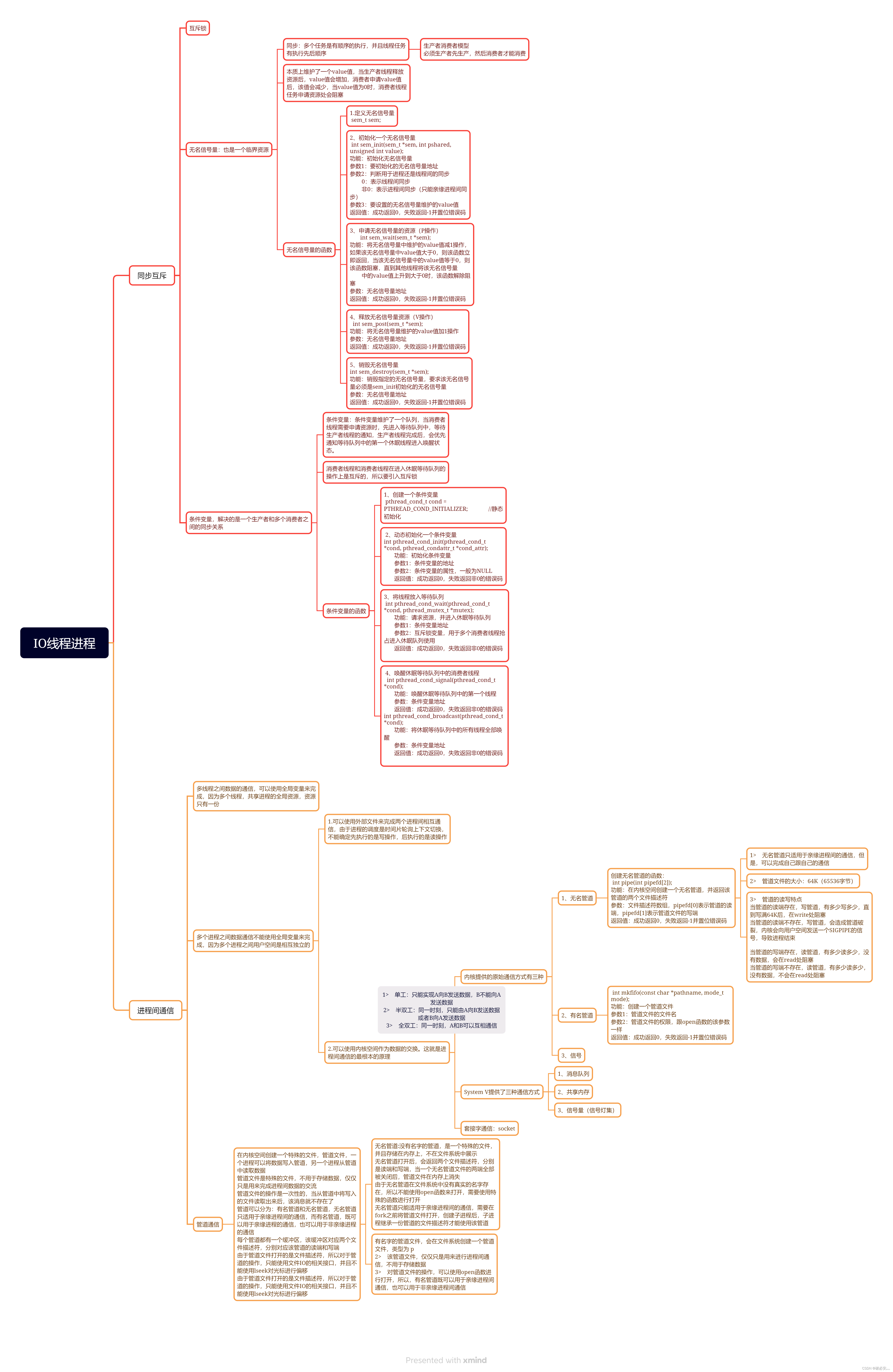
1.8 day6 IO进程线程
发布时间:2024年01月08日
使用有名管道实现两个进程之间的通信
?进程A
#include <myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//创建两个文件描述符用于打开两个管道
int fd1=-1;
int fd2=-1;
//创建一个子进程
int pid=-1;
if((fd1=open("./mkfifo1",O_RDWR))==-1)
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
if((fd2=open("./mkfifo2",O_RDWR))==-1)
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
pid=fork();
if(pid==0)
{
//子
char rbuf[128]="";//创建一个用于接收进程B发来的消息的容器
while(1)
{
bzero(rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));//容器清零
read(fd1,rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));//读取数据
printf("收到消息:%s\n",rbuf);
if(strcmp(rbuf,"quit")==0)//退出条件
{
break;
}
}
close(fd1);//关闭管道
close(fd2);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);//关闭子进程
}else if(pid>0)
{
//父
char wbuf[128]="";//创建一个用于向进程B写入数据的容器
while(1)
{
bzero(wbuf,sizeof(wbuf));//容器清零
read(0,wbuf,sizeof(wbuf));//终端写入
wbuf[strlen(wbuf)-1]=0;//将'\n'替换成'\0'
write(fd2,wbuf,sizeof(wbuf));//写入数据
if(strcmp(wbuf,"quit")==0)
{
break;
}
}
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
wait(NULL);//回收子进程
}else
{
perror("fork error");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}?进程B
#include <myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int fd1=-1;
int fd2=-1;
int pid=-1;
if((fd1=open("./mkfifo1",O_RDWR))==-1)
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
if((fd2=open("./mkfifo2",O_RDWR))==-1)
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
pid=fork();
if(pid==0)
{
//子
char wbuf[128]="";
while(1)
{
bzero(wbuf,sizeof(wbuf));
read(0,wbuf,sizeof(wbuf));
wbuf[strlen(wbuf)-1]=0;
write(fd1,wbuf,sizeof(wbuf));
if(strcmp(wbuf,"quit")==0)
{
break;
}
}
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}else if(pid>0)
{
//父
char rbuf[128]="";
while(1)
{
bzero(rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));
read(fd2,rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));
printf("收到消息:%s\n",rbuf);
if(strcmp(rbuf,"quit")==0)
{
break;
}
}
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
wait(NULL);
}else
{
perror("fork error");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}两个有名管道
#include <myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//创建两个有名管道
if(mkfifo("./mkfifo1",0664)==-1)
{
perror("mkfifo1 error");
return -1;
}
if(mkfifo("./mkfifo2",0664)==-1)
{
perror("mkfifo2 error");
return -1;
}
getchar();//自此处阻塞
system("rm mkfifo1 mkfifo2");//结束时删除两个有名管道
return 0;
}?效果图

 ?
?
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_80793165/article/details/135466900
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- AI剪辑助手:轻松剪辑专注创意,视频批量AI智剪的方法
- 福建泉州一化工厂起火 富维AI神器,FIS烟火识别系统来拯救
- 安防监控系统镜头选型分析,低噪声,低振动,多通道
- 解决RuntimeError: Error compiling objects for extension
- M-G366PDG0规格书
- Mysql笔记
- 论文笔记 | ICLR 2023 ReAct:通过整合推理和行动来增强语言模型
- 基于神经网络的电力系统的负荷预测
- 【PS】制作 素描 + 遗照
- 【EI会议征稿通知】第五届计算机信息和大数据应用国际学术会议(CIBDA 2024)