【GNN2】PyG完成图分类任务,新手入门,保姆级教程
上次讲了如何给节点分类,这次我们来看如何用GNN完成图分类任务,也就是Graph-level的任务。
【GNN 1】PyG实现图神经网络,完成节点分类任务,人话、保姆级教程-CSDN博客

图分类就是以图为单位的分类,举个例子:每个学校都有社交关系网,图分类就是通过这个社交网络判别这个学校是小学、初中、高中还是大学。
实现方法就是通过利用图的结构信息,对图进行嵌入(embed),也就是用向量来表示这个图,使得分类器基于这个向量能够轻松分类,或者说通过对图进行向量表示,使得图的分类尽可能变成一个线性可分的任务。
下图就是形象展示了我们要干的事:把一堆图表示成线性可分的向量们,然后构建个分类器,完成图分类。

图分类的一个经典任务就是分子属性预测,我们可以把原子看成图的节点,化学键看成边,整个分子就是图,我们想知道分子有什么性质(是否是药物小分子,能否和蛋白相互作用等),其实就是看这个图是属于哪一个类别的。
数据集的选择
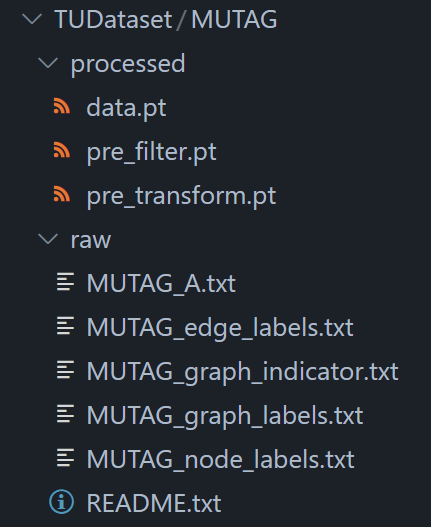
我们这次选择的数据集是TUDatasets,这是TU Dortumnd University收集的大量关于分子特征的图数据,他们还发表了论文TUDataset: A collection of benchmark datasets for learning with graphs。

这么重要的数据集,当然也可以通过PyTorch Geometric直接加载啦。

下面是数据集的大致情况,可以看到这里包括酶、蛋白质还有其他的一些。注意了第一列不是第二列的类别,最后一列class才是。

加载数据
下面我们来加载数据吧!
先说一下TUDataset这个函数,有两个参数,
- root (str) – Root directory where the dataset should be saved.(保存的路径)
- name (str) – The name of the dataset.(名字)
加载完就可以发现数据已经下载到我们指定的root目录了。
# Install required packages.
import os
import torch
os.environ['TORCH'] = torch.__version__
print(torch.__version__)
# !pip install -q torch-scatter -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-${TORCH}.html
# !pip install -q torch-sparse -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-${TORCH}.html
# !pip install -q git+https://github.com/pyg-team/pytorch_geometric.git
import torch
from torch_geometric.datasets import TUDataset
dataset = TUDataset(root='data/TUDataset', name='MUTAG')
# - root (str) – Root directory where the dataset should be saved.(保存的路径)
# - name (str) – The name of the dataset.(名字)
# 查看一些数据集的基本信息
print()
print(f'Dataset: {dataset}:')
print('====================')
print(f'Number of graphs: {len(dataset)}')
print(f'Number of features: {dataset.num_features}')
print(f'Number of classes: {dataset.num_classes}')
data = dataset[0] # Get the first graph object.
print()
print(data)
print('=============================================================')
