GAMES101-Assignment2
GAMES101-Assignment2
文件清单
CMakeLists.txt(项目配置清单,cmake根据此清单进行系统构建、编译、测试)
global.hpp(全局变量声明)
Triangle.hpp(三角形的头文件,定义其相关属性)
Triangle.cpp(画出三角形)
Rasterizer.hpp(光栅器头文件)
Rasterizer.cpp(生成渲染器界面与绘制)
main.cpp
此作业要求如下

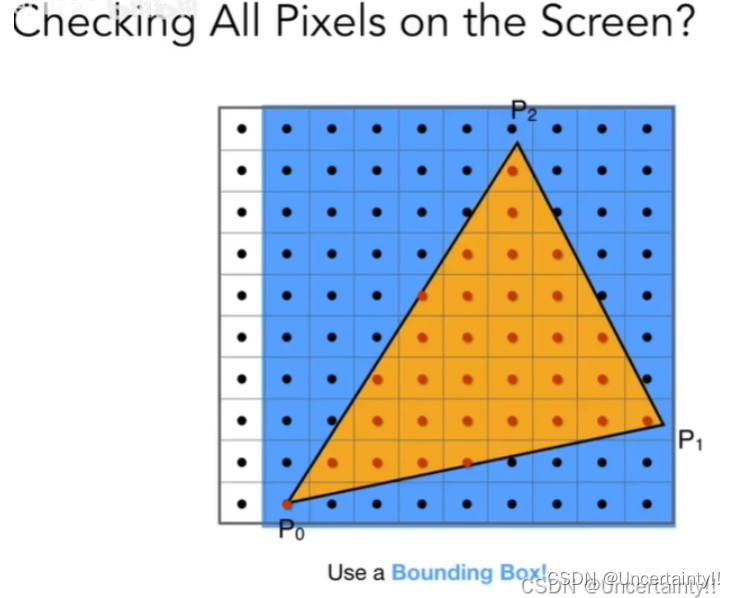

该作业的主要部分:
三角形三个向量、像素中心点与三个顶点组成的向量,二者进行叉积,根据叉积结果是否同正或同负来判断像素中心点是否在三角形内
由于还不熟悉c++,所以并没有用for循环简化程序

光栅化三角形,先设置Bounding box边界初值,迭代找实际边界值,找到边界后,遍历只在该边界内进行,而不用遍历整个屏幕。遍历过程中判断像素中心点是否在三角形内,如果在三角形内,则将该像素的颜色值设置为与顶点相同的颜色,比较该像素的深度值与初始化的深度值,若该深度值小于初始深度值则更新,或者当两个空间三角形在2D平面的投影有重合部分时,重合像素会进行深度值的比较,最终只显示深度最小的那个像素颜色
depth_buf中存着屏幕中所有像素的深度值,初始值深度为无穷大
情况一:两个物体在2D投影处无重合部分,则无重合部分的三角形内部的像素深度-z_interpolated(-z为正数)一定小于无穷大,该像素深度更新为该z插值,颜色更新为对应三角形的颜色
情况二:两个物体在2D投影处有重合部分,重合部分两个三角形一前(第一个z_interpolated)一后(第二个z_interpolated),前面的像素深度一定小于后面的像素深度小于无穷大,故该像素深度更新为最前面的那个深度值,相应像素颜色更新为对应三角形的颜色
参考内容:
1.技术美术成长之路——Games101作业篇(二)、光栅化作业
2.【GAMES101】作业2(提高)(附带解决黑边问题)

CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
project(Rasterizer)
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
include_directories(/usr/local/include)
add_executable(Rasterizer main.cpp rasterizer.hpp rasterizer.cpp global.hpp Triangle.hpp Triangle.cpp)
target_link_libraries(Rasterizer ${OpenCV_LIBRARIES})
global.hpp
//
// Created by LEI XU on 4/9/19.
//
#ifndef RASTERIZER_GLOBAL_H
#define RASTERIZER_GLOBAL_H
//#define MY_PI 3.1415926
//#define TWO_PI (2.0* MY_PI)
#endif //RASTERIZER_GLOBAL_H
Triangle.hpp
//
// Created by LEI XU on 4/11/19.
