生产消费者模型
发布时间:2024年01月18日
生产消费者模型概念
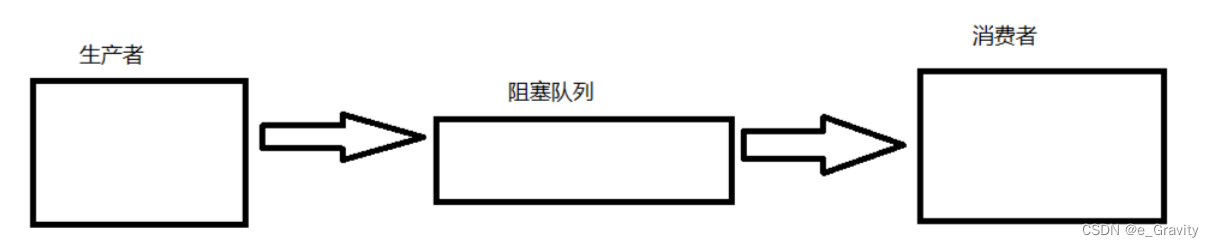
生产者消费者模式就是通过一个容器来解决生产者和消费者的强耦合问题。生产者和消费者彼此之间不直接通讯,而 通过阻塞队列来进行通讯,所以生产者生产完数据之后不用等待消费者处理,直接扔给阻塞队列,消费者不找生产者 要数据,而是直接从阻塞队列里取,阻塞队列就相当于一个缓冲区,平衡了生产者和消费者的处理能力。这个阻塞队 列就是用来给生产者和消费者解耦的。
321原则
- 三种关系:生产者之间互斥,消费者之间互斥,生产者和消费者之间互斥和同步关系
- 两种角色:生产者线程和消费者线程
- 一个交易场所:一个特定结构的缓冲区
生产者消费者模型优点
解耦? 支持并发? 支持忙闲不均?
基于阻塞队列的生产消费模型
实现一个demo:
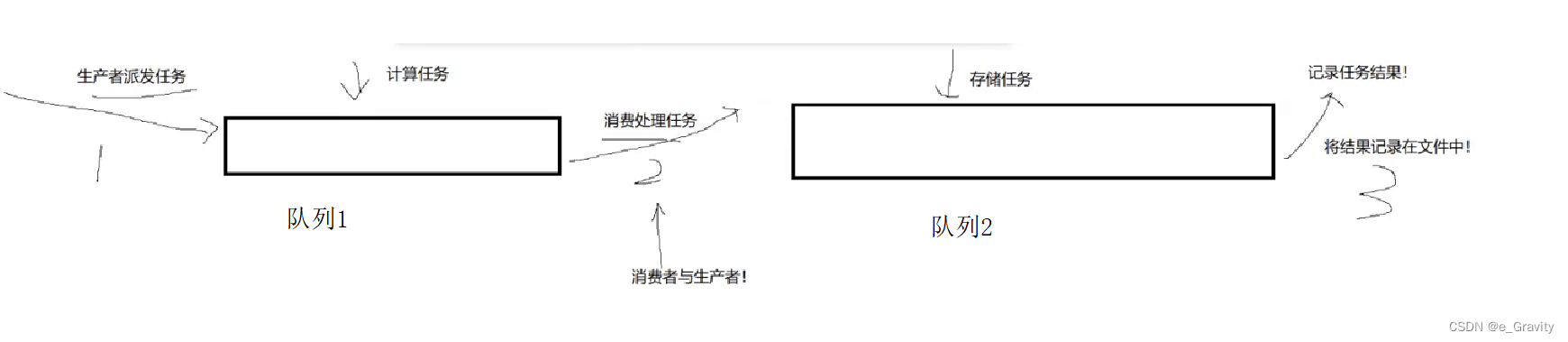
创建3个线程,线程1当作队列1的生产者,线程2既作为队列1的消费者又是队列2的生产者,线程3则是队列2的消费者。给每个线程分配任务实现生产消费模型。
? ? ? ??
BlockQueue.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <pthread.h>
const int gmaxcap = 5;
template <class T>
class BlockQueue
{
public:
BlockQueue(const int &maxcap = gmaxcap) : _maxcap(maxcap)
{
pthread_mutex_init(&_mutex, nullptr);
pthread_cond_init(&_pcond, nullptr);
pthread_cond_init(&_ccond, nullptr);
}
void push(const T &in) // 输入型参数,const &
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex);
// 充当条件判断的语法必须是while,不能用if
while (is_full())
{
// 细节:pthread_cond_wait这个函数的第二个参数,必须是我们正在使用的互斥锁!