# 看一下第一张图的信息
# Gather some statistics about the first graph.
print(f'Number of nodes: {data.num_nodes}')
print(f'Number of edges: {data.num_edges}')
print(f'Average node degree: {data.num_edges / data.num_nodes:.2f}')
print(f'Has isolated nodes: {data.has_isolated_nodes()}')
print(f'Has self-loops: {data.has_self_loops()}')
print(f'Is undirected: {data.is_undirected()}')
Dataset: MUTAG(188):
====================
Number of graphs: 188
Number of features: 7
Number of classes: 2
Data(edge_index=[2, 38], x=[17, 7], edge_attr=[38, 4], y=[1])
=============================================================
Number of nodes: 17
Number of edges: 38
Average node degree: 2.24
Has isolated nodes: False
Has self-loops: False
Is undirected: True
这个数据集有188张图,有两个类。
通过查看第一个图的基本信息,我们可以看到它有17个节点(7维特征向量,用一个7维的向量来描述节点)、38条无向边(4维特征向量,用一个4维的向量给来描述边,因为是入门,这次我们不用)还有一个图的标签y=[1]表示图是哪一类的(1维向量,一个数)。
这里提一个小知识点,在机器学习中,训练之前一般均会对数据集做shuffle,也就是打乱数据之间的顺序,让数据随机化,这样可以避免过拟合。
PyTorch Geometric也提供了很多处理图数据集的方法,比如shuffle(),我们今天就首先对数据集进行打乱,然后选择前150个样本进行训练,剩下的38个进行测试。
torch.manual_seed(12345)
dataset = dataset.shuffle()
train_dataset = dataset[:150]
test_dataset = dataset[150:]
print(f'Number of training graphs: {len(train_dataset)}')
print(f'Number of test graphs: {len(test_dataset)}')
Number of training graphs: 150
Number of test graphs: 38
图的Mini-batching
因为在图分类数据集中的图通常来说都比较小,这样就不能充分利用GPU,所以一个想法就是就是先batch the graph,然后再把图放到GNN中。
在图像和自然语言处理领域,这个过程通常是通过rescaling或者padding来实现的,就是把每个样本转换成统一大小/形状,然后再把它们放到一起。以图片为例,我把所有图片都转换为100*100大小,然后再把这些图像融合成一个大图(或者以其他形式存储),这个存储的变量也是有维度的,这个维度的大小就是在一个batch中样本的个数,也就是batch size。
在GNN中,rescaling和padding要么行不通,要么会造成不必要的内存消耗。
因此,PyTorch Geometric选择了另一种方法来实现多个样本的并行化。在这里,邻接矩阵以对角线方式堆叠(创建一个包含多个孤立子图的大图,A),node和target特征在节点维度上简单地拼接起来(X):
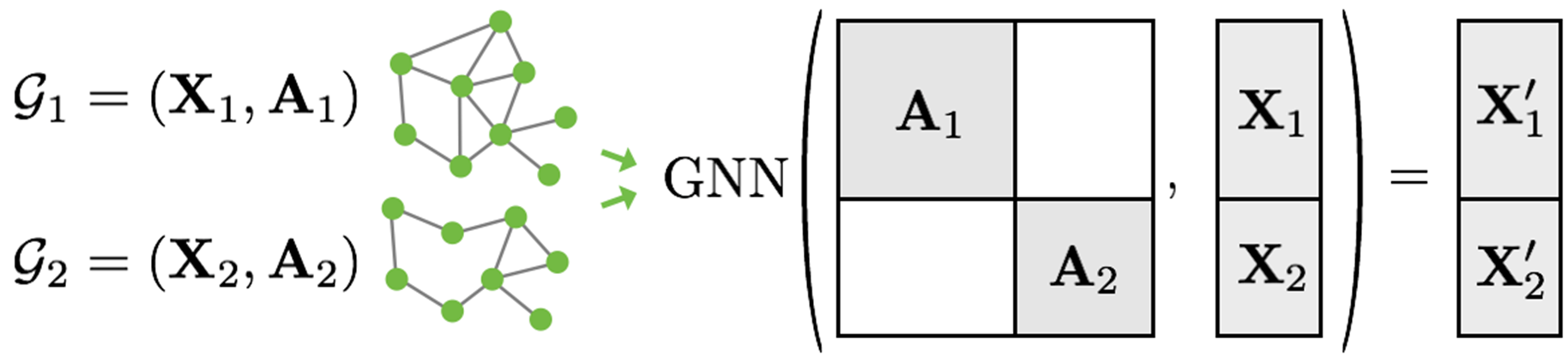
这个过程相对于其他的batching方法有一些关键的优势:
- 依赖于消息传递方案(message passing scheme)的GNN operators不需要修改,因为消息不会在属于不同图的两个节点之间交换;
- 没有计算或内存开销,因为邻接矩阵以稀疏矩阵的方式保存,只保存非零条目,也就是只保留边。
