JAVA学习笔记——第五章 控制结构
发布时间:2024年01月22日
🔥博客主页:?A_SHOWY
🎥系列专栏:力扣刷题总结录?数据结构??云计算??数字图像处理??力扣每日一题_?
流程控制总体介绍:决定程序是如何执行的,主要包括顺序控制、分支控制和循环控制
顺序控制
顺序控制:程序从上到下逐行执行,没有任何判断跳转
一个变量必须要先定义再使用
分支控制if-else
1)单分支
例题:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//1.接收输入的年龄,定义一个scanner对象
//2.把年龄保存到int中
//3.使用if判断,输出对应的信息
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你的年龄");
int age = scanner.nextInt();
if(age > 18) {
System.out.println("你已经达到了18岁,需要负责任");
}
}
}
流程图?

2)双分支
if? else
if(age > 18) {
System.out.println("你已经达到了18岁,需要负责任");
}
else{
System.out.println("你的年龄不大放过你");
}流程图

3)多分支
if? ,else if,...,else
流程图
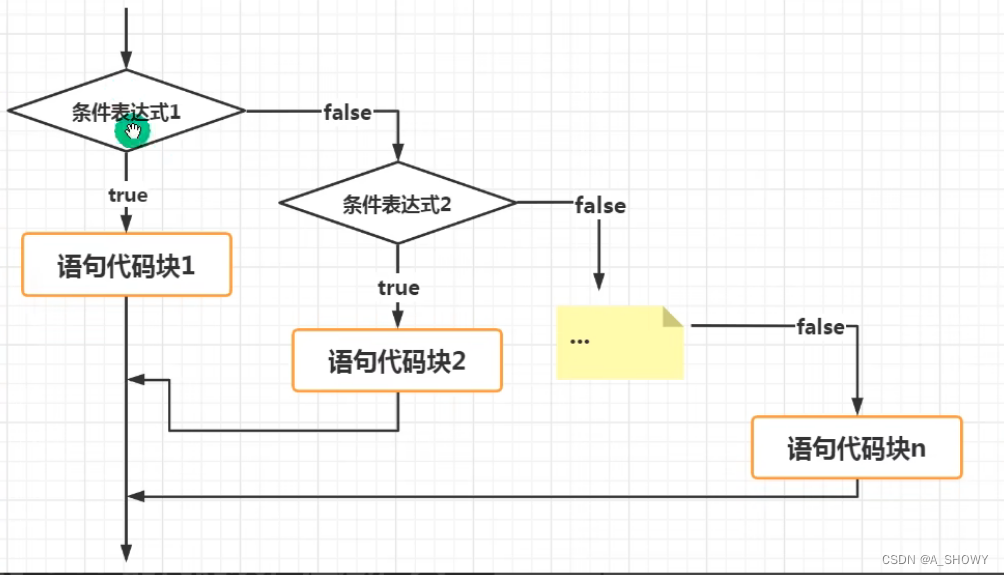
嵌套分支
内层分支+外层分支,分支尽量不要超过3层?
例子2:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner myscanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入歌手的成绩");
double score = myscanner.nextDouble();
if(score > 8.0){
System.out.println("请输入您的性别");
char gender = myscanner.next().charAt(0);//取字符串的第一个字符
if(gender == '男'){
System.out.println("进入男子组");
}
else if(gender == '女'){
System.out.println("进入女子组");
}
else{
System.out.println("输入错误");
}
}
else{
System.out.println("对不起您被淘汰了");
}
}
}分支控制?switch
switch(表达式){
case 常量1://当
语句块1;
break;
。。。
}
switch语句解读:
- switch关键字,表示switch分支
- 表达式对应一个值,运行后肯定是一个值
- 当表达式的值等于常量1,就执行语句块1(不止一句有可能)
