第七站:C++面向对象训练
发布时间:2024年01月15日
1:介绍
创建两个类,一个boy类,一个girl类,实现对两个类的数据输入,并通过main函数,对两个类的成员进行比较匹配
涉及:
vector容器,面向对象,const关键字,? stringstream(sstream.h)?
stringstream用法
stringstream ret;//可以将写入的数据转换成字符串
ret << "姓名:" << name << "-年龄-" << age << "-颜值-" <<yanZhi<< endl;
return ret.str();vector是一个顺序容器(长度自动分配),类型自适应
用法:<vector>头文件
一维:vector<数据类型> 容器名? ?注:类是一种特殊的数据类型,也能放
二维:vector<vector<数据类型>> 容器名
例子:详细例子可以参考主页天天酷跑的游戏
二维的
vector<vector<IMAGE>> ObstractIMG;//image ObstractIMG[][]
IMAGE imgPillar[pillarNum];
一维的
vector<IMAGE> imgHArray;
sprintf_s(name,sizeof(name) ,"res/h1.png");
loadimage(&imgPillar[0], name, 63, 260, true);
通过push.back先往一维里放
imgHArray.push_back(imgPillar[0]);
然后再将一维的放进二维的
ObstractIMG.push_back(imgHArray);分布:
每一个类都有.h声明头文件和.cpp实现文件
2:girl类
.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Boy;
class Girl{
public:
Girl();
~Girl();
Girl( string name, int age, int yanZhi);
string getName()const;
int getAge() const;
int getYanZhi()const;
bool satisfied(const Boy& boy) const;
string describe()const;
static void inputGirls(vector<Girl>& girl);
private:
string name;
int age;
int yanZhi;
};
.cpp
?
#include "Girl.h"
#include <sstream>
#include "Boy.h"
//设置一个颜值系数
#define YANZHI_FACTOR 100
Girl::Girl() {
name = "";
age = 0;
yanZhi = 0;
}
Girl::~Girl() {
}
Girl::Girl( string name, int age, int yanZhi) {
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
this->yanZhi = yanZhi;
}
string Girl::getName() const {
return name;
}
int Girl::getAge() const {
return age;
}
int Girl::getYanZhi() const {
return yanZhi;
}
bool Girl::satisfied(const Boy& b) const{
if (b.getSalary() >= yanZhi * YANZHI_FACTOR) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
string Girl::describe() const {
stringstream ret;//可以将写入的数据转换成字符串
ret << "姓名:" << name << "-年龄-" << age << "-颜值-" <<yanZhi<< endl;
return ret.str();
}
void Girl::inputGirls(vector<Girl>& girl){
string name;
int age;
int yanZhi1;
int n = 1;
while (n) {
cout << "请输入女方第" << n << "个人的年龄:";
cin >> age;
if (age == 0) {
break;
}
cout << "请输入第" << n << "个人的姓名:";
cin >> name;
cout << "请输入第" << n << "个人的颜值:";
cin >> yanZhi1;
n++;
girl.push_back(Girl(name, age, yanZhi1));
}
}
3:boy类
.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Girl;
class Boy{
public :
Boy();
~Boy();
Boy(string name, int age, int salary);
Boy(const Boy& other);
string getName() const;
int getAge() const;
int getSalary() const;
bool satisfied(const Girl& girl) const;
string describe() const;
static void inputBoys(vector<Boy> &boy);
private:
string name;
int age;
int salary;
};
.cpp
?
#include "Boy.h"
#include <sstream>
#include "Girl.h"
//定义一个薪资参数
#define SALARY_FACTOR 0.006
Boy::Boy() {
name = " ";
age = 0;
salary = 0;
}
Boy::Boy(string name, int age, int salary){
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
this->salary = salary;
}
Boy::Boy(const Boy& other){
salary = other.salary;
name = other.name;
age = other.age;
}
Boy::~Boy() {
}
string Boy::getName()const {
return name;
}
int Boy::getAge() const{
return age;
}
int Boy::getSalary()const {
return salary;
}
bool Boy::satisfied(const Girl& girl) const{
if (girl.getYanZhi() >= salary * SALARY_FACTOR) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
string Boy::describe() const {
stringstream ret;//可以将写入的数据转换成字符串
ret << "姓名:" << name << "-年龄-" << age << "-薪资-" <<salary<< endl;
return ret.str();
}
void Boy::inputBoys(vector<Boy> &boy){
string name;
int age;
int salary;
int n = 1;
while (n){
cout << "请输入第" << n << "个人的年龄:";
cin >> age;
if (age == 0) {
break;
}
cout << "请输入第"<<n<<"个人的姓名:";
cin >> name;
cout << "请输入第" << n << "个人的薪资:";
cin >> salary;
n++;
boy.push_back(Boy(name, age, salary));
}
}
4:main主函数
?
#include "Boy.h"
#include "Girl.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void autoCompere(vector<Boy>& boys, vector<Girl> girls) {
for (int i = 0; i < boys.size(); i++){
for (int j = 0; j < girls.size(); j++) {
if (boys[i].satisfied(girls[j]) && girls[j].satisfied(boys[i])) {
cout << boys[i].describe() << "\n---匹配成功---\n" << girls[j].describe()<<endl;
}
else {
cout << "匹配失败!!" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
}
int main(void) {
vector<Boy> boys;
vector<Girl> girls;
Boy::inputBoys(boys);
Girl::inputGirls(girls);
cout << "\n\n----匹配中----" << endl;
autoCompere(boys, girls);
return 0;
}5:实现
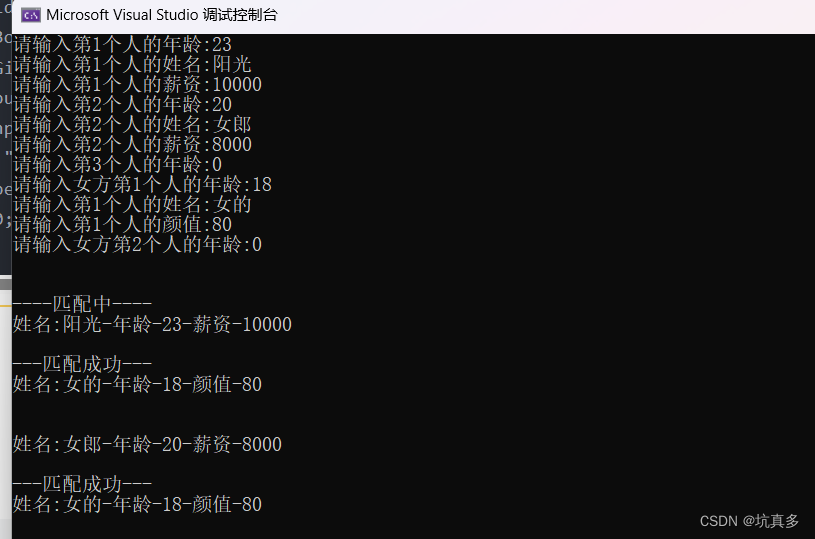
?
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_48397625/article/details/135589753
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Alibaba分布式事务组件Seata AT实战
- 基于Java SSM框架实现企业车辆管理系统项目【项目源码】
- 【教程】Ipa Guard为iOS应用提供免费加密混淆方案
- 山西电力市场日前价格预测【2023-12-17】
- C_4练习题答案
- 前缀和模板题 P8218 【深进1.例1】求区间和
- NoSQL之 Redis配置与优化
- ES:must_not 是否能走索引快速过滤?
- QT属性动画
- 武汉大学:如何应对来自邮件的APT攻击?