//
#ifndef RASTERIZER_TRIANGLE_H
#define RASTERIZER_TRIANGLE_H
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Eigen>
using namespace Eigen;
class Triangle{
public:
Vector3f v[3]; /*the original coordinates of the triangle, v0, v1, v2 in counter clockwise order*/
/*Per vertex values*/
Vector3f color[3]; //color at each vertex;
Vector2f tex_coords[3]; //texture u,v
Vector3f normal[3]; //normal vector for each vertex
//Texture *tex;
Triangle();
void setVertex(int ind, Vector3f ver); /*set i-th vertex coordinates */
void setNormal(int ind, Vector3f n); /*set i-th vertex normal vector*/
void setColor(int ind, float r, float g, float b); /*set i-th vertex color*/
Vector3f getColor() const { return color[0]*255; } // Only one color per triangle.
void setTexCoord(int ind, float s, float t); /*set i-th vertex texture coordinate*/
std::array<Vector4f, 3> toVector4() const;
};
#endif //RASTERIZER_TRIANGLE_H
Triangle.cpp
//
// Created by LEI XU on 4/11/19.
//
#include "Triangle.hpp"
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
Triangle::Triangle() {
v[0] << 0,0,0;
v[1] << 0,0,0;
v[2] << 0,0,0;
color[0] << 0.0, 0.0, 0.0;
color[1] << 0.0, 0.0, 0.0;
color[2] << 0.0, 0.0, 0.0;
tex_coords[0] << 0.0, 0.0;
tex_coords[1] << 0.0, 0.0;
tex_coords[2] << 0.0, 0.0;
}
void Triangle::setVertex(int ind, Vector3f ver){
v[ind] = ver;
}
void Triangle::setNormal(int ind, Vector3f n){
normal[ind] = n;
}
void Triangle::setColor(int ind, float r, float g, float b) {
if((r<0.0) || (r>255.) ||
(g<0.0) || (g>255.) ||
(b<0.0) || (b>255.)) {
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR! Invalid color values");
fflush(stderr);
exit(-1);
}
color[ind] = Vector3f((float)r/255.,(float)g/255.,(float)b/255.);
return;
}
void Triangle::setTexCoord(int ind, float s, float t) {
tex_coords[ind] = Vector2f(s,t);
}
std::array<Vector4f, 3> Triangle::toVector4() const
{
std::array<Eigen::Vector4f, 3> res;
std::transform(std::begin(v), std::end(v), res.begin(), [](auto& vec) { return Eigen::Vector4f(vec.x(), vec.y(), vec.z(), 1.f); });
return res;
}
Rasterizer.hpp
//
// Created by goksu on 4/6/19.
//
#pragma once
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Eigen>
#include <algorithm>
#include "global.hpp"
#include "Triangle.hpp"
using namespace Eigen;
namespace rst
{
enum class Buffers
{
Color = 1,
Depth = 2
};
inline Buffers operator|(Buffers a, Buffers b)
{
return Buffers((int)a | (int)b);
}
inline Buffers operator&(Buffers a, Buffers b)
{
return Buffers((int)a & (int)b);
}
enum class Primitive
{
Line,
Triangle
};
/*
* For the curious : The draw function takes two buffer id's as its arguments. These two structs
* make sure that if you mix up with their orders, the compiler won't compile it.
