ^X (这里 X 是比控制字符加 0x40 的 ASCII 码)
ECHOPRT :如果同时设置了 ICANON 和 IECHO,字符在删除的同时被打印
ECHOKE :如果同时设置了 ICANON ,回显 KILL 时将删除一行中的每个字符
FLUSHO :输出被刷新,这个标志可以通过键入字符 DISCARD 来开关
PENDIN :在读入下一个字符时,输入队列中所有字符被重新输出
TOSTOP :向试图写控制终端的后台进程组发送 SIGTTOU 信号
选择规范输入:
c_lflag |= (ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE);
选择原始输入:
c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG);
- 控制字符(c_cc )
VINTR :中断字符。发出 SIGINT 信号,当设置 ISIG 时可被识别
VQUIT :退出字符。发出 SIGQUIT 信号,当设置 ISIG 时可被识别
VERAS :删除字符。删除上一个还没有删掉的字符,但不删除上一个 EOF 或行首,当设置 ICANON 时可被识别
VKILL :终止字符。删除自上一个 EOF 或行首以来的输入,当设置 ICANON 时可被识别
VEOF :文件尾字符。这个字符使得 tty 缓冲中的内容被送到等待输入的用户程序中,而不必等到 EOL,当设置ICANON 时可被识别
VEOL : 行结束字符,当设置 ICANON 时可被识别
VEOL2 :替换的行结束,当设置 ICANON 时可被识别
VMIN :要读取的最小字符数
VTIME :等待数据的时间(100毫秒)
MIN与TIME组合有以下四种:
//有数据立即读取,并返回读取的字节数,无数据立即返回0
MIN = 0 , TIME = 0;
//在 TIME 指定的时间内有数据则返回读取的字节数,无数据返回0
MIN = 0 , TIME > 0;
//在最少读取到 MIN 个字节数才返回
MIN > 0 , TIME = 0;
//读取到的一个字节时启动计时,此后每收到一个字符都会重新计时,在最少读取到 MIN 个字节数或超时返回读取的字节数
MIN > 0 , TIME > 0;
- 波特率(c_ispeed & c_ospeed)
波特率的设置和读取通过下列函数实现:
/* 获取输入波特率 */
speed_t cfgetispeed(const struct termios *termios_p);
/* 获取输出波特率 */
speed_t cfgetospeed(const struct termios *termios_p);
/* 设置输入波特率 */
int cfsetispeed(struct termios *termios_p, speed_t speed);
/* 设置输出波特率 */
int cfsetospeed(struct termios *termios_p, speed_t speed);
/* 设置输入输出波特率 */
int cfsetspeed(struct termios *termios_p, speed_t speed);
串口应用程序编写
原理图
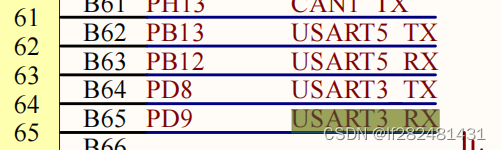
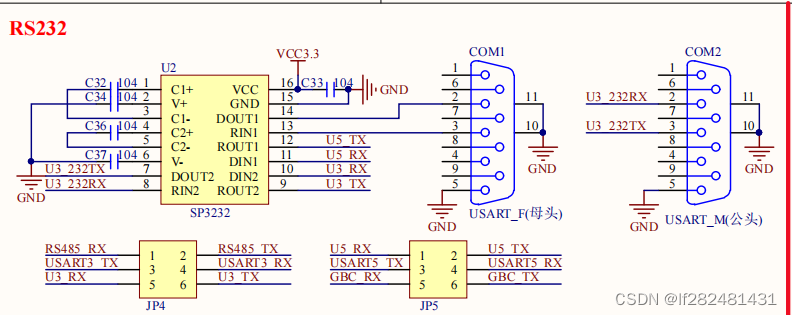
编写设备树
在设备树stm32mp157d-atk.dtsi中引用uart3和uart4节点,并加入如下内容:
&usart3 {
pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep";
pinctrl-0 = <&usart3_pins_mx>;
pinctrl-1 = <&usart3_sleep_pins_mx>;
/delete-property/dmas;
/delete-property/dma-names;
status = "okay";
};
&uart5 {
pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep";
pinctrl-0 = <&uart5_pins_mx>;
pinctrl-1 = <&uart5_sleep_pins_mx>;
/delete-property/dmas;
/delete-property/dma-names;
status = "okay";
};
在设备树stm32mp15-pinctrl.dtsi中引用的&pinctrl节点中加入如下内容:
uart5_pins_mx: uart5_mx-0 {
pins1 {
pinmux = <STM32_PINMUX('B', 12, AF14)>; /* UART5_RX */
bias-disable;
};
pins2 {
pinmux = <STM32_PINMUX('B', 13, AF14)>; /* UART5_TX */
bias-disable;
drive-push-pull;
slew-rate = <0>;
};
};
uart5_sleep_pins_mx: uart5_sleep_mx-0 {
pins {
pinmux = <STM32_PINMUX('B', 12, ANALOG)>, /* UART5_RX */
<STM32_PINMUX('B', 13, ANALOG)>; /* UART5_TX */
