C++ 红黑树
目录
一、红黑树的概念和性质
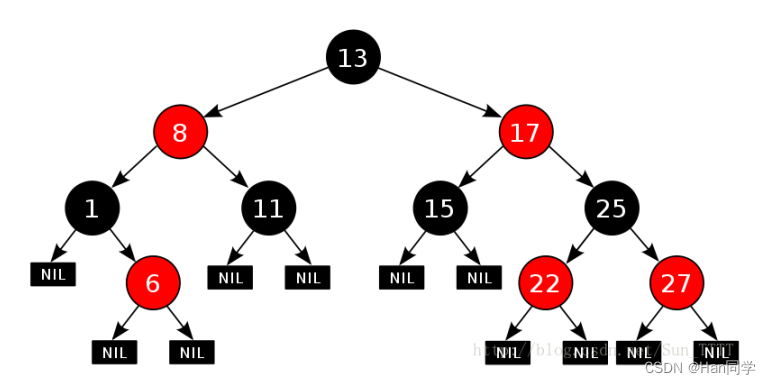
- 每个结点不是红色就是黑色。
- 根节点是黑色的。
- 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的两个孩子结点是黑色的。
- 对于每个结点,从该结点到其所有后代叶结点的简单路径上,均包含相同数目的黑色结点?
- 每个叶子结点都是黑色的。(此处的叶子结点指的是空结点又称NIL节点)
-
满足上面的性质,红黑树就能保证:其最长路径中节点个数不会超过最短路径节点个数的两倍。
-
假设全部的黑色节点有N个
-
最短路径长度: logN
-
整棵树的节点数量: [N,2N]之间
-
最长路径长度: 2logN
-
假设10亿个节点,AVL: 最多查找30次左右,RB:最多查找60次左右
-
二、实现红黑树
1、节点定义+构造
enum Colour
{
RED, BLACK,
};
template<class K,class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;
pair<K, V> _kv;
Colour _col;
RBTreeNode(const pair<K,V>& kv)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_kv(kv)
,_col(RED)
{}
};首先定义了一个枚举类型Colour,其中包含两个枚举值RED和BLACK,用于表示红黑树节点的颜色。
接下来定义了一个模板结构体RBTreeNode,表示红黑树的节点。该结构体包含以下成员变量:
_left:指向左子节点的指针。_right:指向右子节点的指针。_parent:指向父节点的指针。_kv:键值对,使用pair<K, V>类型存储键和值。_col:节点的颜色,使用Colour枚举类型表示,默认为红色(RED)。
结构体还定义了一个构造函数RBTreeNode,接受一个键值对作为参数,并初始化成员变量。在构造函数中,左子节点、右子节点和父节点的指针都被初始化为nullptr,颜色被初始化为红色。
2、插入
template<class K,class V>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (_root == nullptr){
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur){
if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first){
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first){
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(kv);
if (parent->_kv.first > kv.first){
parent->_left = cur;
}
else{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
while (parent && parent->_col == RED){
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (grandfather->_left == parent){
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
// 情况1:u存在且为红,变色处理,并继续往上处理
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
// 继续往上调整
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else // 情况2+3:u不存在/u存在且为黑,旋转+变色
{
// g
// p u
// c
if (cur == parent->_left){
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else{
// g
// p u
// c
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
//parent->_col = RED;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else // (grandfather->_right == parent)
{
// g
// u p
// c
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
// 情况1:u存在且为红,变色处理,并继续往上处理
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
// 继续往上调整
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else // 情况2+3:u不存在/u存在且为黑,旋转+变色
{
// g
// u p
// c
if (cur == parent->_right){
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
else{
// g
// u p
// c
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};首先,定义了一个名为Insert的函数,它接受一个键值对kv作为参数。这个函数的目的是将这个键值对插入到红黑树中。
-
如果根节点为空(也就是说,这是一棵空树),那么我们就创建一个新的节点作为根节点,并将其颜色设置为黑色。然后返回
true表示插入成功。 -
如果根节点不为空,我们就需要找到新节点应该插入的位置。我们创建两个指针
parent和cur,并将它们初始化为根节点。然后我们进入一个循环,不断地将cur向左或向右移动,直到找到新节点应该插入的位置。在这个过程中,我们始终保持parent是cur的父节点。 -
当我们找到新节点应该插入的位置后,我们创建一个新的节点,并将其插入到正确的位置。我们还需要设置新节点的父节点。
-
接下来,我们需要修复可能被新节点破坏的红黑树的性质。我们进入一个循环,只要新节点的父节点存在且颜色为红色,我们就继续循环。在循环中,我们首先找到新节点的祖父节点和叔叔节点。
-
如果新节点的叔叔节点存在且颜色为红色(情况1),我们就将新节点的父节点和叔叔节点的颜色都改为黑色,然后将祖父节点的颜色改为红色。然后我们将祖父节点视为新插入的节点,继续循环。

-
如果新节点的叔叔节点不存在或颜色为黑色(情况2&3),我们就需要进行旋转和颜色调整。具体的操作取决于新节点、其父节点和祖父节点的相对位置。这里有四种可能的情况,分别对应于代码中的四个子情况。

-
最后,我们需要确保根节点的颜色始终为黑色。这是因为在上面的调整过程中,根节点的颜色可能被改变。
-
函数最后返回
true,表示插入操作成功。
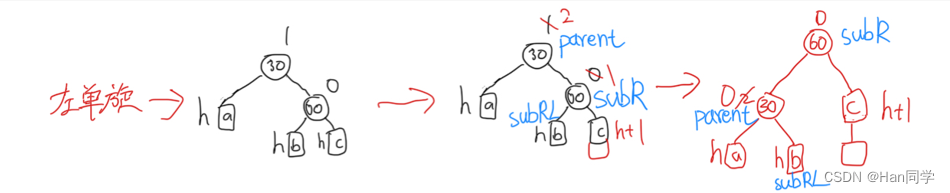
3、左单旋&右单旋
private:
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (ppnode == nullptr) {
_root = subR;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else {
if (ppnode->_left == parent) {
ppnode->_left = subR;
}
else {
ppnode->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = ppnode;
}
}
-
首先,我们定义了三个指针变量:
subR?指向父节点的右子节点,subRL?指向?subR?的左子节点,ppnode?指向父节点的父节点。 -
我们将父节点的右子节点指向?
subRL,这样父节点和?subR?就断开了连接。如果?subRL?不为空,我们还需要将其父节点指针指向父节点。 -
接下来,我们将父节点的父节点指针指向?
subR,将?subR?的左子节点指向父节点。 -
如果父节点的父节点指针?
ppnode?为空,表示父节点是根节点,我们将根节点指针?_root?指向?subR,并将根节点的父节点指针置为空。 -
如果父节点的父节点指针?
