c语言实现HashTable
发布时间:2024年01月11日
概念:哈希表是一种数据结构,它通过将键映射到数组的某个位置来存储和检索值。
第一步,首先定义节点
typedef struct Node {
char *key;
int value;
struct Node *next;
} Node;这里,我定义的键是字符,value是整数。
第二步,自定义hash算法
int hash(char *key) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(key); i++) {
sum += key[i];
}
return sum;
}这里的哈希函数是一个简单的求和函数,返回的是键中的每个字符的ASCII值相加的和
第三步,创建节点
Node *createNode(char *key, int value) {
Node *newNode = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->key = strdup(key);
newNode->value = value;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}strdup() 函数将参数 key?指向的字符串复制到一个字符串指针上去,这个字符串指针事先可以没被初始化。在复制时,strdup() 会给这个指针分配空间,使用 malloc() 函数进行分配,如果不再使用这个指针,相应的用 free() 来释放掉这部分空间。
第四步,插入节点
void insert(Node **table, char *key, int value) {
int index = hash(key) % TABLE_SIZE;
Node *newNode = createNode(key, value);
if (table[index] == NULL) {
table[index] = newNode;
} else {
Node *current = table[index];
while (current->next != NULL) {
current = current->next;
}
current->next = newNode;
}
}
之前的hash算法%TABLE_SIZE,得出索引,如果索引所在的位置上为null,就直接存放,否则就在当前索引的位置的next上看是否为null,这里用了while循环
第五步,搜索节点
int search(Node **table, char *key) {
int index = hash(key) % TABLE_SIZE;
Node *current = table[index];
while (current != NULL) {
if (strcmp(current->key, key) == 0) {
return current->value;
}
current = current->next;
}
return -1;
}搜索节点,同样使用hash函数得到索引,再用?strcmp()函数来判断,如果为0,那就是那个值。否则就继续while循环找当前索引的下一个,因为存进去的时候就是这样存的。
第六步,删除节点
void freeTable(Node **table) {
for (int i = 0; i < TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
Node *current = table[i];
while (current != NULL) {
Node *temp = current;
current = current->next;
free(temp->key);
free(temp);
}
}
}简单遍历,然后free掉。
完整代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#define TABLE_SIZE 10
typedef struct Node {
char *key;
int value;
struct Node *next;
} Node;
int hash(char *key) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(key); i++) {
sum += key[i];
}
return sum;
}
Node *createNode(char *key, int value) {
Node *newNode = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->key = strdup(key);
newNode->value = value;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
void insert(Node **table, char *key, int value) {
int index = hash(key) % TABLE_SIZE;
Node *newNode = createNode(key, value);
if (table[index] == NULL) {
table[index] = newNode;
} else {
Node *current = table[index];
while (current->next != NULL) {
current = current->next;
}
current->next = newNode;
}
}
int search(Node **table, char *key) {
int index = hash(key) % TABLE_SIZE;
Node *current = table[index];
while (current != NULL) {
if (strcmp(current->key, key) == 0) {
return current->value;
}
current = current->next;
}
return -1;
}
void freeTable(Node **table) {
for (int i = 0; i < TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
Node *current = table[i];
while (current != NULL) {
Node *temp = current;
current = current->next;
free(temp->key);
free(temp);
}
}
}
int main() {
Node **table = (Node **)malloc(TABLE_SIZE * sizeof(Node *));
for (int i = 0; i < TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
table[i] = NULL;
}
insert(table, "apple", 1);
insert(table, "banana", 2);
insert(table, "orange", 3);
printf("apple: %d\n", search(table, "apple"));
printf("banana: %d\n", search(table, "banana"));
printf("orange: %d\n", search(table, "orange"));
printf("grape: %d\n", search(table, "grape"));
freeTable(table);
return 0;
}
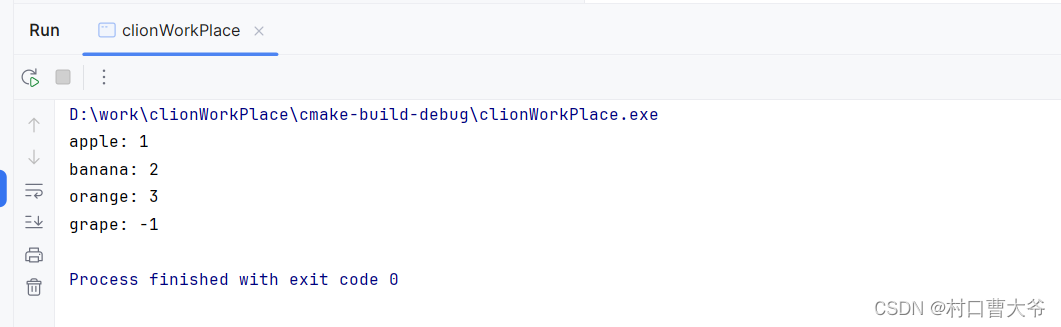
运行结果:
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_63251896/article/details/135515449
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!