- break,表示退出switch
- 如果和常量1没有匹配就继续匹配case常量2
- 如果一个也没匹配,就default
流程图
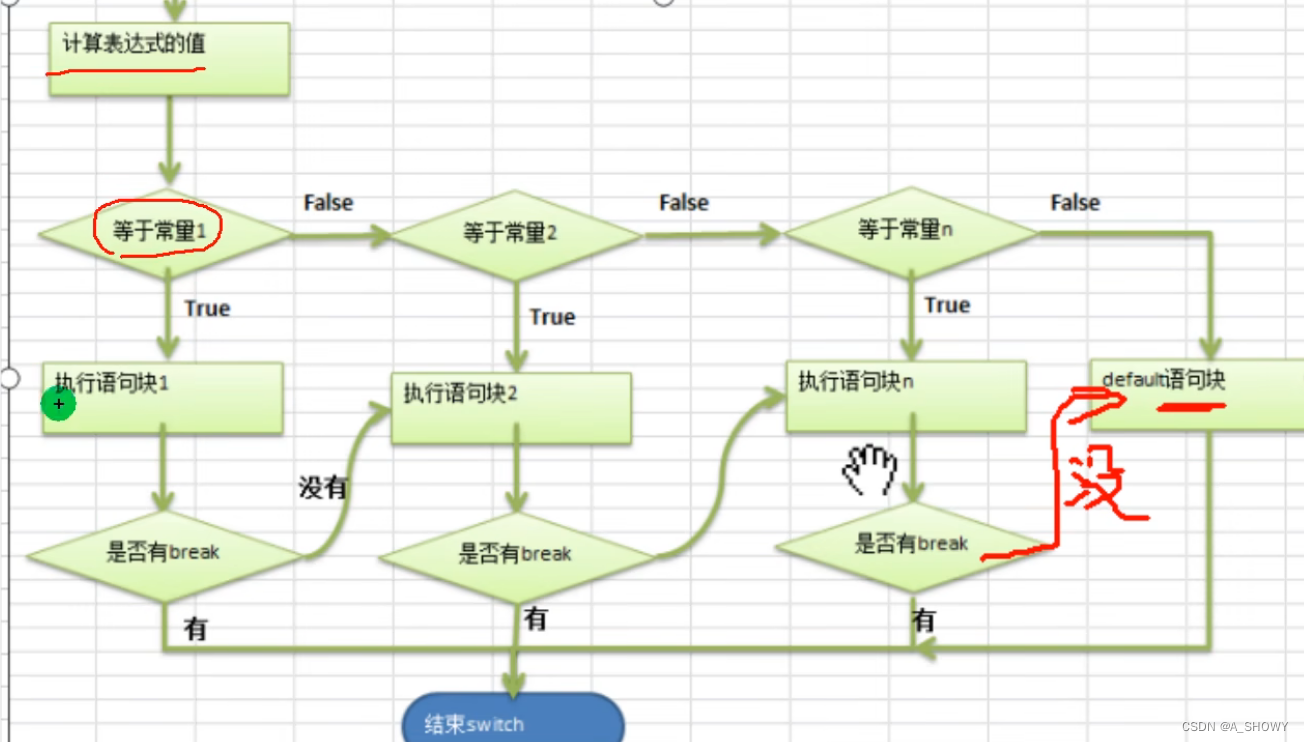
例子: ?
?
import java.util.Scanner;
public class demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner myscanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个字符a-g");
char c1 = myscanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (c1){
case 'a' :
System.out.println("今天是星期一");
break;
case 'b' :
System.out.println("今天是星期二");
break;
case 'c' :
System.out.println("今天是星期三");
break;
default :
System.out.println("你输入的字符不正确");
}
System.out.println("退出了switch继续执行");
}
}
switch细节:
- 表达式的数据类型,应和case后的常量类型一致
- switch中表达式的返回值只能是byte,short,char,enum【枚举】,string
- case子句中的值必须是常量不能是变量
- 当没有case匹配时,默认执行default
- 如果没有break,程序会顺序执行到switch结尾,直到遇到break
练习: ?
?
import java.util.Scanner;
public class demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner myscanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入a-e");
char c1 = myscanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (c1){
case 'a' :
System.out.println("A");
break;
case 'b' :
System.out.println("B");
break;
case 'c' :
System.out.println("C");
break;
case 'd' :
System.out.println("D");
break;
case 'e' :
System.out.println("E");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入错误");
}
}
}