// a. pthread_cond_wait: 该函数调用的时候,会以原子性的方式,将锁释放,并将自己挂起
// b. pthread_cond_wait: 该函数在被唤醒返回的时候,会自动的重新获取你传入的锁
pthread_cond_wait(&_pcond, &_mutex); // 因为生产条件不满足,无法生产,此时我们的生产者进行等待
}
_q.push(in);
pthread_cond_signal(&_ccond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex);
}
void pop(T *out) // 输出型参数:*, // 输入输出型:&
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex);
while (is_empty())
{
pthread_cond_wait(&_ccond, &_mutex);
}
*out = _q.front();
_q.pop();
pthread_cond_signal(&_pcond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex);
}
~BlockQueue()
{
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&_pcond);
pthread_cond_destroy(&_ccond);
}
private:
bool is_empty()
{
return _q.empty();
}
bool is_full()
{
return _q.size() == _maxcap;
}
private:
std::queue<T> _q;
int _maxcap; // 队列中元素的上限
pthread_mutex_t _mutex;
pthread_cond_t _pcond; // 生产者对应的条件变量
pthread_cond_t _ccond; // 消费者对应的条件变量
};MainCp.cc
#include "BlockQueue.hpp"
#include "Task.hpp"
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <ctime>
//C:计算
//S: 存储
template<class C, class S>
class BlockQueues
{
public:
BlockQueue<C> *c_bq;
BlockQueue<S> *s_bq;
};
void *productor(void *bqs_)
{
BlockQueue<CalTask> *bq = (static_cast<BlockQueues<CalTask, SaveTask> *>(bqs_))->c_bq;
while (true)
{
//生产活动
int x = rand() % 100 + 1;
int y = rand() % 10;
int operCode = rand() % oper.size();
CalTask t(x, y, oper[operCode], mymath);
bq->push(t);
std::cout << "productor thread, 生产计算任务: " << t.toTaskString() << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return nullptr;
}
void *consumer(void *bqs_)
{
BlockQueue<CalTask> *bq = (static_cast<BlockQueues<CalTask, SaveTask> *>(bqs_))->c_bq;
BlockQueue<SaveTask> *save_bq = (static_cast<BlockQueues<CalTask, SaveTask> *>(bqs_))->s_bq;
while (true)
{
// 消费活动
CalTask t;
bq->pop(&t);
std::string result = t();
std::cout << "cal thread,完成计算任务: " << result << " ... done"<< std::endl;
SaveTask save(result, Save);
save_bq->push(save);
std::cout << "cal thread,推送存储任务完成..." << std::endl;
//sleep(1);
}
return nullptr;
}
void *saver(void *bqs_)
{
BlockQueue<SaveTask> *save_bq = (static_cast<BlockQueues<CalTask, SaveTask> *>(bqs_))->s_bq;
while(true)
{
SaveTask t;
save_bq->pop(&t);
t();
std::cout << "save thread,保存任务完成..." << std::endl;
}
return nullptr;
}
int main()
{
srand((unsigned long)time(nullptr) ^ getpid());
BlockQueues<CalTask, SaveTask> bqs;
bqs.c_bq = new BlockQueue<CalTask>();
bqs.s_bq = new BlockQueue<SaveTask>();
pthread_t c, p, s;
pthread_create(&p, nullptr, productor, &bqs);
pthread_create(&c, nullptr, consumer, &bqs);
pthread_create(&s, nullptr, saver, &bqs);
pthread_join(p, nullptr);
pthread_join(c, nullptr);
pthread_join(s, nullptr);
delete bqs.c_bq;
delete bqs.s_bq;
return 0;
}Task.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdio>
#include <functional>
class CalTask
{
using func_t = std::function<int(int,int,char)>;
// typedef std::function<int(int,int)> func_t;
public:
CalTask()
{}
CalTask(int x, int y, char op, func_t func)
:_x(x), _y(y), _op(op), _callback(func)
{}
std::string operator()()
{
int result = _callback(_x, _y, _op);
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof buffer, "%d %c %d = %d", _x, _op, _y, result);
return buffer;
}
std::string toTaskString()
{
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof buffer, "%d %c %d = ?", _x, _op, _y);
return buffer;
}
private:
int _x;
int _y;
char _op;
func_t _callback;
};
const std::string oper = "+-*/%";
int mymath(int x, int y, char op)
{
int result = 0;
switch (op)
{
case '+':
result = x + y;
break;
case '-':
result = x - y;
break;
case '*':
result = x * y;
break;
case '/':
{
if (y == 0)
{
std::cerr << "div zero error!" << std::endl;
result = -1;
}
else
result = x / y;
}
break;
case '%':
{
if (y == 0)
{
std::cerr << "mod zero error!" << std::endl;
result = -1;
}
else
result = x % y;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
return result;
}
class SaveTask
{
typedef std::function<void(const std::string&)> func_t;
public:
SaveTask()
{}
SaveTask(const std::string &message, func_t func)
: _message(message), _func(func)
{}
void operator()()
{
_func(_message);
}
private:
std::string _message;
func_t _func;
};
void Save(const std::string &message)
{
const std::string target = "./log.txt";
FILE *fp = fopen(target.c_str(), "a+");
if(!fp)
{
std::cerr << "fopen error" << std::endl;
return;
}
fputs(message.c_str(), fp);
fputs("\n", fp);
fclose(fp);
}生产消费模型高效在哪
可以在生产之前和消费之后,让线程并行执行
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_64263546/article/details/135663343
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!