算法:BFS宽度优先遍历
发布时间:2023年12月20日
本篇总结的是BFS算法,BFS算法相比起DFS算法来说还是比较简单的
BFS与Queue相结合
N叉树的层序遍历
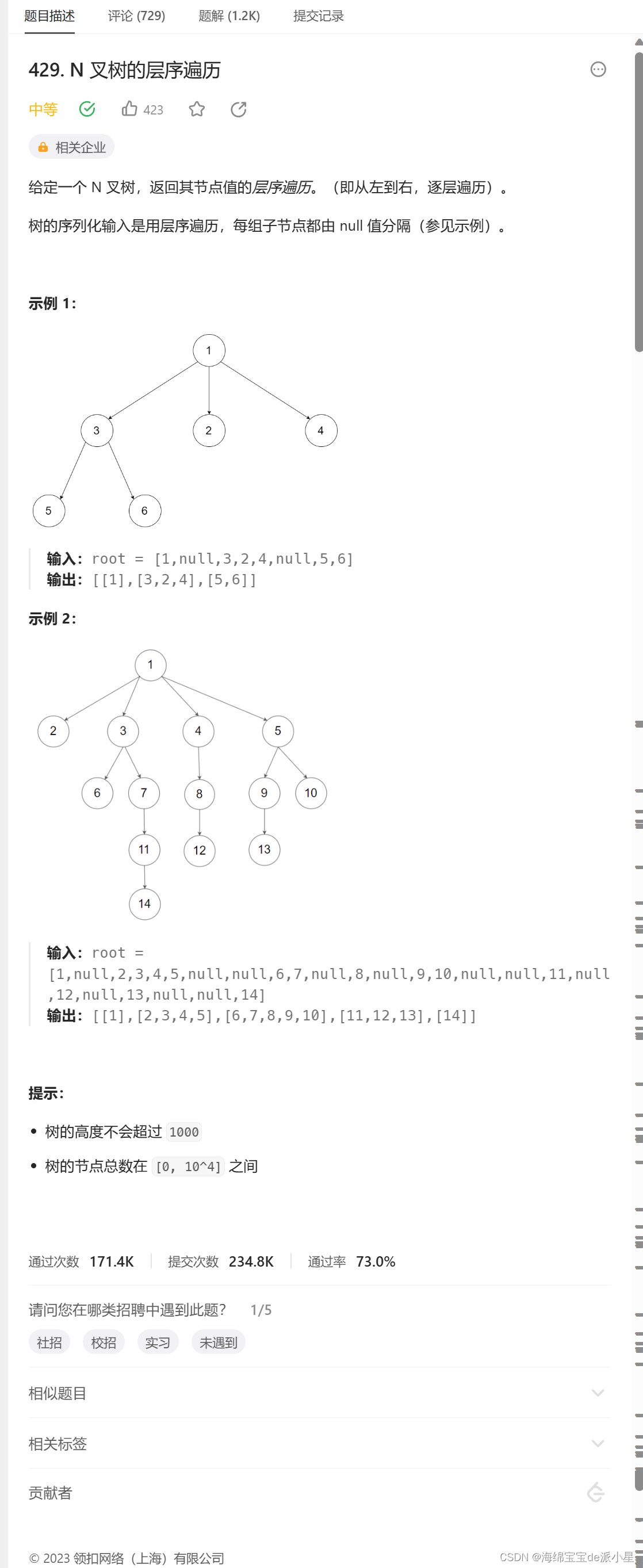
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root)
{
vector<vector<int>> ret;
if(root == nullptr)
return ret;
queue<Node*> qe;
qe.push(root);
while(!qe.empty())
{
int size = qe.size();
vector<int> tmp;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
// 取队列头节点
Node* front = qe.front();
qe.pop();
// 把值入到数组中
tmp.push_back(front->val);
// 如果有孩子,就把孩子入到队列中
for(int j = 0; j < (front->children).size(); j++)
qe.push((front->children)[j]);
}
ret.push_back(tmp);
}
return ret;
}
};
二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
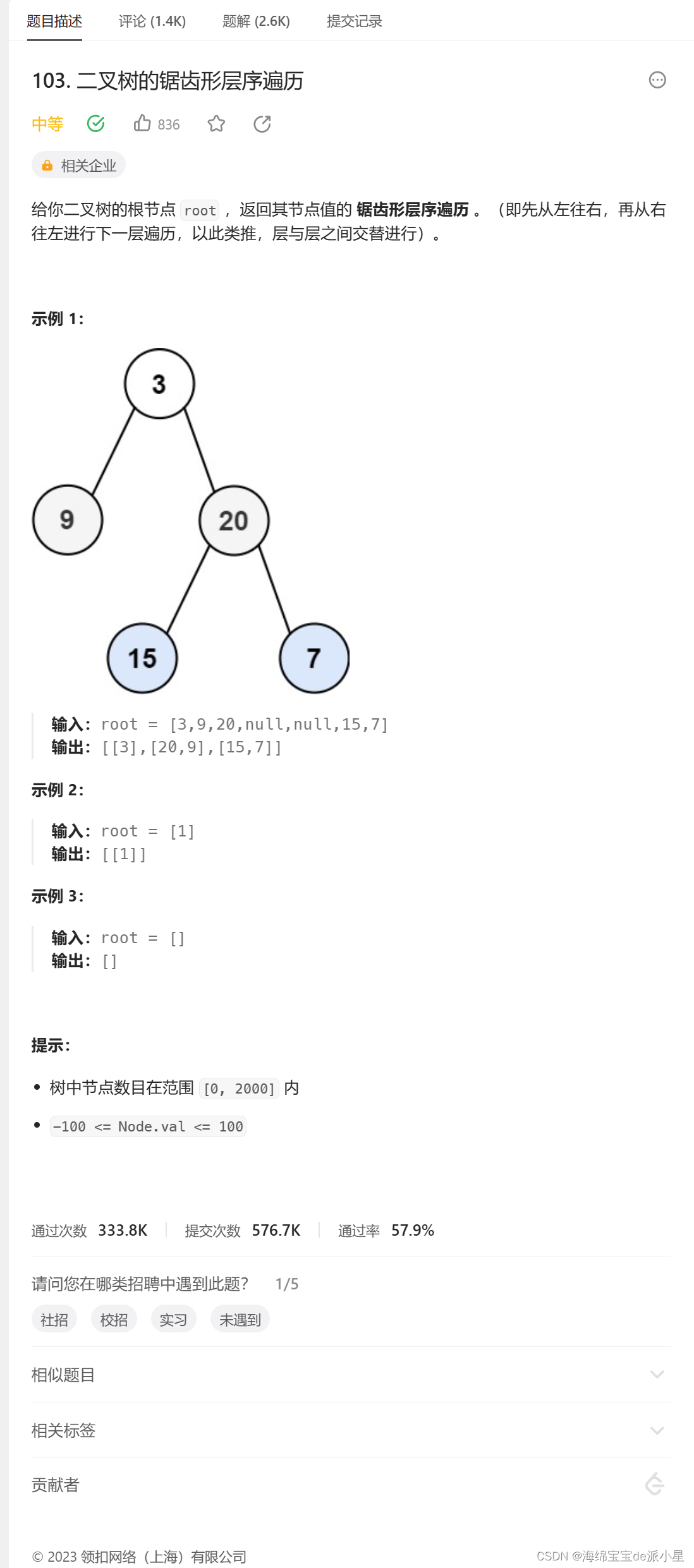
这里提供一种双端队列的做法,也可以在合适的层数逆序
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(root == nullptr)
return res;
bool status = true;
queue<TreeNode*> qe;
qe.push(root);
while(!qe.empty())
{
int size = qe.size();
deque<int> v;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
TreeNode* front = qe.front();
qe.pop();
if(status)
v.push_back(front->val);
else
v.push_front(front->val);
if(front->left)
qe.push(front->left);
if(front->right)
qe.push(front->right);
}
res.push_back(vector<int>(v.begin(), v.end()));
status = !status;
}
return res;
}
};
二叉树的最大宽度
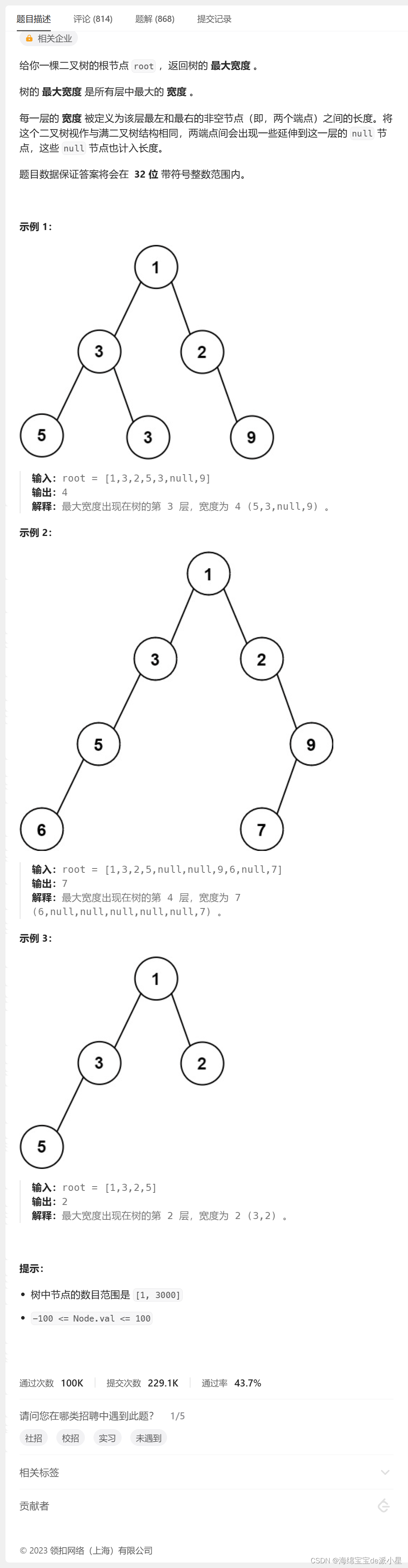
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution
{
public:
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root)
{
// 用数组来模拟队列,有助于最后计算,这里没用
queue<pair<TreeNode*, unsigned int>> v;
v.push(make_pair(root, 1));
unsigned int lenth = 0;
