浅拷贝和深拷贝
发布时间:2024年01月16日
深拷贝和浅拷贝是只针对Object和Array这样的引用数据类型的。
一、概念描述。
1.浅拷贝: 拷贝的对象的属性分为基本类型值和引用类型的值
? ? ? ? ①基本类型:拷贝的就是基本类型的值
? ? ? ? ②引用类型:拷贝的就是内存地址(新旧对象共享同一块内存,如果改了新对象的值也是会影响旧对象的值的)
2.深拷贝:?深拷贝是将一个对象从内存中完整的拷贝一份出来,从堆内存中开辟一个新的区域存放新对象(新旧对象不共享同一块内存,相互不影响)
二、赋值和浅拷贝的区别。
? ? ? ? 赋值:一个对象赋值给一个新变量的时候,赋值的是对象在栈中的地址,而不是堆中的数据,两个对象是相互影响联动的。
? ? ? ? 浅拷贝:按位拷贝对象,它会创建一个新的对象,这个对象有着原始对象属性值的一份精确拷贝。但只是复制对象空间而不复制资源。
三、堆内存和栈内存。
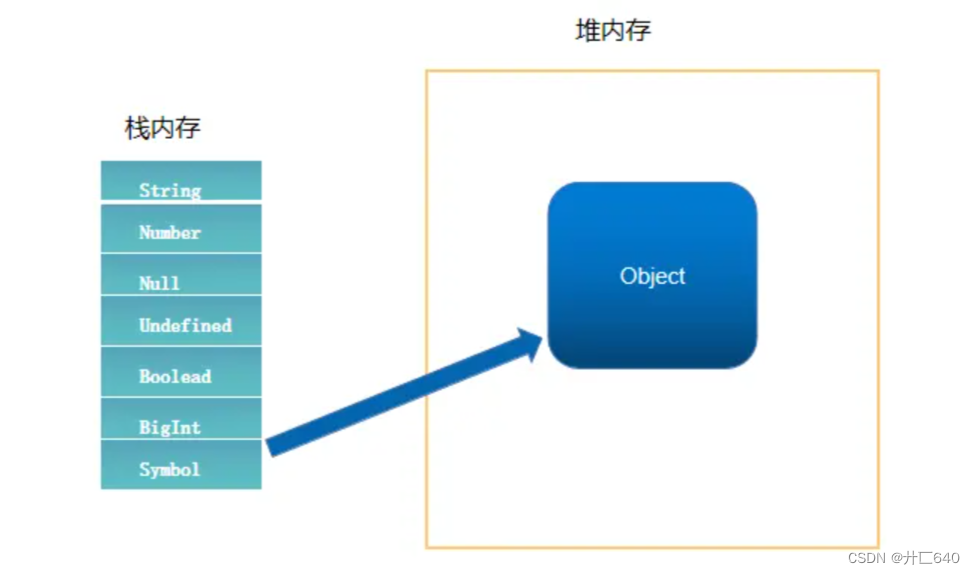
四、赋值和浅拷贝举例。
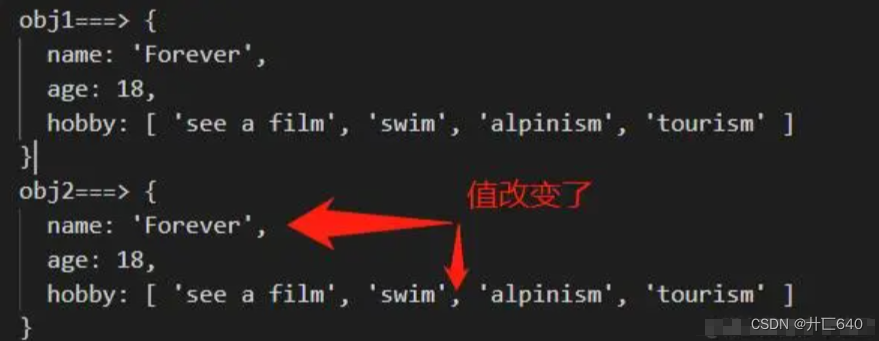
1.赋值。
// 对象赋值
let obj1 = {
name: 'Chen',
age: 18,
hobby: ['see a film', 'write the code', 'play basketball', 'tourism']
}
let obj2 = obj1;
obj2.name = 'Forever';
obj2.hobby[1] = 'swim';
obj2.hobby[2] = 'alpinism';
console.log('obj1===>', obj1);
console.log('obj2===>', obj2);
2.浅拷贝。
// 浅拷贝
let obj1 = {
name: 'Chen',
age: 18,
hobby: ['see a film', 'write the code', 'play basketball', 'tourism']
}
let obj3 = {...obj1};
obj3.name = 'Forever';
obj3.hobby[1] = 'swim';
obj3.hobby[2] = 'alpinism';
console.log('obj1===>', obj1);
console.log('obj3===>', obj3);

五、浅拷贝的实现。
1.展开运算符(...)?