PyTorch Geometric在torch_geometrics .data. dataloader类的帮助下自动处理将多个图批处理为一个大图(batching multiple graphs into a single giant graph):
from torch_geometric.loader import DataLoader
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=False)
for step, data in enumerate(train_loader):
print(f'Step {step + 1}:')
print('=======')
print(f'Number of graphs in the current batch: {data.num_graphs}')
print(data)
print()
for step, data in enumerate(test_loader):
print(f'Step {step + 1}:')
print('=======')
print(f'Number of graphs in the current batch: {data.num_graphs}')
print(data)
print()
Step 1:
=======
Number of graphs in the current batch: 64
DataBatch(edge_index=[2, 2572], x=[1168, 7], edge_attr=[2572, 4], y=[64], batch=[1168], ptr=[65])
Step 2:
=======
Number of graphs in the current batch: 64
DataBatch(edge_index=[2, 2554], x=[1153, 7], edge_attr=[2554, 4], y=[64], batch=[1153], ptr=[65])
Step 3:
=======
Number of graphs in the current batch: 22
DataBatch(edge_index=[2, 868], x=[393, 7], edge_attr=[868, 4], y=[22], batch=[393], ptr=[23])
Step 1:
=======
Number of graphs in the current batch: 38
DataBatch(edge_index=[2, 1448], x=[657, 7], edge_attr=[1448, 4], y=[38], batch=[657], ptr=[39])
我们选择将batch_size设置为64,可以看到分成了3个随机打乱的mini-batches。
对于每个 Batch对象都有一个对应的batch vector,这就是起到一个索引的作用,即将每个节点映射到batch中各自的图上。
batch = [ 0 , … , 0 , 1 , … , 1 , 2 , … ] \textrm{batch} = [ 0, \ldots, 0, 1, \ldots, 1, 2, \ldots ] batch=[0,…,0,1,…,1,2,…]
训练GNN
图分类任务的GNN训练一般是这样的流程:
- 通过几次信息传递(message passing)对每个节点进行嵌入
- 把节点嵌入聚合成图嵌入(readout layer)
- 根据图嵌入向量训练最终的分类器
有很多论文开发了很多readout层,不过其实用的最多的还是直接把节点嵌入求平均:
x G = 1 ∣ V ∣ ∑ v ∈ V x v ( L ) \mathbf{x}_{\mathcal{G}} = \frac{1}{|\mathcal{V}|} \sum_{v \in \mathcal{V}} \mathcal{x}^{(L)}_v xG?=∣V∣1?v∈V∑?xv(L)?
PyTorch Geometric提供了torch_geometric.nn.global_mean_pool这个函数。输入:①mini batch中所有node的embeddings;②分配向量batch;输出:每个batch中每个图经过计算得到的graph embedding,大小是 [batch_size, hidden_channels]
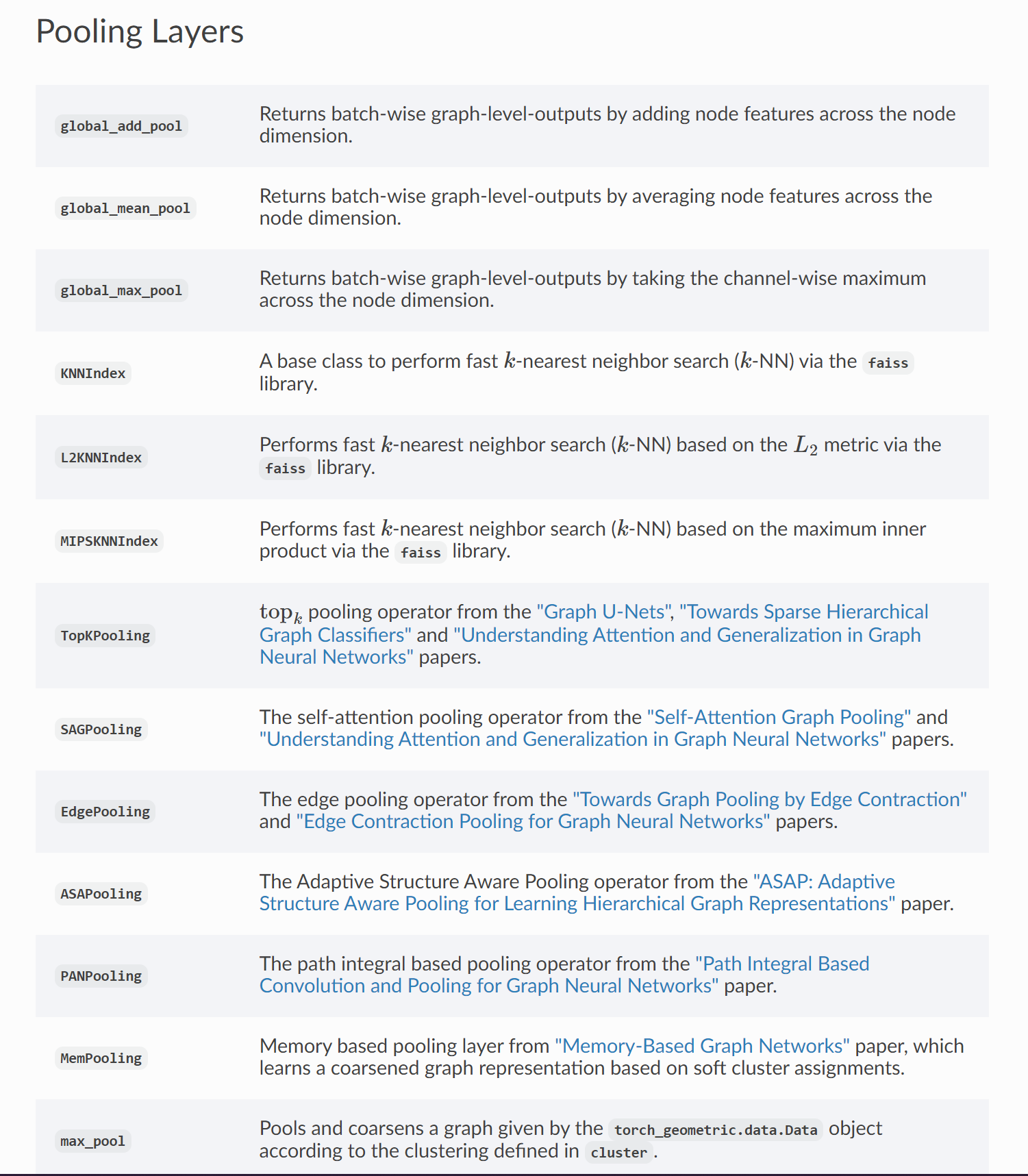