ppnode?不为空,我们需要根据父节点在其父节点的位置来更新指、针。如果父节点是其父节点的左子节点,我们将?subR?设置为其父节点的左子节点;否则,将?subR?设置为其父节点的右子节点。同时,我们还需要更新?subR?的父节点指针为?ppnode。
private:
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root) {
_root = subL;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else {
if (ppnode->_left == parent) {
ppnode->_left = subL;
}
else {
ppnode->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = ppnode;
}
}
-
首先,我们定义了三个指针变量:
subL?指向父节点的左子节点,subLR?指向?subL?的右子节点,ppnode?指向父节点的父节点。 -
我们将父节点的左子节点指向?
subLR,这样父节点和?subL?就断开了连接。如果?subLR?不为空,我们还需要将其父节点指针指向父节点。 -
接下来,我们将父节点的父节点指针指向?
subL,将?subL?的右子节点指向父节点,以完成右旋转操作。 -
如果父节点是根节点?
_root,我们将根节点指针?_root?指向?subL,并将根节点的父节点指针置为空。 -
如果父节点的父节点指针?
ppnode?不为空,我们需要根据父节点在其父节点的位置来更新指针。如果父节点是其父节点的左子节点,我们将?subL?设置为其父节点的左子节点;否则,将?subL?设置为其父节点的右子节点。同时,我们还需要更新?subL?的父节点指针为?ppnode。
4、中序遍历
public:
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_kv.first << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}5、检查平衡
private:
bool _Check(Node* root,int blackNum,int benchmark)
{
if (root == nullptr) {
if (benchmark != blackNum) {
cout<< "某条路径黑色节点的数量不相等" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
blackNum++;
if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent && root->_parent->_col == RED) {
cout << "存在连续的红色节点" << endl;
return false;
}
return _Check(root->_left, blackNum, benchmark)
&& _Check(root->_right, blackNum, benchmark);
}_Check函数是一个递归函数,用于检查从给定节点到其所有叶子节点的所有路径是否都包含相同数量的黑色节点,并且没有连续的红色节点。
-
如果当前节点为空,那么我们就检查到达这个叶子节点的路径上的黑色节点数量是否等于基准值。如果不等于,那么就返回
false。否则,返回true。 -
如果当前节点是黑色的,那么我们就将黑色节点的数量加一。
-
如果当前节点是红色的,并且它的父节点也是红色的,那么就返回
false,因为这违反了红黑树的性质。 -
最后,我们递归地检查当前节点的左子节点和右子节点。
public:
bool IsBalance()
{
if (_root && _root->_col == RED) {
cout << "根节点的颜色是红色" << endl;
return false;
}
int benchmark = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur) {
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
benchmark++;
cur = cur->_left;
}
return _Check(_root, 0, benchmark);
}IsBalance函数首先检查根节点是否是黑色的。如果根节点是红色的,那么就返回false。- 然后,我们计算从根节点到左子树的最左叶子节点的路径上的黑色节点数量,作为基准值。
- 最后,我们调用
_Check函数,检查整棵树是否满足红黑树的性质。如果满足,那么就返回true。否则,返回false。
6、获取树的高度
public:
int Height()
{
return _Height(_root);
}
private:
int _Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftH = _Height(root->_left);
int rightH = _Height(root->_right);
return leftH > rightH ? leftH + 1 : rightH + 1;
}-
Height?函数:这是一个获取树的高度的函数,用于计算树的高度。它调用了私有函数?_Height?来进行递归计算。 -
_Height?函数:这是一个私有的获取节点高度的函数,用于递归地计算节点的高度。如果当前节点为空,返回 0;否则,计算左子树和右子树的高度,返回较大的高度加 1。
7、查找
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur){
if (cur->_kv.first < key){
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first > key){
cur = cur->_left;
}
else{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}8、析构
public:
~RBTree()
{
_Destroy(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
private:
void _Destroy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_Destroy(root->_left);
_Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
}测试
void Test_RBTree1()
{
//int a[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 };
int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14, };
RBTree<int, int> t1;
for (auto e : a)
{
t1.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
cout << e << "插入:" << t1.IsBalance() << endl;
}
t1.InOrder();
cout << t1.IsBalance() << endl;
}
void Test_RBTree2()
{
srand(time(0));
const size_t N = 5000000;
RBTree<int, int> t;
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
size_t x = rand() + i;
t.Insert(make_pair(x, x));
//cout << t.IsBalance() << endl;
}
cout << t.IsBalance() << endl;
cout << t.Height() << endl;
}
完整版
#pragma once
enum Colour
{
RED, BLACK,
};
template<class K,class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;
pair<K, V> _kv;
Colour _col;
RBTreeNode(const pair<K,V>& kv)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_kv(kv)
,_col(RED)
{}
};
template<class K,class V>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