};
};
usart3_pins_mx: usart3_mx-0 {
pins1 {
pinmux = <STM32_PINMUX('D', 8, AF7)>; /* USART3_TX */
bias-disable;
drive-push-pull;
slew-rate = <0>;
};
pins2 {
pinmux = <STM32_PINMUX('D', 9, AF7)>; /* USART3_RX */
bias-disable;
};
};
usart3_sleep_pins_mx: usart3_sleep_mx-0 {
pins {
pinmux = <STM32_PINMUX('D', 8, ANALOG)>, /* USART3_TX */
<STM32_PINMUX('D', 9, ANALOG)>; /* USART3_RX */
};
};
在设备树stm32mp157d-atk.dts的aliases节点中增加如下内容:
//usart3的设备文件名是ttySTM1
//uart5的设备文件名是ttySTM2
serial1 = &usart3;
serial2 = &uart5;
用make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-none-linux-gnueabihf- dtbs -j8编译设备树,然后用新的.dtb文件启动系统
编写应用程序
编写一个应用程序,从串口读取数据,然后显示读取到的字节数,并将读取的数据返回到PC,程序包含以下几个部分:
- 打开串口设备
- 配置串口设备
- 读写串口设备
完整的应用程序如下:
#include <stdio.h> /* Standard input/output definitions */
#include <string.h> /* String function definitions */
#include <unistd.h> /* UNIX standard function definitions */
#include <fcntl.h> /* File control definitions */
#include <errno.h> /* Error number definitions */
#include <termios.h> /* POSIX terminal control definitions */
int set_port(int fd, int baud_rate, int n_bits, char parity, int n_stop)
{
struct termios options;
/* 读取配置 */
if(tcgetattr(fd, &options) < 0)
{
perror("SetupSerial 1");
return -1;
}
options.c_iflag = 0x00;
options.c_oflag = 0x00;
options.c_cflag = 0x00;
options.c_lflag = 0x00;
/* 禁用软件流控 */
options.c_iflag &= ~(IXON | IXOFF | IXANY);
if((parity == 'O') || (parity == 'E')) {
/* 启用输入奇偶校验并剥离奇偶校验位 */
options.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP);
}
/* 选择原始输出 */
options.c_oflag &= ~OPOST;
/* 设置字符大小 */
options.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
switch(n_bits)
{
case 7:
options.c_cflag |= CS7;
break;
case 8:
default:
options.c_cflag |= CS8;
break;
}
/* 设置奇偶校验 */
switch(parity)
{
case 'O':
options.c_cflag |= PARENB;
options.c_cflag |= PARODD;
break;
case 'E':
options.c_cflag |= PARENB;
options.c_cflag &= ~PARODD;
break;
case 'N':
default:
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
break;
}
/* 禁用硬件流控制 */
options.c_cflag &= ~CRTSCTS;
/* 设置停止位 */
switch(n_stop)
{
case 2:
options.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;
break;
case 1:
default:
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
break;
}
/* 启用接收器,并忽略 modem 控制线 */
options.c_cflag |= CLOCAL | CREAD;
/* 选择原始输入 */
options.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG);