用到一个小算法,让分数除以60,case0的时候就是不及格,case1的时候就是及格
import java.util.Scanner;
public class demo5 {
public static void main(String [] args){
Scanner myscanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入成绩");
double score = myscanner.nextDouble();
if(score >= 60 && score <= 100){
switch ((int)score/60){
case 0 :
System.out.println("不合格");
break;
case 1 :
System.out.println("合格");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入的有错误");
}
}
else {
System.out.println("请输入0-100的分数");
}
}
}
?循环控制for
流程图(和c++没啥区别)

for循环注意事项和细节:
- 循环条件返回的是bool值的表达式
- for(;循环判断条件;)中的初始化和变量迭代可以写到其他地方,但是分号不能省
- for(;;)表示一个无限循环
- 循环初始值和变量迭代都可以有多条,中间用,隔开?
循环控制 while
while(循环条件){}

练习:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class demo6 {
public static void main(String [] args) {
int i = 1;
while(i <= 100){
if(i % 3 == 0){
System.out.println(i);}
i++;
}
int j = 40;
while(j <= 100){
if(j % 2 ==0){
System.out.println(j);
j +=2;
}
}
}
}
循环控制do- while
do{
? ? ? ?循环体(语句);
? ? ? ?循环变量迭代;
}while(循环条件);
先执行再判断,所以至少执行一次。循环前先执行一次(还钱先揍一顿)

例
import java.util.Scanner;
public class dowhile {
public static void main(String[] args){
int i = 1;
int sum = 0;
do{
if(i % 5 == 0 && i % 3 != 0) {
System.out.println(i);
sum++;
}
i++;
}while(i <= 200);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
?多重循环控制(难点)
例题:

先打印一个?
public class demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){//层数
//输出前面的空格
for(int j = 5 - i; j >= 1; j--){
System.out.print(' ');
}
for(int j = 1; j <= 2 * i - 1;j++ ){
System.out.print('*');
}
System.out.println(' ');
}
}
}
然后改进成
import java.util.Scanner;
public class demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){//层数
//输出前面的空格
for(int j = 5 - i; j >= 1; j--){
System.out.print(' ');
}
for(int j = 1; j <= 2 * i - 1;j++ ){
if(j == 1 || j == 2 * i -1 || i == 5){
System.out.print('*');}
else{
System.out.print(' ');
}
}
System.out.println(' ');
}
}
}
?做活:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args){
int totalLevel = 8;
for(int i = 1; i <= totalLevel; i++){//层数
//输出前面的空格
for(int j = totalLevel - i; j >= 1; j--){
System.out.print(' ');
}
for(int j = 1; j <= 2 * i - 1;j++ ){
if(j == 1 || j == 2 * i -1 || i == totalLevel){
System.out.print('*');}
else{
System.out.print(' ');
}
}
System.out.println(' ');
}
}
}
break
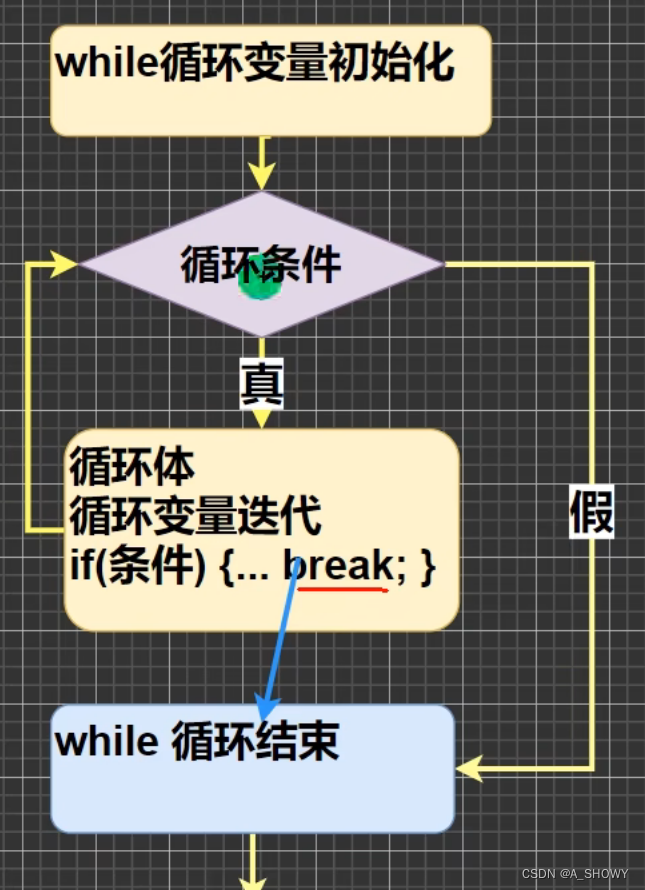
例:?

