5文件操作
发布时间:2024年01月13日
包含头文件<fstream>
操作文件三大类:
- ofstream : 写文件
- ifstream :读文件
- fstream : 读写文件
5.1文本文件
-文件以ascii的形式存储在计算机中
5.1.1写文件
步骤:
- 包含头文件? ? #include "fstream"
- 创建流对象? ? ofstream ofs;
- 打开文件? ? ? ?ofs.open(“文件格式”,打开方式);
- 写数据? ? ? ? ? ?ofs << "写入数据";
- 关闭文件? ? ? ?ofs.close();
| 打开方式 | 解释 |
| ios::binary | 二进制方式 |
| ios::in | 为读文件而打开文件 |
| ios::out | 为写文件而打开文件 |
| ios::ate | 初始位置:文件尾 |
| ios::app | 追加方式写文件 |
| ios::trunc | 如果文件存在先删除再创建 |
注意:文件打开方式可配合使用,利用|操作符
例如:二进制方式尾部写入文件 ios::binary | ios::ate | ios::out
代码示例:?
写文件简单代码示例:
#include "iostream"
#include "fstream"
using namespace std;
void test()
{
std::ofstream ofs;
ofs.open("test.txt",ios::out);
ofs << "服了" << endl;
ofs << "但不后悔" << endl;
ofs.close();
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}读文件简单演示(四种方式):
- ?按行读取
- 按行读取数组接收
- 按行读取string接收
- 单个字符读取
代码示例:
#include "iostream"
#include "fstream"
#include "string"
using namespace std;
void read_file_test()
{
std::ifstream ifs;
ifs.open("test.txt", ios::in);
if(ifs.is_open())
{
cout << "文件打开成功" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "文件打开失败" << endl;
return;
}
//方式一 按行读取
char buff1[1024] = { 0 };
while (ifs >> buff1)
{
cout << buff1 << endl;
}
//方式二
char buff2[1024] = { 0 };
while (ifs.getline(buff2, sizeof(buff2)))
{
cout << buff2 << endl;
}
//方式三 string
string buff_str;
while (getline(ifs, buff_str))
{
cout << buff_str << endl;
}
//方式四 读取单个字符效率低
char c;
while ((c = ifs.get()) != EOF)
{
cout << c;
}
ifs.close();
}
int main()
{
read_file_test();
return 0;
}5.2二进制文件
-文件以二进制的形式存储在计算机中
5.2.1写文件
主要利用流对象调用对象函数write
函数原型:ostream& write (const char* buffer,int len);
buffer 指向内存中一段存储空间,len是写入的字节数
代码示例:
#include "iostream"
#include "fstream"
using namespace std;
using namespace std;
//二进制的形式不只可以操作基本类型也可以操作自定义类型
class dog
{
public:
char m_name;
int m_age;
public:
dog()
{
m_name = 'A';
m_age = 19;
}
};
void write_file_binary()
{
std::ofstream ofs;
ofs.open("write_file_binary.txt", ios::out | ios::binary);
dog d;
string s = "无语";
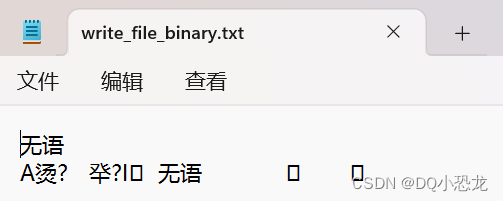
ofs << "无语" << endl;
ofs.write((const char*)&d, sizeof(dog));
ofs.write((const char*)&s, sizeof(s));
ofs.close();
}
int main()
{
write_file_binary();
system("pause");
return 0;
}?运行结果:
5.2.2读文件
主要利用流对象调用对象函数read
函数原型:istream& read(char *buffer,int len);
buffer指向内存中一段存储空间,len是读的字节数。
代码示例:
#include "iostream"
#include "fstream"
using namespace std;
using namespace std;
//二进制的形式不只可以操作基本类型也可以操作自定义类型
class dog
{
public:
char m_name;
int m_age;
public:
dog()
{
m_name = 'A';
m_age = 19;
}
};
void read_file_binary()
{
std::ifstream ifs;
ifs.open("write_file_binary.txt", ios::in | ios::binary);
if (ifs.is_open())
{
}
else
{
cout << "打开失败!" << endl;
}
dog d;
ifs.read((char*)&d, sizeof(dog));
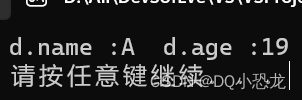
cout << "d.name :" << d.m_name << " " << "d.age :" << d.m_age << endl;
ifs.close();
}
int main()
{
read_file_binary();
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果:
?
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_55414382/article/details/135570273
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- springboot/java/php/node/python电子产品网上销售系统【计算机毕设】
- k8s卸载
- C学习_程序执行步骤-1.16
- 【Hayo AI】文字生图,图生图,图片换脸,视频换脸 —— Hayo AI 无所不能。
- JS实现:HTML页面一键分享到微博、QQ空间、QQ好友
- 第十二届“中关村青联杯”全国研究生数学建模竞赛-C题:移动通信中的无线信道“指纹”特征建模
- Springboot解决跨域问题
- vue子组件实时获取父组件的数据
- 文章解读与仿真程序复现思路——电网技术EI\CSCD\北大核心《计及改进阶梯型碳交易和热电联产机组灵活输出的园区综合能源系统低碳调度》
- AI大模型中的Bert