~RBTree()
{
_Destroy(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur) {
if (cur->_kv.first < key) {
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first > key) {
cur = cur->_left;
}
else {
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (_root == nullptr){
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur){
if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first){
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first){
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(kv);
if (parent->_kv.first > kv.first){
parent->_left = cur;
}
else{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
while (parent && parent->_col == RED){
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (grandfather->_left == parent){
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
// 情况1:u存在且为红,变色处理,并继续往上处理
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
// 继续往上调整
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else // 情况2+3:u不存在/u存在且为黑,旋转+变色
{
// g
// p u
// c
if (cur == parent->_left){
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else{
// g
// p u
// c
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
//parent->_col = RED;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else // (grandfather->_right == parent)
{
// g
// u p
// c
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
// 情况1:u存在且为红,变色处理,并继续往上处理
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
// 继续往上调整
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else // 情况2+3:u不存在/u存在且为黑,旋转+变色
{
// g
// u p
// c
if (cur == parent->_right){
RotateL(grandfather);
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
else{
// g
// u p
// c
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
}
//根据规则检查
bool IsBalance()
{
if (_root && _root->_col == RED) {
cout << "根节点的颜色是红色" << endl;
return false;
}
int benchmark = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur) {
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
benchmark++;
cur = cur->_left;
}
return _Check(_root, 0, benchmark);
}
int Height()
{
return _Height(_root);
}
private:
void _Destroy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_Destroy(root->_left);
_Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
}
int _Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int leftH = _Height(root->_left);
int rightH = _Height(root->_right);
return leftH > rightH ? leftH + 1 : rightH + 1;
}
bool _Check(Node* root,int blackNum,int benchmark)
{
if (root == nullptr) {
if (benchmark != blackNum) {
cout<< "某条路径黑色节点的数量不相等" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
blackNum++;
if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent && root->_parent->_col == RED) {
cout << "存在连续的红色节点" << endl;
return false;
}
return _Check(root->_left, blackNum, benchmark)
&& _Check(root->_right, blackNum, benchmark);
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_kv.first << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (ppnode == nullptr) {
_root = subR;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else {
if (ppnode->_left == parent) {
ppnode->_left = subR;
}
else {
ppnode->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = ppnode;
}
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root) {
_root = subL;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else {
if (ppnode->_left == parent) {
ppnode->_left = subL;
}
else {
ppnode->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = ppnode;
}
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 抖店的经营需要注意什么?时间在哪结果就在哪,新手做店必看教程
- Halcon根据特征值选择区域select_shape
- 架构设计模式详解:夯实架构设计的基础
- Library Genesis (创世纪图书馆)最新镜像地址,可直接访问!不逊于 Z-Library 的优质电子书库
- Python mesh网格ply数据转STL数据
- 神经网络-搭建小实战和Sequential的使用
- 4 - JdbcTemplate
- 地产营销的用数场景有哪些?如何用数赋能地产营销?
- C# winform控件(combobox,webBrowser,button,char,RichTextBox )
- 信息系统中的需求分析