【C语言/数据结构】二叉树(层序遍历|判断完全二叉树|性质)
?🌈个人主页:秦jh__https://blog.csdn.net/qinjh_?spm=1010.2135.3001.5343
🔥?系列专栏:《数据结构》https://blog.csdn.net/qinjh_/category_12536791.html?spm=1001.2014.3001.5482
 ????
????
目录
?
???前言
????💬 hello! 各位铁子们大家好哇。
? ? ? ? ? ? ?今日更新了树的层序,判断完全二叉树相关内容
????🎉 欢迎大家关注🔍点赞👍收藏??留言📝
?层序遍历
层序遍历需要用到队列的思想。
这里先给出要用的队列相关函数
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
pq->ptail = pq->phead = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
//删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
QNode* del = pq->phead;
pq->phead = pq->phead->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
if (pq->phead == NULL)
{
pq->ptail = NULL;
}
pq->size--;
}
//取队头
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->phead->val;
}
//判断是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL;
}
//节点个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}队列的声明
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode* QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDataType val;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
注意:第一行typedef的是节点的指针。因为队列里存放二叉树的节点的指针时,我们才可以通过节点的指针找到下一个节点。?
?层序遍历函数实现
// 层序遍历
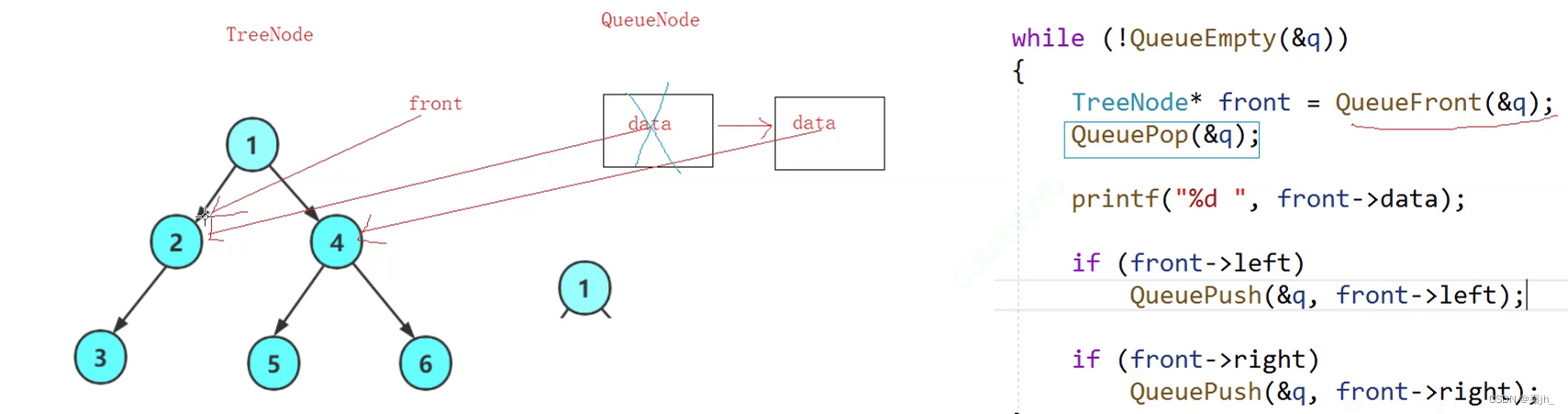
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
QueuePush(&q, root);
int levelSize = 1;
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
// 一层一层出
while (levelSize--)
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", front->data);
if (front->left)
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
if (front->right)
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
printf("\n");
levelSize = QueueSize(&q);
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
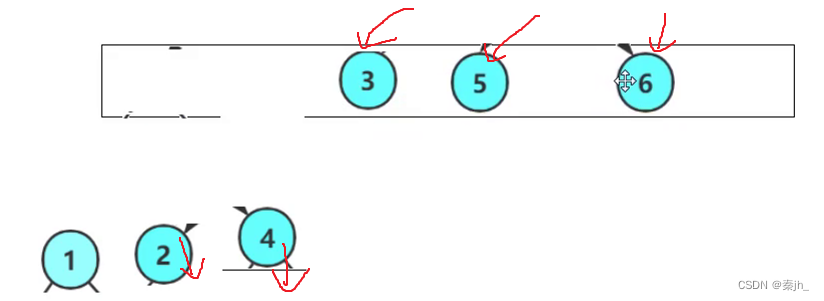
分析:将根结点push进队列,然后取队头,打印,删队头。再把该节点的两个子节点push进队列。如此循环,直到队列为空。Pop删除时,我们free掉的是队列的Node,不是树的Node,二者不会相互影响。取队头时,返回值是队列里节点的值,这个值就是树的节点的指针。levelSize控制一层一层出,打印出来的效果是一层一层的。某一层打印结束时,levelSize更新为队列里的节点个数,如此循环,就能一层一层打印。
 ??
?? ?
?
 ??
??
判断二叉树是否为完全二叉树
?函数实现
// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
QueuePush(&q, root);
int levelSize = 1;
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front == NULL)
break;
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
// 前面遇到空以后,后面还有非空就不是完全二叉树
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}分析:前面的过程与层序相似,只不过在遇到空时,就结束循环。接着来到第二个while循环,当遇到非空时,if语句执行,就会直接返回false。如果后面都是空,if语句就不执行,最后就会返回true。
二叉树性质
 ?
?
这里分析第3个,其余在前几篇博客已说明。(n0表示度为0,n2表示度为2)
?分析:第3个的意思是,度为0的节点的个数是度为2的节点个数+1。
?当只有一个节点时,n0为1个,n2为0个。增加一个节点,减少一个n0,增加一个n0,所以n0不变。再如下图所示,再增加一个节点,n2就变为1个,n0也会增加1个,但是n1就会减少。因此有关系:n0=n2+1.
 ?
?
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 九州金榜|孩子厌学是家庭原因吗?
- 芯片验证入门踩坑指南(1)
- PDF修改技巧之:如何简单方便的编辑PDF文件?
- uniapp实现文字超出宽度自动滚动(在宽度范围之内不滚动、是否自动滚动、点击滚动暂停)
- 腾讯云:AI云探索之路
- selenium+python自动化测试之使用webdriver操作浏览器的方法
- 亚马逊鲲鹏系统给我带来的真实体验感
- 如何在网络爬虫中解决CAPTCHA?使用Python进行网络爬虫
- 最近国外老客户的订单也逐渐推迟
- Python语言基础