while(!v.empty())
{
// 计算一下这中间长度的差
lenth = max(lenth, v.back().second - v.front().second + 1);
int size = v.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
// 取头
auto front = v.front();
v.pop();
// 如果有左或者有右节点,就进去
if(front.first->left)
v.push(make_pair(front.first->left, (front.second) * 2));
if(front.first->right)
v.push(make_pair(front.first->right, (front.second) * 2 + 1));
}
}
return lenth;
}
};
BFS和FLoodFill相结合
图像渲染

class Solution
{
int dx[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int dy[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
public:
vector<vector<int>> floodFill(vector<vector<int>>& image, int sr, int sc, int color)
{
int oldcolor = image[sr][sc];
int newcolor = color;
if(oldcolor == newcolor)
return image;
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({sr, sc});
while(!q.empty())
{
auto [a, b] = q.front();
q.pop();
image[a][b] = newcolor;
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = dx[k] + a, y = dy[k] + b;
if(x >= 0 && x < image.size() && y >=0 && y < image[0].size() && image[x][y] == oldcolor)
q.push({x, y});
}
}
return image;
}
};
岛屿数量

class Solution
{
int res = 0;
int dx[4] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
int dy[4] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid)
{
vector<vector<bool>> check;
check.resize(grid.size(), vector<bool>(grid[0].size(), false));
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++)
{
if (grid[i][j] == '1' && check[i][j] == false)
{
check[i][j] = true;
q.push({ i, j });
while (!q.empty())
{