还有很多其他的pooling函数,之后会试试的。
完整的架构我们直接通过print(model)就可以看到,这个模型可以实现端到端的图分类了!
from torch.nn import Linear
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch_geometric.nn import GCNConv
from torch_geometric.nn import global_mean_pool
class GCN(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_channels):
super(GCN, self).__init__()
torch.manual_seed(12345)
self.conv1 = GCNConv(dataset.num_node_features, hidden_channels)
self.conv2 = GCNConv(hidden_channels, hidden_channels)
self.conv3 = GCNConv(hidden_channels, hidden_channels)
self.lin = Linear(hidden_channels, dataset.num_classes)
def forward(self, x, edge_index, batch):
# 1. Obtain node embeddings
x = self.conv1(x, edge_index)
x = x.relu()
x = self.conv2(x, edge_index)
x = x.relu()
x = self.conv3(x, edge_index)
# 2. Readout layer
x = global_mean_pool(x, batch) # [batch_size, hidden_channels]
# 3. Apply a final classifier
x = F.dropout(x, p=0.5, training=self.training)
x = self.lin(x)
return x
model = GCN(hidden_channels=64)
print(model)
GCN(
(conv1): GCNConv(7, 64)
(conv2): GCNConv(64, 64)
(conv3): GCNConv(64, 64)
(lin): Linear(in_features=64, out_features=2, bias=True)
)
我们为GCN层选择的激活函数是 R e L U ( x ) = max ? ( x , 0 ) \mathrm{ReLU}(x) = \max(x, 0) ReLU(x)=max(x,0) (除了最后的readout layer)。
让我们训练一下我们的模型吧,看看它在测试集上表现如何!
from IPython.display import Javascript
display(Javascript('''google.colab.output.setIframeHeight(0, true, {maxHeight: 300})'''))
model = GCN(hidden_channels=64)
# 模型的核心,64个hidden_channels,类似于神经网络的隐藏层的神经元个数
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
def train():
model.train()
# 把模型设置为训练模式
for data in train_loader: # Iterate in batches over the training dataset.
out = model(data.x, data.edge_index, data.batch) # Perform a single forward pass.
loss = criterion(out, data.y) # Compute the loss.
loss.backward() # Derive gradients.
# 计算梯度
optimizer.step() # Update parameters based on gradients.
# 根据上面计算的梯度更新参数
optimizer.zero_grad() # Clear gradients.
