基于DRIVE数据集的视网膜UNet分割
发布时间:2024年01月21日
1 数据集介绍
这是一个非常小的数据集,非常适合用于视觉分割任务练手。数据集的文件夹如图所示:
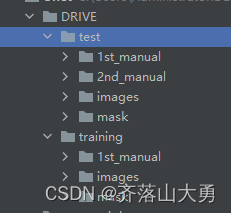
图1-1文件夹结构
test中存放的是测试图片,training中存放的是20张用于训练的图片。imges文件夹中存放的是20张原始图片,mask中存放的是掩码,用于获取感兴趣的区域。manual中存放的是人工标注的groundtruth。

图1-2 原始图片

图1-3 groundtruth?
2 数据集的加载
获取数据集中image和对应的mask
class DriveDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, root: str, train: bool, transforms=None):
super(DriveDataset, self).__init__()
self.flag = "training" if train else "test"
data_root = os.path.join(root, "DRIVE", self.flag)
# 使用断言,目录不存在,则发出警告
assert os.path.exists(data_root), f"path '{data_root}' does not exists."
# 在transform 中对图像预处理
self.transforms = transforms
"""
(os.path.join(data_root, "images") 获得目录
os.listdir(os.path.join(data_root, "images")) 获取目录下的文件名,返回列表
[i for i in ...] 使用for循环形成新的列表
"""
img_names = [i for i in os.listdir(os.path.join(data_root, "images")) if i.endswith(".tif")]
# 获取图片与GT的完整路径
self.img_list = [os.path.join(data_root, "images", i) for i in img_names]
self.manual = [os.path.join(data_root, "1st_manual", i.split("_")[0] + "_manual1.gif")
for i in img_names]
# check files
for i in self.manual:
if os.path.exists(i) is False:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"file {i} does not exists.")
self.roi_mask = [os.path.join(data_root, "mask", i.split("_")[0] + f"_{self.flag}_mask.gif")
for i in img_names]
# check files
for i in self.roi_mask:
if os.path.exists(i) is False:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"file {i} does not exists.")
def __getitem__(self, idx):
img = Image.open(self.img_list[idx]).convert('RGB')
manual = Image.open(self.manual[idx]).convert('L')
# 0:背景,1:前景,而此时的mask中的前景像素值是255,所以÷255,令其为1
manual = np.array(manual) / 255
roi_mask = Image.open(self.roi_mask[idx]).convert('L')
# 将不感兴趣区域的no_roi区域的像素值设置成255(不参与计算LOSS)
roi_mask = 255 - np.array(roi_mask)
# 使用np.clip()方法,为叠加了manual(GT)与roi_mask后的像素设置像素的上下限
mask = np.clip(manual + roi_mask, a_min=0, a_max=255)
# 这里转回PIL的原因是,transforms中是对PIL数据进行处理
mask = Image.fromarray(mask)
if self.transforms is not None:
img, mask = self.transforms(img, mask)
return img, mask
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_list)
@staticmethod
def collate_fn(batch):
images, targets = list(zip(*batch))
batched_imgs = cat_list(images, fill_value=0)
batched_targets = cat_list(targets, fill_value=255)
return batched_imgs, batched_targets
3. 建立UNet模型
from typing import Dict
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import netron
class DoubleConv(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, mid_channels=None):
if mid_channels is None:
mid_channels = out_channels
super(DoubleConv, self).__init__(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, mid_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
class Down(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(Down, self).__init__(
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2),
DoubleConv(in_channels, out_channels)
)
class Up(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, bilinear=True):
super(Up, self).__init__()
if bilinear:
self.up = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
self.conv = DoubleConv(in_channels, out_channels, in_channels // 2)
