自定义注解与拦截器实现不规范sql拦截(拦截器实现篇)
最近考虑myBatis中sql语句使用规范的问题,如果漏下条件或者写一些不规范语句会对程序性能造成很大影响。最好的方法就是利用代码进行限制,通过拦截器进行sql格式的判断在自测环节就能找到问题。写了个简单情景下的demo,并通过idea插件来将myBatis的mapper方法都打上拦截器判断的注解,多少自动化一点。
需求简介
使用myBatis拦截器对Mapper的sql进行判断,对增加了自定义注解修饰的方法进行where条件的判断,存在where子句再执行,否则抛出异常。
具体实现
自定义注解
// 标志注解,用来表示mapper方法需要经过where条件存在与否的判断
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface WhereConditionCheck {
}
限定method修饰,同时指定runtime,以在运行过程中判断是否被该注解修饰。
拦截器实现类
WhereConditionInterceptor拦截器判断类
@Intercepts({
// 拦截query方法
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}),
@Signature(type = Executor.class,method = "update",args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class})
})
@Component
@Slf4j
// 利用myBatis拦截器去获取对应的语句,where条件放行,无where阻止
public class WhereConditionInterceptor implements Interceptor {
首先利用@Intercepters注解,定义拦截器拦截的方法。这些方法来自Mybatis执行时调用的Executor接口的实现类,并通过args参数的设置来唯一指定同名的重载方法。
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 获取sql信息
MappedStatement mappedStatement = (MappedStatement) invocation.getArgs()[0];
Object parameter = invocation.getArgs()[1]; // 参数
BoundSql sql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 获取原始调用方法的注解信息
String id = mappedStatement.getId();
String className = id.substring(0, id.lastIndexOf("."));
String methodName = id.substring(id.lastIndexOf(".") + 1);
Method[] methods = Class.forName(className).getMethods();
// 不考虑方法重载
for(Method method:methods){
if(method.getName().equals(methodName) && method.isAnnotationPresent(WhereConditionCheck.class)){
// 执行拦截
boolean checkResult = checkIfWhereExist(sql);
if(!checkResult){
// 根据sql类型判断抛出异常的语句
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = mappedStatement.getSqlCommandType();
if(sqlCommandType.equals(SqlCommandType.SELECT)) {
log.error("query error, sql='" + sql.getSql() + "''");
throw new RuntimeException("Query methods must contain where condition. method:" + id);
} else if(sqlCommandType.equals(SqlCommandType.DELETE)) {
log.error("delete error, sql='" + sql.getSql() + "''");
throw new RuntimeException("Delete methods must contain where condition. method:" + id);
}
}
}
}
return invocation.proceed();
}
重写intercept方法,利用invocation来获取之前定义的拦截方法的具体参数对象,利用第一个参数MappedStatement对象来获取具体的sql信息。需要注意的是,为了获取原Mapper接口中定义方法的注解信息,我们需要利用getId获取完整的接口名和类名,并利用反射获取对应的方法对象,以判断对应方法是否存在@WhereConditionCheck注解。
private boolean checkIfWhereExist(BoundSql sql){
String sqlStr = sql.getSql();
sqlStr = sqlStr.toUpperCase();
return sqlStr.contains("WHERE");
}
具体的判断就直接将字符串转成大写后进行匹配即可。
简单使用
Mapper接口
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user where code = #{code}")
@WhereConditionCheck
public User findUserByCode(String code);
@Select("select * from user")
// 全量查询,需要拦截
@WhereConditionCheck
public List<User> findUserListWhole();
简单设置两个方法,where子句和全量查询。
controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class WhereConditionCheckController {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/queryWhole")
// 全量查询
public String getWholeUser(){
try {
List<User> userList = userMapper.findUserListWhole();
return JSONObject.toJSONString(userList);
}catch(Exception ex){
// 获取异常栈最底层以显示自定义信息
Throwable cause = ex;
Throwable result = null;
while(cause != null){
result = cause;
cause = cause.getCause();
}
return result.getMessage();
}
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/queryByCode")
// where查询
public String getUser(String code){
try{
User user = userMapper.findUserByCode(code);
return JSONObject.toJSONString(user);
}catch(Exception ex){
/// 获取异常栈最底层以显示自定义信息
Throwable cause = ex;
Throwable result = null;
while(cause != null){
result = cause;
cause = cause.getCause();
}
return result.getMessage();
}
}
}
对两个方法进行使用访问。需要注意的是,为了返回拦截器中抛出方法设定的message,需要捕获到异常栈中底层的exception进行输出。
效果展示
postman进行调用:
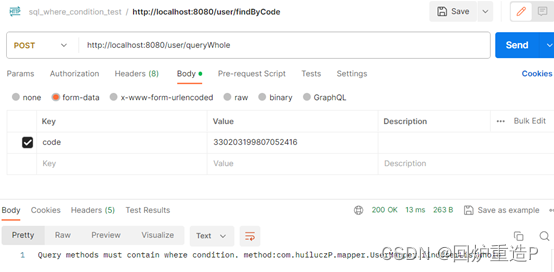
全量查询被拒绝。
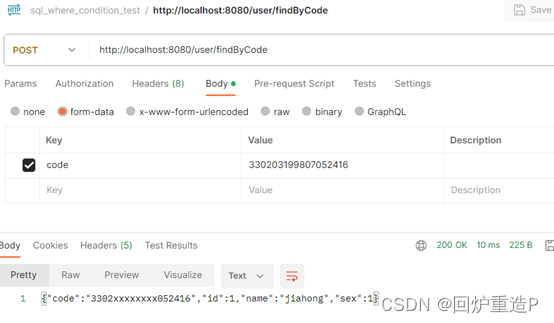
这边有做一个脱敏处理,不用管。可以看出能正常查询出来。
总结
简单展示了使用Mybatis拦截器进行where子句判断的方式,用完整的类名和方法名去定位自定义注解,比较麻烦的其实是如何显示最原始的异常信息。开头说的使用插件自动添加自定义注解的实现,放在自定义注解与拦截器实现不规范sql拦截(自定义注解填充插件篇)中来讲。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- java日期时间操作
- simulink查表模块1-D Lookup Table
- Windows 源码编译 MariaDB
- jetbrains IDEs插件发布报错:Invalid plugin descriptor ‘description‘.的问题原因和解决办法
- 再获殊荣!苏州金龙获中国汽车工程学会科学技术奖三等奖
- openmediavault(OMV) (18)云相册(2)photoprism
- 如何编写自动化测试用例,一篇带你解决
- 各数据库表名大小写问题
- 【hcie-cloud】【10】华为云Stack资源与服务扩建【扩容工程简介、扩容管理规模、计算资源扩容与减容】【上】
- Web自动化之验证码识别彻底解决方案