// 展开运算符... 实现浅拷贝
let obj1 = {
name: 'Chen',
hobby: ['see a film', 'write the code', 'play basketball', 'tourism']
}
let obj2 = {...obj1};
obj2.hobby[1] = 'swim';
obj2.hobby[2] = 'alpinism';
obj2.name = 'Forever';
console.log('obj1===>', obj1); // obj1===> { name: 'Chen',hobby: [ 'see a film', 'swim','alpinism', 'tourism']}
console.log('obj2===>', obj2); // obj2===> { name: 'Forever',hobby: [ 'see a film', 'swim','alpinism', 'tourism']}
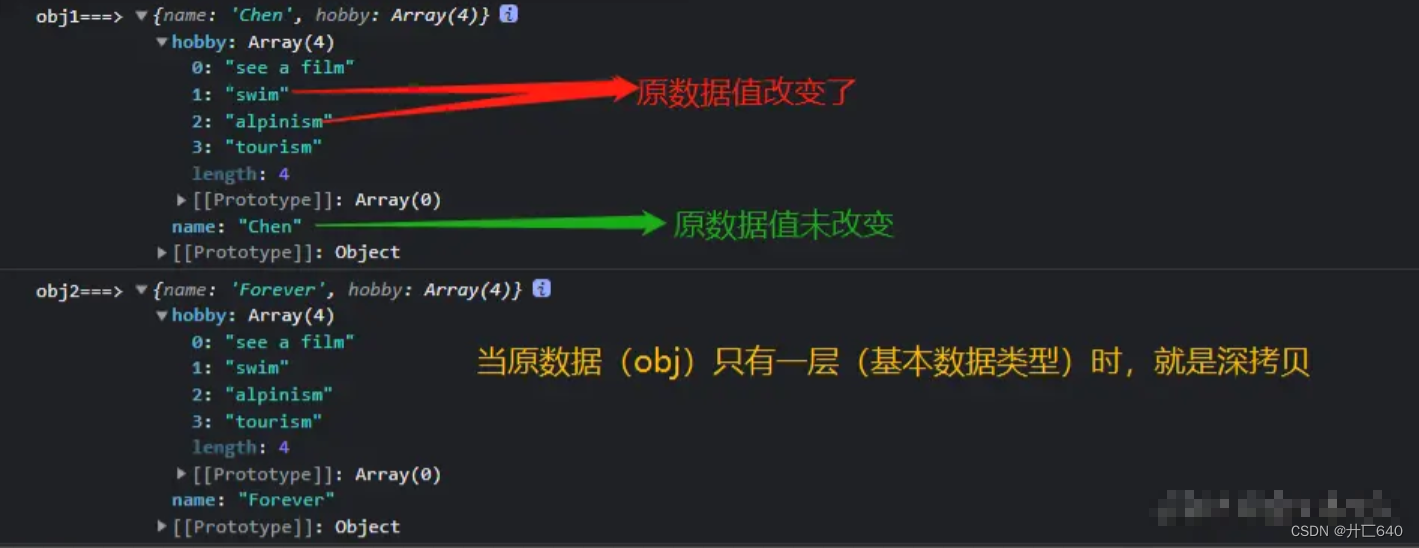
2.Object.assign()
// Object.assign() 实现浅拷贝
let obj1 = {
name: "Chen",
hobby: ["see a film", "write the code", "play basketball", "tourism"],
};
let obj2 = Object.assign({}, obj1);
obj2.hobby[1] = "swim";
obj2.hobby[2] = "alpinism";
obj2.name = "Forever";
console.log("obj1===>", obj1); // obj1===> {name: 'Chen',hobby: [ 'see a film', 'swim', 'alpinism', 'tourism' ]}
console.log("obj2===>", obj2); // obj2===> {name: 'Forever',hobby: [ 'see a film', 'swim', 'alpinism', 'tourism' ]}
?
?3. Array.prototype.concat()
// Array.prototype.concat() 实现浅拷贝
let arr1 = [
{
name: 'Chen'
},
'see a film',
'write the code',
'play basketball',
'tourism'
];
let arr2 = arr1.concat([]);
arr2[0].name = 'Forever';
arr2[1] = 'play games';
console.log('arr1===>', arr1); // arr1===> [{ name: 'Forever' },'see a film','write the code','play basketball', 'tourism']
console.log('arr2===>', arr2); // arr2===> [{ name: 'Forever' },'play games','write the code', 'play basketball', 'tourism']
4.? Array.prototype.slice()
// Array.prototype.concat() 实现浅拷贝
let arr1 = [
{
name: 'Chen'
},
'see a film',
'write the code',
'play basketball',
'tourism'
];
let arr2 = arr1.slice();
arr2[0].name = 'Forever';
arr2[1] = 'play games';
console.log('arr1===>', arr1); // arr1===> [{ name: 'Forever' },'see a film','write the code','play basketball', 'tourism']
console.log('arr2===>', arr2); // arr2===> [{ name: 'Forever' },'play games','write the code', 'play basketball', 'tourism']
?六、深拷贝实现。
? 1.JSON.parse(JSON.stringify())
// JSON.parse(JSON.stringify())实现深拷贝Object
let obj1 = {
name: 'Chen',
hobby: ['see a film', 'write the code', 'play basketball', 'tourism']
}
let obj2 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj1));
console.log(obj1 === obj2); // false
obj2.name = 'Forever';
obj2.hobby[1] = 'swim';
obj2.hobby[2] = 'alpinism';
console.log('obj1===>', obj1);
// obj1===> { name: 'Chen',hobby: ['see a film', 'write the code', 'play basketball', 'tourism']}
console.log('obj2===>', obj2);
// obj2===> { name: 'Forever',hobby: ['see a film', 'swim', 'alpinism', 'tourism']}
?2.JSON.stringify()的缺点:
undefined、任意的函数以及 symbol 值,在序列化过程中会被忽略(出现在非数组对象的属性值中时)或者被转换成?null(出现在数组中时)。函数、undefined 被单独转换时,会返回 undefined,如JSON.stringify(function(){})?or?JSON.stringify(undefined).- 对包含循环引用的对象(对象之间相互引用,形成无限循环)执行此方法,会抛出错误。
- 所有以 symbol 为属性键的属性都会被完全忽略掉,即便?
