【SpringBoot篇】基于Redis实现生成全局唯一ID的方法

🍔生成全局唯一ID
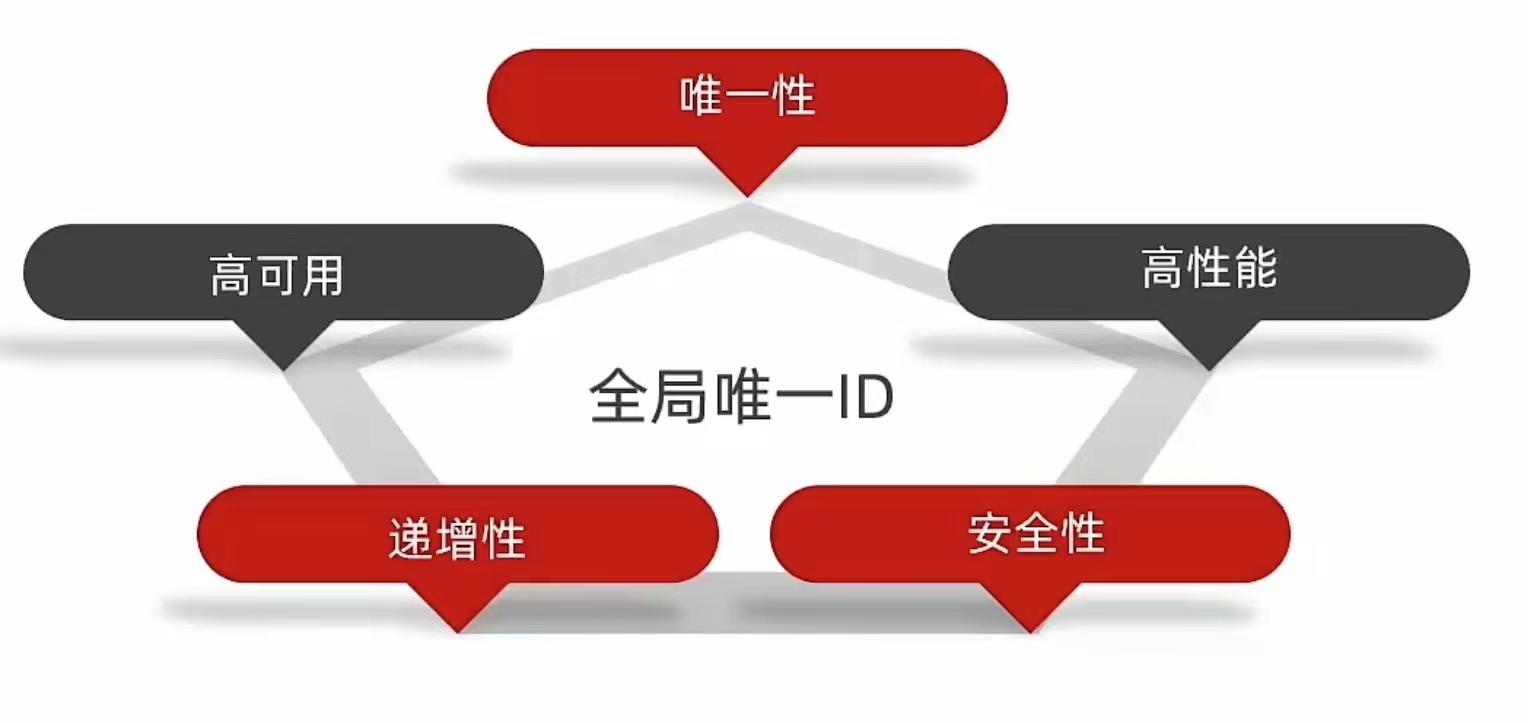
是一种在分布式系统下用来生成全局唯一id的工具
在项目中生成全局唯一ID有很多好处,其中包括:
- 数据库主键:在数据库中,唯一ID可以作为主键,确保每条记录的唯一性,便于快速检索和更新数据。
- 分布式系统:在分布式系统中,生成全局唯一ID可以避免不同节点生成相同的ID,确保整个系统的数据一致性。
- 日志追踪:在日志系统中,给每条日志分配唯一ID可以方便进行日志的追踪和分析。
- 安全性:某些场景下,需要对数据进行加密或者数据权限控制,唯一ID可以作为安全机制的一部分。
- 缓存键值:在缓存系统中,使用唯一ID作为键值可以避免不同数据之间的冲突。
- 数据分片:在分布式存储系统中,唯一ID可以作为数据分片的标识,便于数据的存储和查询。
总之,生成全局唯一ID有助于提高系统的可用性、数据的完整性和安全性,同时也方便数据的管理和分析。因此,在许多项目中都会需要生成全局唯一ID来满足系统的需求。
🌹为什么要生成全局唯一id
生成全局唯一ID的主要目的是确保系统中的实体(如对象、记录、消息等)具有唯一性标识。以下是一些常见的原因:
- 数据唯一性:全局唯一ID可以确保在系统中每个实体都有一个独一无二的标识符,避免数据冲突和重复。
- 数据库索引:全局唯一ID通常用作数据库表的主键或索引,以提高数据查询和检索的效率。
- 分布式系统:在分布式系统中,各个节点可能同时生成ID,为了避免ID的冲突,需要使用全局唯一ID算法确保整个系统中的ID唯一性。
- 数据跟踪与关联:通过给实体分配唯一ID,可以轻松追踪和关联数据,例如日志记录、事务管理、审计等。
- 安全性和权限控制:全局唯一ID可以用于确保数据的安全性和权限控制,限制对特定实体的访问和操作。
- 缓存与缓存失效:在缓存系统中,使用全局唯一ID作为缓存键,可以确保不同实体之间的键不会冲突,并且在缓存失效时能够正确地重新加载数据。
总结来说,生成全局唯一ID有助于确保数据的唯一性、提高系统的可用性和性能,并支持数据跟踪、安全性和权限控制等功能。这在许多系统和应用中都是一个重要的需求。
🌺生成全局id的方法
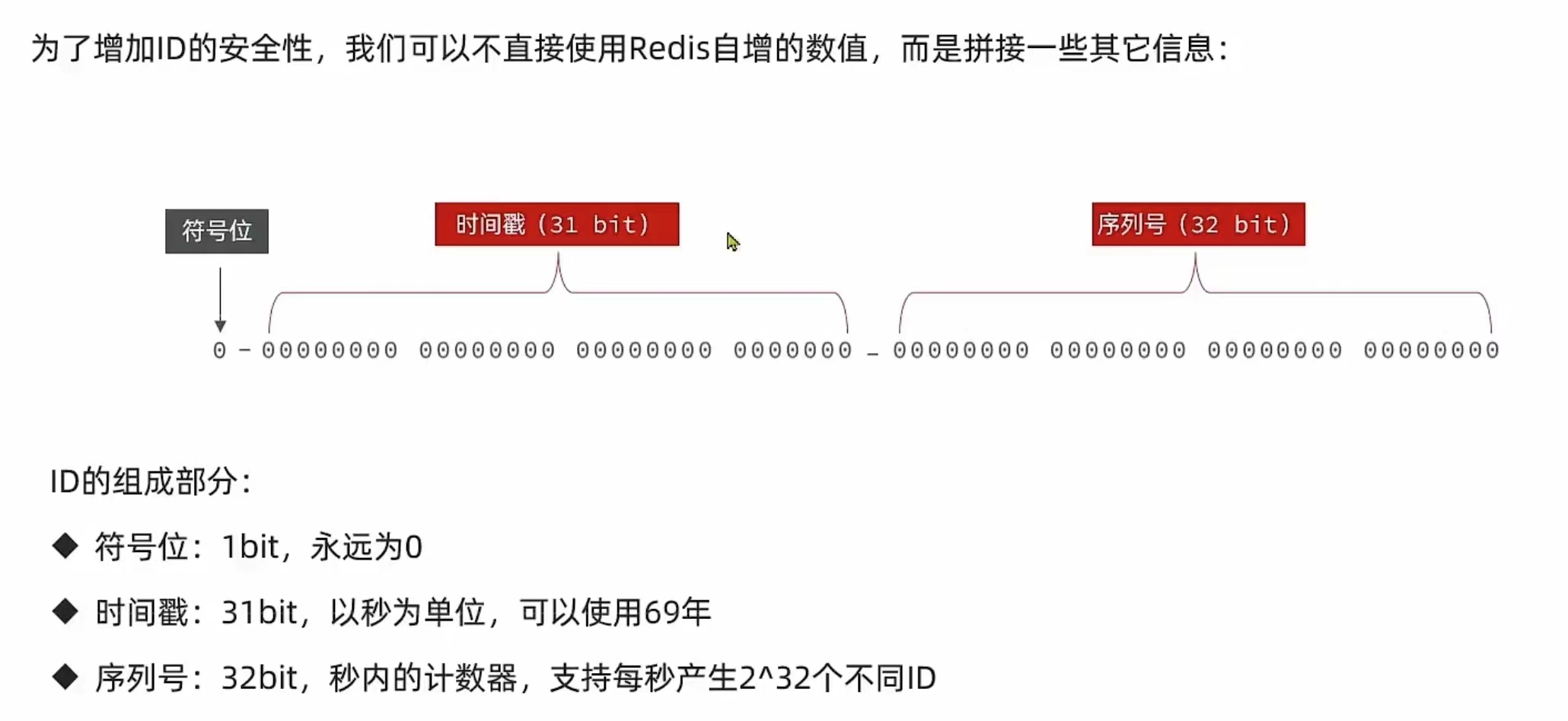
?代码实现
ID生成器的算法如下
我们要先生成时间戳,在生成序列号,然后进行拼接
package com.hmdp.utils;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneOffset;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
@Component
public class RedisIdWorker {
/**
* 开始时间戳
*/
private static final long BEGIN_TIMESTAMP = 1640995200L;
/**
* 序列号的位数
*/
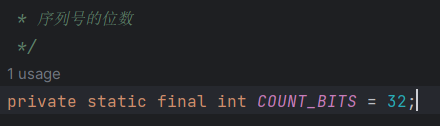
private static final int COUNT_BITS = 32;