import java.util.Scanner;
public class demo10 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner myscanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int chance = 3;
for(int i = chance; i >= 0; i--){
System.out.println("请输入用户名和密码");
String name = myscanner.next();
String password = myscanner.next();
if("cpy".equals(name) && "666".equals(password)) {
System.out.println("密码正确");
}
else{
chance --;
System.out.println("你还有" + chance + "次输入机会");
}
}
}
}
?这里要注意字符串相等的判断要用equals方法
例2: ?
?
Math.random()//这个函数是生成【0,1)的小数
100 * Math.random()//【0,100)
int(100 * Math.random())//【0,99】
int(100 * Math.random()) + 1//【1,100】public class demo11 {
public static void main(String[] args){
for(;;){
int a = (int)(Math.random() * 100) + 1;
System.out.println(a);
if(a == 97) break;
}
}
}
continue
跳过这次循环,进入下一次循环的判断
return
跳出所在的方法,如果用在main,就是跳出整个程序。
总的练习:
例1:
public class lianxi1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
double a = 100000;
int cishu = 0;
while(a > 1000){
if(a > 50000) {
a = a - a * 0.05;
cishu ++;
}
else {
a -= 1000;
cishu ++;
}
}
System.out.println(cishu);
System.out.println(a);
}
}
?例2:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class lianxi2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner myscanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double a = myscanner.nextDouble();
double b = a / 100;//百位
double c = a % 100 / 10;//十位
double d = a % 10;//个位
if(b * b * b + c * c * c + d * d *d == a){
System.out.println("这个数是水仙花数");
}
else{
System.out.println("这个数不是");
}
}
}
例3
import java.util.Scanner;
public class lianxi3 {
public static void main(String[] args){
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if (i % 5 != 0) {
System.out.print(i);
count++;
}
if(count == 5){
System.out.println('\n');
count = 0;
}
}
}
}
?例4

import java.util.Scanner;
public class lianxi4 {
public static void main(String[] args){
for(char c1 = 'a'; c1 <= 'z';c1++){
System.out.print(c1);
}
for(char c2 = 'Z';c2 >= 'A';c2--){
System.out.print(c2);
}
}
}
?锻炼到的是字符可以当成一个整数使用
例5:
?要考虑到1 / i如果不改成1.0,最后结果总是1.0,考虑类型转换
import java.util.Scanner;
public class lianxi5 {
public static void main(String[] args){
double a= 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++){
if(i % 2 != 0){
a += 1.0 / i;
}
else {
a -= 1.0 / i;
}
}
System.out.println(a);
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/showy0/article/details/135717425
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!