* Aka : Type safety
* */
struct pos_buf_id
{
int pos_id = 0;
};
struct ind_buf_id
{
int ind_id = 0;
};
struct col_buf_id
{
int col_id = 0;
};
class rasterizer
{
public:
rasterizer(int w, int h);
pos_buf_id load_positions(const std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f>& positions);
ind_buf_id load_indices(const std::vector<Eigen::Vector3i>& indices);
col_buf_id load_colors(const std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f>& colors);
void set_model(const Eigen::Matrix4f& m);
void set_view(const Eigen::Matrix4f& v);
void set_projection(const Eigen::Matrix4f& p);
void set_pixel(const Eigen::Vector3f& point, const Eigen::Vector3f& color);
void clear(Buffers buff);
void draw(pos_buf_id pos_buffer, ind_buf_id ind_buffer, col_buf_id col_buffer, Primitive type);
std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f>& frame_buffer() { return frame_buf; }
private:
void draw_line(Eigen::Vector3f begin, Eigen::Vector3f end);
void rasterize_triangle(const Triangle& t);
// VERTEX SHADER -> MVP -> Clipping -> /.W -> VIEWPORT -> DRAWLINE/DRAWTRI -> FRAGSHADER
private:
Eigen::Matrix4f model;
Eigen::Matrix4f view;
Eigen::Matrix4f projection;
std::map<int, std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f>> pos_buf;
std::map<int, std::vector<Eigen::Vector3i>> ind_buf;
std::map<int, std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f>> col_buf;
std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f> frame_buf;
std::vector<float> depth_buf;
int get_index(int x, int y);
int width, height;
int next_id = 0;
int get_next_id() { return next_id++; }
};
}
Rasterizer.cpp
// clang-format off
//
// Created by goksu on 4/6/19.
//
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include "rasterizer.hpp"
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <math.h>
rst::pos_buf_id rst::rasterizer::load_positions(const std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f> &positions)
{
auto id = get_next_id();
pos_buf.emplace(id, positions);
return {id};
}
rst::ind_buf_id rst::rasterizer::load_indices(const std::vector<Eigen::Vector3i> &indices)
{
auto id = get_next_id();
ind_buf.emplace(id, indices);
return {id};
}
rst::col_buf_id rst::rasterizer::load_colors(const std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f> &cols)
{
auto id = get_next_id();
col_buf.emplace(id, cols);
return {id};
}
auto to_vec4(const Eigen::Vector3f& v3, float w = 1.0f)
{
return Vector4f(v3.x(), v3.y(), v3.z(), w);
}
static bool insideTriangle(int x, int y, const Vector3f* _v)
{
// TODO : Implement this function to check if the point (x, y) is inside the triangle represented by _v[0], _v[1], _v[2]
//---------------------------------------------
//method: cross product,P(x,y) V_0 V_1 V_2
//vec{V_0,V_1}^vec{V_0,P} vec{V_1,V_2}^vec{V_1,P} vec{V_2,V_0}^vec{V_2,P}
Vector3f a(_v[1].x()-_v[0].x(),_v[1].y()-_v[0].y(),0);//vec{V_0,V_1} //homogeneous coordinate
Vector3f p0(x-_v[0].x(),y-_v[0].y(),0);//vec{V_0,P}
Vector3f r0=a.cross(p0);//result of the first cross product:a new vector (0,0,z)
Vector3f b(_v[2].x()-_v[1].x(),_v[2].y()-_v[1].y(),0);//vec{V_1,V_2}
Vector3f p1(x-_v[1].x(),y-_v[1].y(),0);//vec{V_1,P}