else:
self.up = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, in_channels // 2, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.conv = DoubleConv(in_channels, out_channels)
def forward(self, x1: torch.Tensor, x2: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x1 = self.up(x1)
# [N, C, H, W]
diff_y = x2.size()[2] - x1.size()[2]
diff_x = x2.size()[3] - x1.size()[3]
# padding_left, padding_right, padding_top, padding_bottom
x1 = F.pad(x1, [diff_x // 2, diff_x - diff_x // 2,
diff_y // 2, diff_y - diff_y // 2])
x = torch.cat([x2, x1], dim=1)
x = self.conv(x)
return x
class OutConv(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, in_channels, num_classes):
super(OutConv, self).__init__(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, num_classes, kernel_size=1)
)
class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
in_channels: int = 1,
num_classes: int = 2,
bilinear: bool = True,
base_c: int = 64):
super(UNet, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.bilinear = bilinear
self.in_conv = DoubleConv(in_channels, base_c)
self.down1 = Down(base_c, base_c * 2)
self.down2 = Down(base_c * 2, base_c * 4)
self.down3 = Down(base_c * 4, base_c * 8)
factor = 2 if bilinear else 1
self.down4 = Down(base_c * 8, base_c * 16 // factor)
self.up1 = Up(base_c * 16, base_c * 8 // factor, bilinear)
self.up2 = Up(base_c * 8, base_c * 4 // factor, bilinear)
self.up3 = Up(base_c * 4, base_c * 2 // factor, bilinear)
self.up4 = Up(base_c * 2, base_c, bilinear)
self.out_conv = OutConv(base_c, num_classes)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
x1 = self.in_conv(x)
x2 = self.down1(x1)
x3 = self.down2(x2)
x4 = self.down3(x3)
x5 = self.down4(x4)
x = self.up1(x5, x4)
x = self.up2(x, x3)
x = self.up3(x, x2)
x = self.up4(x, x1)
logits = self.out_conv(x)
return {"out": logits}4 编写损失函数和评价函数
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def build_target(target: torch.Tensor, num_classes: int = 2, ignore_index: int = -100):
"""build target for dice coefficient"""
dice_target = target.clone()
if ignore_index >= 0:
ignore_mask = torch.eq(target, ignore_index)
dice_target[ignore_mask] = 0
# [N, H, W] -> [N, H, W, C]
dice_target = nn.functional.one_hot(dice_target, num_classes).float()
dice_target[ignore_mask] = ignore_index
else:
dice_target = nn.functional.one_hot(dice_target, num_classes).float()
return dice_target.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
def dice_coeff(x: torch.Tensor, target: torch.Tensor, ignore_index: int = -100, epsilon=1e-6):
# Average of Dice coefficient for all batches, or for a single mask
# 计算一个batch中所有图片某个类别的dice_coefficient
d = 0.
batch_size = x.shape[0]
for i in range(batch_size):
x_i = x[i].reshape(-1)
t_i = target[i].reshape(-1)
if ignore_index >= 0:
# 找出mask中不为ignore_index的区域
roi_mask = torch.ne(t_i, ignore_index)
x_i = x_i[roi_mask]
t_i = t_i[roi_mask]
inter = torch.dot(x_i, t_i)
sets_sum = torch.sum(x_i) + torch.sum(t_i)
if sets_sum == 0:
sets_sum = 2 * inter
d += (2 * inter + epsilon) / (sets_sum + epsilon)
return d / batch_size
def multiclass_dice_coeff(x: torch.Tensor, target: torch.Tensor, ignore_index: int = -100, epsilon=1e-6):
"""Average of Dice coefficient for all classes"""
dice = 0.