auto [a, b] = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = dx[k] + a, y = dy[k] + b;
if (x >= 0 && x < grid.size() && y >= 0 && y < grid[0].size() && grid[x][y] == '1' && check[x][y] == false)
{
check[x][y] = true;
q.push({ x, y });
}
}
}
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
岛屿的最大面积

class Solution
{
public:
int maxAreaOfIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid)
{
int res = 0, maxsize = 0, dx[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
vector<vector<bool>> check(grid.size(), vector<bool>(grid[0].size(), false));
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
for(int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].size(); j++)
{
if(check[i][j] == false && grid[i][j] == 1)
{
check[i][j] = true;
q.push({i, j});
res++;
while(!q.empty())
{
auto [a, b] = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = dx[k] + a, y = dy[k] + b;
if(x >= 0 && x < grid.size() && y >= 0 && y < grid[0].size() && grid[x][y] == 1 && check[x][y] == false)
{
check[x][y] = true;
q.push({x, y});
res++;
}
}
}
maxsize = max(res, maxsize);
res = 0;
}
}
}
return maxsize;
}
};
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_73899585/article/details/134912879
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Java多线程技术五——单例模式与多线程-备份
- 2024年建筑工程行业资格考试计划出来了你准备考啥?
- ant-design-vue的日期组件a-range-picker赋值的问题
- Spring Security工作原理(一)
- 什么是TCP协议?以及TCP协议的作用
- 机器人说明书---名词解释023课_python语言_基础
- 在Oracle数据库中,你可以使用LENGTH和LENGTHB函数来判断一个字符串是否包含中文。
- 当忘记Windows 10的PIN码时,你就来对地方法了
- 复试 || 就业day11(2024.01.07)算法篇
- 使用Java版工程行业管理系统源码,提升工程管理的效率和精度