Vector3f r1=b.cross(p1);//result of the second cross product
Vector3f c(_v[0].x()-_v[2].x(),_v[0].y()-_v[2].y(),0);//vec{V_2,V_0}
Vector3f p2(x-_v[2].x(),y-_v[2].y(),0);//vec{V_2,P}
Vector3f r2=c.cross(p2);//result of the third cross product
if (r0.z()>0 && r1.z()>0 && r2.z()>0 || r0.z()<0 && r1.z()<0 && r2.z()<0)
return true;
return false;
/*
Matrix<float,3,3> rcp;//result_cross_product[3]:restore the result of cross product
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
Vector3f vec(_v[i+1].x()-_v[i].x(),_v[i+1].y()-_v[i].y(),0);
Vector3f vec_p(x-_v[i].x(),y-_v[i].y(),0);
rcp.row(i)=vec.cross(vec_p);//result of cross product is a new vector (0,0,z)
}
//(x,y) is inside the triangle if point(x,y) is on the same side of three vector
if ((rcp(0,2)>0 && rcp(1,2)>0 && rcp(2,2)>0) || (rcp(0,2)<0 && rcp(1,2)<0 && rcp(2,2)<0))
return true;
return false;*/
}
static std::tuple<float, float, float> computeBarycentric2D(float x, float y, const Vector3f* v)
{
float c1 = (x*(v[1].y() - v[2].y()) + (v[2].x() - v[1].x())*y + v[1].x()*v[2].y() - v[2].x()*v[1].y()) / (v[0].x()*(v[1].y() - v[2].y()) + (v[2].x() - v[1].x())*v[0].y() + v[1].x()*v[2].y() - v[2].x()*v[1].y());
float c2 = (x*(v[2].y() - v[0].y()) + (v[0].x() - v[2].x())*y + v[2].x()*v[0].y() - v[0].x()*v[2].y()) / (v[1].x()*(v[2].y() - v[0].y()) + (v[0].x() - v[2].x())*v[1].y() + v[2].x()*v[0].y() - v[0].x()*v[2].y());
float c3 = (x*(v[0].y() - v[1].y()) + (v[1].x() - v[0].x())*y + v[0].x()*v[1].y() - v[1].x()*v[0].y()) / (v[2].x()*(v[0].y() - v[1].y()) + (v[1].x() - v[0].x())*v[2].y() + v[0].x()*v[1].y() - v[1].x()*v[0].y());
return {c1,c2,c3};
}
void rst::rasterizer::draw(pos_buf_id pos_buffer, ind_buf_id ind_buffer, col_buf_id col_buffer, Primitive type)
{
auto& buf = pos_buf[pos_buffer.pos_id];
auto& ind = ind_buf[ind_buffer.ind_id];
auto& col = col_buf[col_buffer.col_id];
float f1 = (50 - 0.1) / 2.0;
float f2 = (50 + 0.1) / 2.0;
Eigen::Matrix4f mvp = projection * view * model;
for (auto& i : ind)
{
Triangle t;
Eigen::Vector4f v[] = {
mvp * to_vec4(buf[i[0]], 1.0f),
mvp * to_vec4(buf[i[1]], 1.0f),
mvp * to_vec4(buf[i[2]], 1.0f)
};
//Homogeneous division
for (auto& vec : v) {
vec /= vec.w();
}
//Viewport transformation
for (auto & vert : v)
{
vert.x() = 0.5*width*(vert.x()+1.0);
vert.y() = 0.5*height*(vert.y()+1.0);
vert.z() = vert.z() * f1 + f2;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
t.setVertex(i, v[i].head<3>());
t.setVertex(i, v[i].head<3>());
t.setVertex(i, v[i].head<3>());
}
auto col_x = col[i[0]];
auto col_y = col[i[1]];
auto col_z = col[i[2]];
t.setColor(0, col_x[0], col_x[1], col_x[2]);
t.setColor(1, col_y[0], col_y[1], col_y[2]);
t.setColor(2, col_z[0], col_z[1], col_z[2]);
rasterize_triangle(t);
}
}
//Screen space rasterization
void rst::rasterizer::rasterize_triangle(const Triangle& t) {
auto v = t.toVector4();//3 point's homogeneous coordinate (x,y,z,1).v[][]={(x_1,y_1z_1,1),(x_2...)}
// TODO : Find out the bounding box of current triangle.
// iterate through the pixel and find if the current pixel is inside the triangle
// If so, use the following code to get the interpolated z value.