# 清除梯度,为下一个批次的数据做准备,相当于从头开始
def test(loader):
model.eval()
# 把模型设置为评估模式
correct = 0
# 初始化correct为0,表示预测对的个数
for data in loader: # Iterate in batches over the training/test dataset.
out = model(data.x, data.edge_index, data.batch)
# 预测的输出值
pred = out.argmax(dim=1) # Use the class with highest probability.
# 每个类别对应一个概率,概率最大的就是对应的预测值
correct += int((pred == data.y).sum()) # Check against ground-truth labels.
# 如果一样,就是True,也就是1,correct就+1
# 准确率就是正确的/总的
return correct / len(loader.dataset) # Derive ratio of correct predictions.
for epoch in range(1, 171):
train()
train_acc = test(train_loader)
test_acc = test(test_loader)
print(f'Epoch: {epoch:03d}, Train Acc: {train_acc:.4f}, Test Acc: {test_acc:.4f}')

可以看到,我们的模型有0.76的测试集准确度。
波动的原因可以认为是测试集太小了,通常来说,如果数据集比较大这种波动情况就会消失。
换个架构看看效果怎么样
我们可以做的更好吗?当然可以。
正如多篇论文指出的那样(Xu et al. (2018), Morris et al. (2018)),应用邻域归一化降低了gnn在识别某些图结构方面的表达能力(neighborhood normalization decrease the expressivity of GNNs in distingushiing certain graph structures)。
另一种替代公式( Morris et al. (2018))完全省略了邻域归一化,并在GNN层中添加了一个简单的跳过连接,以保留中心节点信息:
x
v
(
?
+
1
)
=
W
1
(
?
+
1
)
x
v
(
?
)
+
W
2
(
?
+
1
)
∑
w
∈
N
(
v
)
x
w
(
?
)
\mathbf{x}_v^{(\ell+1)} = \mathbf{W}^{(\ell + 1)}_1 \mathbf{x}_v^{(\ell)} + \mathbf{W}^{(\ell + 1)}_2 \sum_{w \in \mathcal{N}(v)} \mathbf{x}_w^{(\ell)}
xv(?+1)?=W1(?+1)?xv(?)?+W2(?+1)?w∈N(v)∑?xw(?)?
这个layer也可以在PyG中轻松调用,也就是GraphConv。
也就是说,我们想用PyG’s GraphConv 而不是 GCNConv,然后看看效果怎么样。
from torch_geometric.nn import GraphConv
class GNN(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_channels):
super(GNN, self).__init__()
torch.manual_seed(12345)
self.conv1 = GraphConv(dataset.num_node_features, hidden_channels) # TODO
self.conv2 = GraphConv(hidden_channels, hidden_channels) # TODO