replacer?参数中强制指定包含了它们。 - Date 日期调用了 toJSON() 将其转换为了 string 字符串(同 Date.toISOString()),因此会被当做字符串处理。
- NaN 和 Infinity 格式的数值及 null 都会被当做 null。
- 其他类型的对象,包括 Map/Set/WeakMap/WeakSet,仅会序列化可枚举的属性。
JSON.stringify({}); // '{}'
JSON.stringify(true); // 'true'
JSON.stringify("foo"); // '"foo"'
JSON.stringify([1, "false", false]); // '[1,"false",false]'
JSON.stringify({ x: 5 }); // '{"x":5}'
JSON.stringify({ x: 5, y: 6 });
// "{"x":5,"y":6}"
JSON.stringify([new Number(1), new String("false"), new Boolean(false)]);
// '[1,"false",false]'
JSON.stringify({ x: undefined, y: Object, z: Symbol("") });
// '{}'
JSON.stringify([undefined, Object, Symbol("")]);
// '[null,null,null]'
JSON.stringify({ [Symbol("foo")]: "foo" });
// '{}'
JSON.stringify({ [Symbol.for("foo")]: "foo" }, [Symbol.for("foo")]);
// '{}'
JSON.stringify({ [Symbol.for("foo")]: "foo" }, function (k, v) {
if (typeof k === "symbol") {
return "a symbol";
}
});
// undefined
// 不可枚举的属性默认会被忽略:
JSON.stringify(
Object.create(null, {
x: { value: "x", enumerable: false },
y: { value: "y", enumerable: true },
}),
);
// "{"y":"y"}"
?七、手写浅拷贝和深拷贝
1.浅拷贝:
// 浅拷贝
let shalldowCopy = (obj) => {
// 只拷贝引用类型
if (typeof obj !== 'object' || obj == null) return
let objCopy = obj instanceof Array ? [] : {}
for (let key in obj){
//不要隐式
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)){
objCopy[key] = obj[key]
}
}
return objCopy
}
//测试
let obj = {
name: '小黑子',
age: 18,
hobby: {
type: 'coding'
}
}
let arr = ['a', {n: 1}, 1, undefined, null]
let newObj = shalldowCopy(obj)
let newArr = shalldowCopy(arr)
obj.age = 20
obj.hobby.type = 'swimming'
arr[0] = 'b'
arr[1].n = 2
console.log(newObj);
// { name: '小黑子', age: 18, hobby: { type: 'swimming' } }
console.log(newArr);
// [ 'a', { n: 2 }, 1, undefined, null ]2.深拷贝
let deepCopy = (obj) => {
if(typeof obj!== 'object' || obj == null) return
let objCopy = obj instanceof Array ? [] : {}
for (let key in obj){
if(obj.hasOwnProperty(key)){
// 与浅拷贝相比只是这里有差异其余原理都一样
if(obj[key] instanceof Object){
objCopy[key] = deepCopy(obj[key])
} else {
objCopy[key] = obj[key]
}
}
}
return objCopy
}
// 测试
const obj5 = {
name:'你好',
age:18,
like:{
type:'coding'
}
}
const res = deepCopy(obj5)
console.log(res) // { name: '你好', age: 18, like: { type: 'coding' } }
obj5.like.type = 'sleeping'
console.log(res) // { name: '你好', age: 18, like: { type: 'coding' } }
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_55806761/article/details/135550559
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- STL第一讲
- 使用开源技术快速上手 Web 前端开发(内含PPT课件)
- 做题笔记:SQL Sever 方式做牛客SQL的题目--SQL215
- Anaconda3 2021.11安装
- Thread-Per-Message设计模式
- 面试题-MySQL如何定位慢查询
- 找不到vcruntime140_1.dll无法继续执行怎么办?全面分析修复方法
- 期末大作业【学生选课与成绩管理系统1】Java+MySQL数据库+可视化图形界面
- HTML教程
- 深度强化学习的变道策略:Harmonious Lane Changing via Deep Reinforcement Learning