//auto[alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(x, y, t.v);
//float w_reciprocal = 1.0/(alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
//float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
//z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
// TODO : set the current pixel (use the set_pixel function) to the color of the triangle (use getColor function) if it should be painted.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Define bound of box
//INT_MAX: infnity represented by top limitation of integer
int BoxMin_X =INT_MAX,BoxMin_Y=INT_MAX;
//INT_MIN: infnity represented by bottom limitation of integer
int BoxMax_X =INT_MIN,BoxMax_Y=INT_MIN;
//depth buffer
//int depth_buf=INT_MAX;
//iterate to find bound
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
BoxMin_X=std::min(BoxMin_X,(int)v[i][0]);
BoxMin_Y=std::min(BoxMin_Y,(int)v[i][1]);
BoxMax_X=std::max(BoxMax_X,(int)v[i][0]);
BoxMax_Y=std::max(BoxMax_Y,(int)v[i][1]);
}
//iterate pixel inside of bounding box
for (int i = BoxMin_X; i <= BoxMax_X; i++)
{
for (int j = BoxMin_Y; j <= BoxMax_Y; j++)
{
//float x=i+0.5,y=i+0.5;
//check if center of current pixel is inside the triangle
if (insideTriangle(i,j,t.v))//if centric pixel(x,y) is insidez. three point v[0],v[1],v[2]in triangle
{
//interpolated depth value
auto[alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(i+0.5, j+0.5, t.v);
float w_reciprocal = 1.0/(alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
//interpolated depth value is compared with depth_buffer
//-z is a positive number
if (-z_interpolated < depth_buf[get_index(i,j)])//get buffer index of pixel(x,y)
{
//get color of 1 out of 3 vertex in triangle,then set this color to current pixel
set_pixel({i,j,1},t.getColor());//(x,y,1) homogeneous coord,num 1 represent a point
//update depth buffer
depth_buf[get_index(i,j)] = -z_interpolated;
}
}
}
}
}
void rst::rasterizer::set_model(const Eigen::Matrix4f& m)
{
model = m;
}
void rst::rasterizer::set_view(const Eigen::Matrix4f& v)
{
view = v;
}
void rst::rasterizer::set_projection(const Eigen::Matrix4f& p)
{
projection = p;
}
void rst::rasterizer::clear(rst::Buffers buff)
{
if ((buff & rst::Buffers::Color) == rst::Buffers::Color)
{
std::fill(frame_buf.begin(), frame_buf.end(), Eigen::Vector3f{0, 0, 0});
}
if ((buff & rst::Buffers::Depth) == rst::Buffers::Depth)
{
std::fill(depth_buf.begin(), depth_buf.end(), std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity());
}
}
rst::rasterizer::rasterizer(int w, int h) : width(w), height(h)
{
frame_buf.resize(w * h);
depth_buf.resize(w * h);
}
int rst::rasterizer::get_index(int x, int y)
{
return (height-1-y)*width + x;
}
void rst::rasterizer::set_pixel(const Eigen::Vector3f& point, const Eigen::Vector3f& color)
{
//old index: auto ind = point.y() + point.x() * width;
auto ind = (height-1-point.y())*width + point.x();
frame_buf[ind] = color;
}
// clang-format on
main.cpp
// clang-format off
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include "rasterizer.hpp"
#include "global.hpp"
#include "Triangle.hpp"
constexpr double MY_PI = 3.1415926;
//移动相机到原点
Eigen::Matrix4f get_view_matrix(Eigen::Vector3f eye_pos)
{
Eigen::Matrix4f view = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();
Eigen::Matrix4f translate;
translate << 1,0,0,-eye_pos[0],
0,1,0,-eye_pos[1],
0,0,1,-eye_pos[2],
0,0,0,1;
view = translate*view;
return view;
}
//移动3D物体,该例中不用处理旋转变换
Eigen::Matrix4f get_model_matrix(float rotation_angle)
{
Eigen::Matrix4f model = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();
return model;
}
//将空间中的三角形投影到屏幕范围内(也就是标准立方体cube中)
//输入视场角fov,宽高比aspect_ration,视场近处面坐标zNear和远处面坐标zFar
Eigen::Matrix4f get_projection_matrix(float eye_fov, float aspect_ratio,
float zNear, float zFar)
{
// Students will implement this function
Eigen::Matrix4f projection = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();
// TODO: Implement this function
// Create the projection matrix for the given parameters.
// Then return it.