for channel in range(x.shape[1]):
dice += dice_coeff(x[:, channel, ...], target[:, channel, ...], ignore_index, epsilon)
return dice / x.shape[1]
def dice_loss(x: torch.Tensor, target: torch.Tensor, multiclass: bool = False, ignore_index: int = -100):
# Dice loss (objective to minimize) between 0 and 1
x = nn.functional.softmax(x, dim=1)
fn = multiclass_dice_coeff if multiclass else dice_coeff
return 1 - fn(x, target, ignore_index=ignore_index)5.开始训练
def main(args):
device = torch.device(args.device if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
batch_size = args.batch_size
# segmentation nun_classes + background
num_classes = args.num_classes + 1
# using compute_mean_std.py
mean = (0.709, 0.381, 0.224)
std = (0.127, 0.079, 0.043)
# 用来保存训练以及验证过程中信息
results_file = "results{}.txt".format(datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S"))
train_dataset = DriveDataset(args.data_path,
train=True,
transforms=get_transform(train=True, mean=mean, std=std))
val_dataset = DriveDataset(args.data_path,
train=False,
transforms=get_transform(train=False, mean=mean, std=std))
num_workers = 0
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
num_workers=num_workers,
shuffle=True,
pin_memory=True,
collate_fn=train_dataset.collate_fn)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset,
batch_size=1,
num_workers=num_workers,
pin_memory=True,
collate_fn=val_dataset.collate_fn)
for img,lab in train_loader:
print(img.shape)
print(lab.shape)
model = create_model(num_classes=num_classes)
model.to(device)
params_to_optimize = [p for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad]
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(
params_to_optimize,
lr=args.lr, momentum=args.momentum, weight_decay=args.weight_decay
)
scaler = torch.cuda.amp.GradScaler() if args.amp else None
# 创建学习率更新策略,这里是每个step更新一次(不是每个epoch)
lr_scheduler = create_lr_scheduler(optimizer, len(train_loader), args.epochs, warmup=True)
if args.resume:
checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume, map_location='cpu') # load模型
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model'])
optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer'])
lr_scheduler.load_state_dict(checkpoint['lr_scheduler'])
args.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch'] + 1
if args.amp:
scaler.load_state_dict(checkpoint["scaler"])
best_dice = 0.0
start_time = time.time()
for epoch in range(args.start_epoch, args.epochs):
mean_loss, lr = train_one_epoch(model, optimizer, train_loader, device, epoch, num_classes,
lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler, print_freq=args.print_freq, scaler=scaler)
confmat, dice = evaluate(model, val_loader, device=device, num_classes=num_classes)
val_info = str(confmat)
print(val_info)
print(f"dice coefficient: {dice:.3f}")
# write into txt
with open(results_file, "a") as f:
# 记录每个epoch对应的train_loss、lr以及验证集各指标
train_info = f"[epoch: {epoch}]\n" \
f"train_loss: {mean_loss:.4f}\n" \
f"lr: {lr:.6f}\n" \
f"dice coefficient: {dice:.3f}\n"
f.write(train_info + val_info + "\n\n")
if args.save_best is True:
if best_dice < dice:
best_dice = dice
else:
continue
save_file = {"model": model.state_dict(),
"optimizer": optimizer.state_dict(),
"lr_scheduler": lr_scheduler.state_dict(),
"epoch": epoch,
"args": args}
if args.amp:
save_file["scaler"] = scaler.state_dict()
if args.save_best is True:
torch.save(save_file, "save_weights/best_model.pth")
else:
torch.save(save_file, "save_weights/model_{}.pth".format(epoch))
total_time = time.time() - start_time
total_time_str = str(datetime.timedelta(seconds=int(total_time)))
print("training time {}".format(total_time_str))
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42982824/article/details/135698926
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 二分类任务、多分类任务、多标签分类任务、回归任务的代码实现上的区别和联系
- 拿来就可以套用的网络口碑营销组合方案
- openmediavault配置SMB/CIFS共享
- 例行性工作
- 绝地求生游戏最终排名预测--数据分析实战
- Linux mcd命令教程:如何在MS-DOS文件系统中切换工作目录(附实例教程和注意事项)
- DDP分布式训练的官方demo及相关知识
- OpenCV-Python(32):尺度不变特征SIFT算法
- 每日一题 162. 寻找峰值(中等,二分搜索)
- 1128:图像模糊处理(C语言)