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public RedisIdWorker(StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate) {
this.stringRedisTemplate = stringRedisTemplate;
}
public long nextId(String keyPrefix) {
// 1.生成时间戳
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
long nowSecond = now.toEpochSecond(ZoneOffset.UTC);
long timestamp = nowSecond - BEGIN_TIMESTAMP;
// 2.生成序列号
// 2.1.获取当前日期,精确到天
String date = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy:MM:dd"));
// 2.2.自增长
long count = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().increment("icr:" + keyPrefix + ":" + date);
// 3.拼接并返回
return timestamp << COUNT_BITS | count;
}
}
这段代码的 timestamp << COUNT_BITS | count;是怎么算出序列号的
在这段代码中,timestamp << COUNT_BITS | count 是通过位运算来生成最终的ID值。
首先,timestamp 是时间戳,代表了从开始时间戳到当前时间的秒数差。COUNT_BITS 是序列号的位数,这里是32位。
位运算符 << 是左移操作符,将 timestamp 的二进制表示向左移动 COUNT_BITS 位,就是将时间戳占据高位。这样做是为了给序列号腾出足够的空间。
然后,使用位运算符 | 进行按位或操作,将左移后的时间戳与序列号 count 进行按位或操作,合并它们的二进制表示。
最终得到的结果就是一个64位的ID,其中高位是时间戳部分,低位是序列号部分。
编写代码进行测试
package com.hmdp;
import com.hmdp.entity.Shop;
import com.hmdp.service.impl.ShopServiceImpl;
import com.hmdp.utils.CacheClient;
import com.hmdp.utils.RedisIdWorker;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.geo.Point;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisGeoCommands;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import static com.hmdp.utils.RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_KEY;