// n=zNear f=zFar
// calculate r l t b according to eye_fov and aspect_ratio
// tan(eye_fov/2)=t/|n|,aspect_ratio=r/t
// t=2|n|tan(eye_fov/2),r=t*aspect_ratio,l=-r,b=-t
float t=2*abs(zNear)*tan(eye_fov/2),b=-t;
float r=aspect_ratio*t,l=-r;
//perspective projection M_{projection}= M_{orthographics}*M_{persp to ortho}
Eigen::Matrix4f M_persp_to_ortho,M_ortho,M_scale,M_translate;
M_persp_to_ortho << zNear,0,0,0,
0,zNear,0,0,
0,0,zNear+zFar,-zNear*zFar,
0,0,1,0;
//M_{orthographics}=scale*translate
M_scale << 2/(r-l),0,0,0,
0,2/(t-b),0,0,
0,0,2/(zNear-zFar),0,
0,0,0,1;
M_translate << 1,0,0,-(r+l)/2,
0,1,0,-(t+b)/2,
0,0,1,-(zNear+zFar)/2,
0,0,0,1;
M_ortho=M_scale*M_translate;
projection=M_ortho*M_persp_to_ortho*projection;//右侧第一个projection是初始化的单位阵
return projection;
}
int main(int argc, const char** argv)
{
float angle = 0;
bool command_line = false;
std::string filename = "output.png";
if (argc == 2)
{
command_line = true;
filename = std::string(argv[1]);
}
rst::rasterizer r(700, 700);//实例化光栅器为r(width,height)
Eigen::Vector3f eye_pos = {0,0,5};//相机初始位置
std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f> pos //3D物体三角形位置
{
{2, 0, -2},
{0, 2, -2},
{-2, 0, -2},
{3.5, -1, -5},
{2.5, 1.5, -5},
{-1, 0.5, -5}
};
std::vector<Eigen::Vector3i> ind //第一个三角形第一个点下标0,下标0,1,2分别对应第一个物体的3个点
{
{0, 1, 2},
{3, 4, 5}
};
std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f> cols //两个三角形的6个顶点的颜色(RGB)
{
{217.0, 238.0, 185.0},
{217.0, 238.0, 185.0},
{217.0, 238.0, 185.0},
{185.0, 217.0, 238.0},
{185.0, 217.0, 238.0},
{185.0, 217.0, 238.0}
};
auto pos_id = r.load_positions(pos);//导入两个三角形
auto ind_id = r.load_indices(ind);//导入6个顶点对应的下标
auto col_id = r.load_colors(cols);//导入6个顶点的颜色
int key = 0;
int frame_count = 0;//帧的数量
if (command_line)//判断终端命令非空
{
r.clear(rst::Buffers::Color | rst::Buffers::Depth);
r.set_model(get_model_matrix(angle));//设置model矩阵
r.set_view(get_view_matrix(eye_pos));//设置camera矩阵
r.set_projection(get_projection_matrix(45, 1, 0.1, 50));//设置投影矩阵
r.draw(pos_id, ind_id, col_id, rst::Primitive::Triangle);//画出空间中的2个三角形
cv::Mat image(700, 700, CV_32FC3, r.frame_buffer().data());
image.convertTo(image, CV_8UC3, 1.0f);//convert to source pixel values to target data type
cv::cvtColor(image, image, cv::COLOR_RGB2BGR);
cv::imwrite(filename, image);
return 0;
}
while(key != 27)//如果没有按键ESC则继续
{
r.clear(rst::Buffers::Color | rst::Buffers::Depth);//清楚帧缓存
//重新设置矩阵
r.set_model(get_model_matrix(angle));
r.set_view(get_view_matrix(eye_pos));
r.set_projection(get_projection_matrix(45, 1, 0.1, 50));
r.draw(pos_id, ind_id, col_id, rst::Primitive::Triangle);
cv::Mat image(700, 700, CV_32FC3, r.frame_buffer().data());
image.convertTo(image, CV_8UC3, 1.0f);
cv::cvtColor(image, image, cv::COLOR_RGB2BGR);
cv::imshow("image", image);
key = cv::waitKey(10);
std::cout << "frame count: " << frame_count++ << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
// clang-format on
Results





本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- es索引数据过滤查询
- 百度搜索智能精选是什么东西、怎么加入?
- 单片机和Linux嵌入式区别
- Oracle merge into 语句用法 Oracle merge into 批量更新 关联更新 批量修改 关联修改
- 计算机网络-各层协议
- 【白盒测试】逻辑覆盖和路径测试的设计方法
- java实现定时任务
- 嵌入式科普(5)ARM GNU Toolchain相关概念和逻辑
- 第十一篇 前沿趋势与展望:深入探索GraphQL、RESTful API、WebSocket、SSE及QUIC与HTTP/3
- ASP.NET Core中实现个人资料上传图片功能