/* 设置波特率 */
switch(baud_rate)
{
case 2400:
cfsetispeed(&options, B2400);
cfsetospeed(&options, B2400);
break;
case 4800:
cfsetispeed(&options, B4800);
cfsetospeed(&options, B4800);
break;
case 9600:
cfsetispeed(&options, B9600);
cfsetospeed(&options, B9600);
break;
case 115200:
default:
cfsetispeed(&options, B115200);
cfsetospeed(&options, B115200);
break;
}
/* 设置读取超时和每次读取的最小字节数 */
options.c_cc[VMIN] = 1;
options.c_cc[VTIME] = 1;
/* 刷新缓冲区 */
tcflush(fd, TCIFLUSH);
/* 配置串口 */
if((tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &options))!=0)
{
perror("com set error");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int open_port(const char *com)
{
int fd;
/* 打开串口 */
fd = open(com, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY);
if (fd == -1)
{
/* 打开失败 */
perror("open_port");
}
else
{
/* 设置为阻塞式读取 */
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, 0);
}
return (fd);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
int result;
char buffer[64];
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: \n");
printf("%s </dev/ttySAC1 or other>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 打开串口设备 */
fd = open_port(argv[1]);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open %s err!\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 设置串口设备 */
result = set_port(fd, 115200, 8, 'N', 1);
if(result < 0)
{
printf("set port err!\n");
return -1;
}
while(1)
{
/* 读取串口接收到的数据 */
result = read(fd, &buffer, sizeof(buffer));
if(result > 0)
{
printf(" read %d bytes\r\n", result);
/* 通过串口发送数据 */
result = write(fd, &buffer, result);
}
else
perror(NULL);
}
return 0;
}
上机测试
- 根据原理图修改设备树,主要是使能需要用到的串口,然后编译设备树,用新的设备树启动串口
- 从这里下载代码,并进行编译,然后将编译得到的可执行程序拷贝到目标板的root目录中
- 连接串口线到电脑
- 在终端运行命令./uart_teat.out /dev/ttySTM2进行串口测试,其中/dev/ttySTM2是串口设备文件名,如下分别是串口测试软件输出和串口调试软件的截图
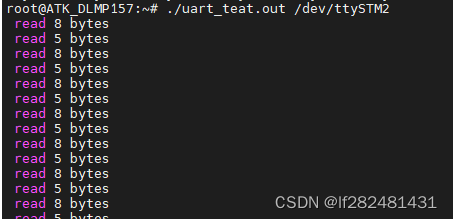
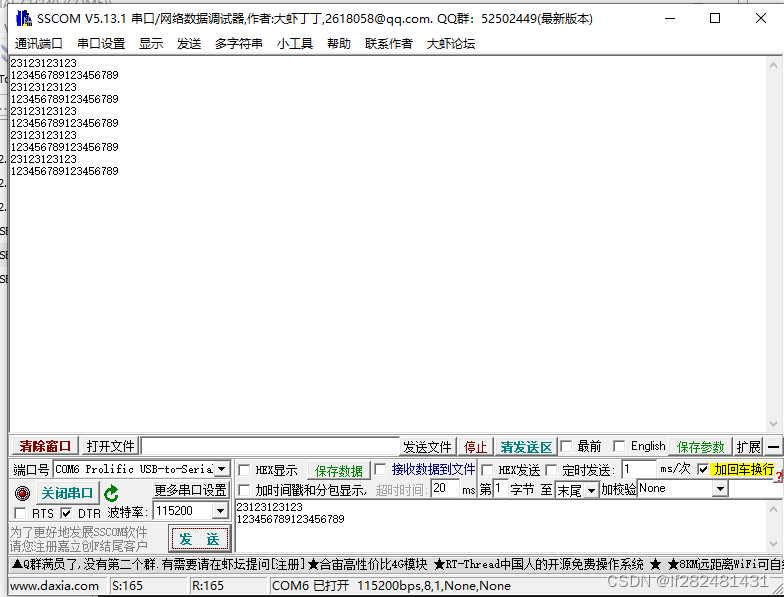
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/lf282481431/article/details/135208795
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Day03 链表
- 软件测试工程师简历项目经验怎么写?--9999个已成功入职的软件测试工程师真实简历
- PLM系统哪家好?如何选择最适合您的供应商?
- 【Java】 Java MySQL 实现读写分离方案
- 【python】—— 集合
- Elment UI的el-table-column表头旁边有点击按钮类似的操作
- CleanMyMac X2024免费许可证及功能详细讲解
- SQL 数据操作技巧:SELECT INTO、INSERT INTO SELECT 和 CASE 语句详解
- Cisco无线Mobility Express配置Image TFTP服务器
- 运维笔记之centos7安装mysql数据库