self.conv3 = GraphConv(hidden_channels, hidden_channels) # TODO
self.lin = Linear(hidden_channels, dataset.num_classes)
def forward(self, x, edge_index, batch):
x = self.conv1(x, edge_index)
x = x.relu()
x = self.conv2(x, edge_index)
x = x.relu()
x = self.conv3(x, edge_index)
x = global_mean_pool(x, batch)
x = F.dropout(x, p=0.5, training=self.training)
x = self.lin(x)
return x
model = GNN(hidden_channels=64)
print(model)
GNN(
(conv1): GraphConv(7, 64)
(conv2): GraphConv(64, 64)
(conv3): GraphConv(64, 64)
(lin): Linear(in_features=64, out_features=2, bias=True)
)
from IPython.display import Javascript
display(Javascript('''google.colab.output.setIframeHeight(0, true, {maxHeight: 300})'''))
model = GNN(hidden_channels=64)
print(model)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
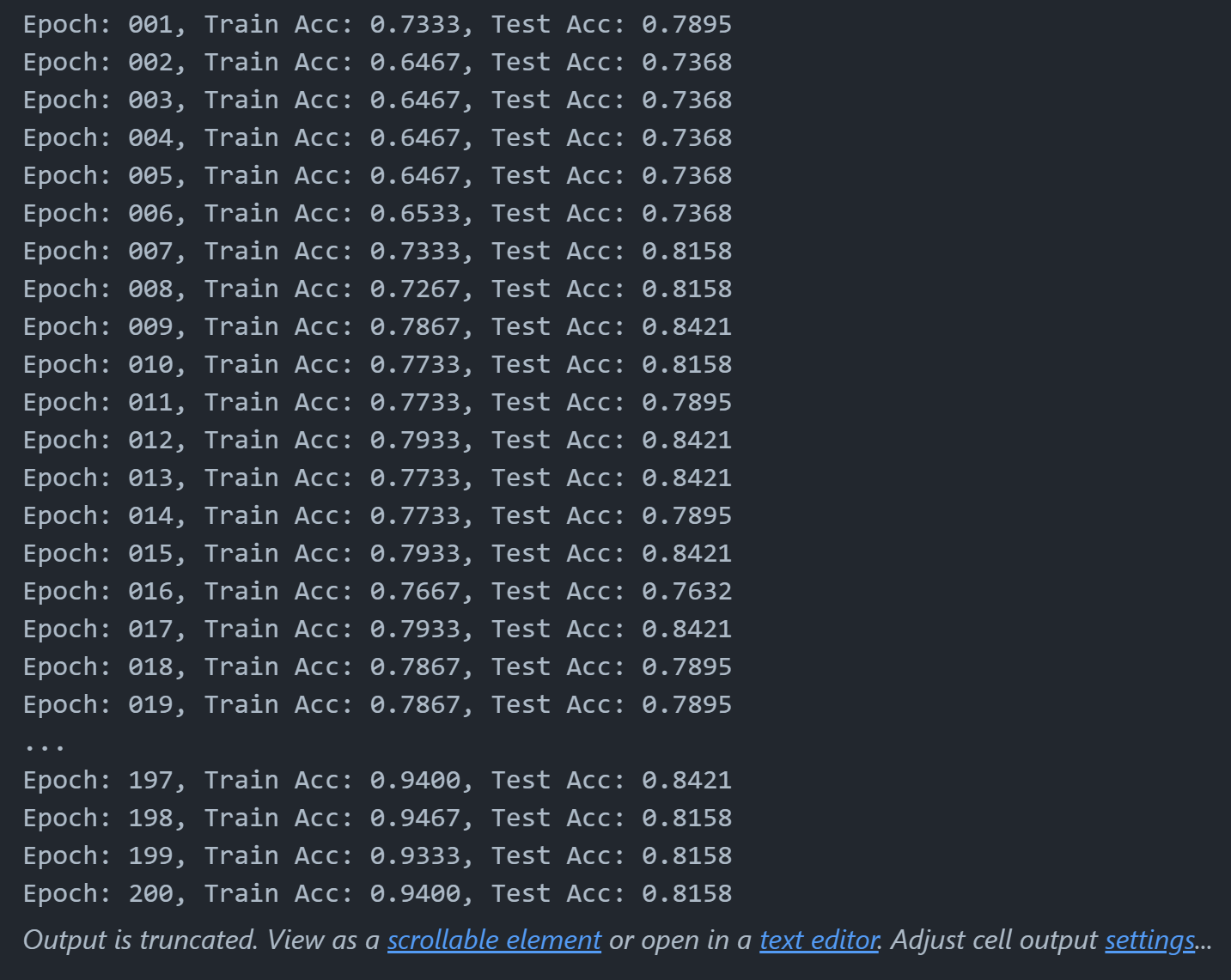
for epoch in range(1, 201):
train()
train_acc = test(train_loader)
test_acc = test(test_loader)
print(f'Epoch: {epoch:03d}, Train Acc: {train_acc:.4f}, Test Acc: {test_acc:.4f}')
GNN(
(conv1): GraphConv(7, 64)
(conv2): GraphConv(64, 64)
(conv3): GraphConv(64, 64)
(lin): Linear(in_features=64, out_features=2, bias=True)
)
总结
我们学习了如何应用GNN完成图分类,调用了GraphConv和GCNConv两种架构,举一反三,之后想用什么layer就用什么layer。
此外我们还学习了如何让单个的图组成batch,从而更好地利用GPU,以及如何应用readout layer从node embedding中得到graph embedding。
参考资料:
3. Graph Classification.ipynb - Colaboratory (google.com)
如果觉得还不错,记得点赞+收藏哟!谢谢大家的阅读!( ̄︶ ̄)↗
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- vue2使用文件上传读取本地照片并转化base64格式进行展示
- 【花艺电商】SpringBoot集成MyBatis-Plus、Swagger2、SpringSecurity、OAuth2等技术整合开发
- IP与子网掩码之间的关系
- 德特森:如何判断减压阀的好坏?
- 云手机:私域运营的黑科技
- AntV-G6 -- 将G6图表应用到项目中
- 视频号小店如何找货源?新手看这篇就够了!
- nginx查看连接数的几种方法
- Java---Collection讲解(二)
- Oracle修改用户密码