import static com.hmdp.utils.RedisConstants.SHOP_GEO_KEY;
@SpringBootTest
class HmDianPingApplicationTests {
@Resource
private CacheClient cacheClient;
@Resource
private ShopServiceImpl shopService;
@Resource
private RedisIdWorker redisIdWorker;
private ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(500);
@Test
void testIdWorker() throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(300);
Runnable task = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
long id = redisIdWorker.nextId("order");
System.out.println("id = " + id);
}
latch.countDown();
};
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 300; i++) {
es.submit(task);
}
latch.await(); //等待上面的结束
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("time = " + (end - begin));
}
@Test
void testSaveShop() throws InterruptedException {
Shop shop = shopService.getById(1L);
cacheClient.setWithLogicalExpire(CACHE_SHOP_KEY + 1L, shop, 10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
在技术的道路上,我们不断探索、不断前行,不断面对挑战、不断突破自我。科技的发展改变着世界,而我们作为技术人员,也在这个过程中书写着自己的篇章。让我们携手并进,共同努力,开创美好的未来!愿我们在科技的征途上不断奋进,创造出更加美好、更加智能的明天!

本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【漏洞复现】网神-SecGate-3600防火墙-sys_hand-任意文件上传
- ini文件操作基于ini-parser-netstandard
- 为什么杭州的独角兽公司的技术专家都是阿里巴巴出来的?
- Flask 小程序菜品搜索
- 【vue-cli详细介绍】
- 图像处理工具包Pillow的使用分享
- 商品小程序(6.商品详情)
- 与AI合作 -- 单例工厂2遗留的问题:bard的错误
- Java原生网络BIO
- nginx-proxy-manager初次登录502 bad gateway