使用Scikit Learn 进行识别手写数字

使用Scikit Learn 进行识别手写数字
作者:i阿极
作者简介:数据分析领域优质创作者、多项比赛获奖者:博主个人首页
😊😊😊如果觉得文章不错或能帮助到你学习,可以点赞👍收藏📁评论📒+关注哦!👍👍👍
📜📜📜如果有小伙伴需要数据集和学习交流,文章下方有交流学习区!一起学习进步!💪
大家好,我i阿极。喜欢本专栏的小伙伴,请多多支持
1、前言
Scikit learn 是机器学习社区中使用最广泛的机器学习库之一,其背后的原因是代码的简便性以及机器学习开发人员构建机器学习模型所需的几乎所有功能的可用性。在本文中,我们将学习如何使用 sklearn 在手写数字数据集上训练 MLP 模型。其他一些好处是:
1、它提供分类、回归和聚类算法,例如SVM算法、随机森林、梯度提升和k 均值。
2、它还设计用于与Python 的科学和数值库NumPy和SciPy一起运行。
2、导入库和数据集
首先,让我们导入模型所需的库并加载数据集数字。
# importing the hand written digit dataset
from sklearn import datasets
# digit contain the dataset
digits = datasets.load_digits()
# dir function use to display the attributes of the dataset
dir(digits)
结果:
['DESCR', 'data', 'feature_names', 'frame', 'images', 'target', 'target_names']
3、打印一组图像的功能
将图片值输出为一系列数字
print(digits.images[0])
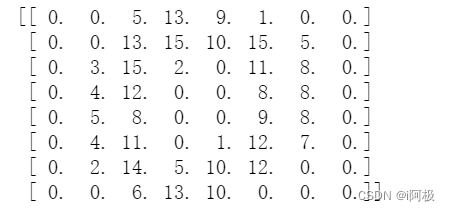
原始数字具有更高的分辨率,并且在为 scikit-learn 准备数据集时降低了分辨率,以便训练机器学习系统更轻松、更快地识别这些数字。因为在如此低的分辨率下,即使是人类也很难识别某些数字。输入照片的低质量也会限制我们在这些设置中的神经网络。
# importing the matplotlib libraries pyplot function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# defining the function plot_multi
def plot_multi(i):
nplots = 16
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 15))
for j in range(nplots):
plt.subplot(4, 4, j+1)
plt.imshow(digits.images[i+j], cmap='binary')
plt.title(digits.target[i+j])
plt.axis('off')
# printing the each digits in the dataset.
plt.show()
plot_multi(0)

4、使用数据集训练神经网络
神经网络是一组算法,尝试使用类似于人脑工作方式的技术来识别一批数据中的潜在关系。在这种情况下,神经网络是神经元系统,本质上可能是有机的或人造的。
输入层由 64 个节点组成,每个节点对应输入图片中的每个像素。它们只是将输入值发送到下一层的神经元。
这是一个密集的神经网络,这意味着每层中的每个节点都链接到前一层和后一层中的所有节点。
输入层需要一维数组,而图像数据集是二维的。结果,发生了扁平化所有图像的过程:
# converting the 2 dimensional array to one dimensional array
y = digits.target
x = digits.images.reshape((len(digits.images), -1))
# gives the shape of the data
x.shape
输出:
(1797, 64)
# printing the one-dimensional array's values
x[0]

5、用于训练和测试的数据分割
当机器学习算法用于根据未用于训练模型的数据进行预测时,将使用训练-测试分割过程来衡量其性能。
这是一种快速而简单的技术,可让您针对预测建模挑战比较机器学习算法的性能。
# Very first 1000 photographs and
# labels will be used in training.
x_train = x[:1000]
y_train = y[:1000]
# The leftover dataset will be utilised to
# test the network's performance later on.
x_test = x[1000:]
y_test = y[1000:]
多层感知器分类器的使用
# importing the MLP classifier from sklearn
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
# calling the MLP classifier with specific parameters
mlp = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(15,),
activation='logistic',
alpha=1e-4, solver='sgd',
tol=1e-4, random_state=1,
learning_rate_init=.1,
verbose=True)
现在是时候在训练数据上训练我们的 MLP 模型了。
mlp.fit(x_train, y_train)

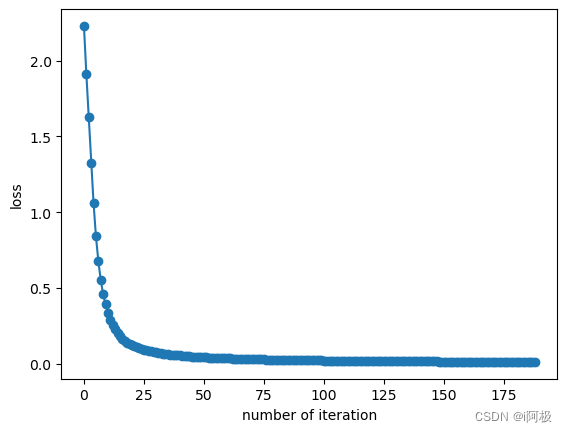
上图显示了 MLPClassifier 及其各自配置的最后 5 个 epoch 的损失。
将结果可视化
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 1)
axes.plot(mlp.loss_curve_, 'o-')
axes.set_xlabel("number of iteration")
axes.set_ylabel("loss")
plt.show()
6、模型评估
现在让我们使用识别数据集或它刚刚记住的数据集来检查模型的性能。我们将使用剩余的测试数据来完成此操作,以便我们可以检查模型是否已经学习了数字中的实际模式 。
predictions = mlp.predict(x_test)
predictions[:50]
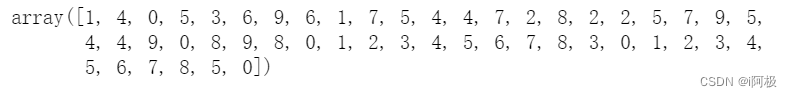
但真实标签或者我们可以说真实标签如下所示。
y_test[:50]
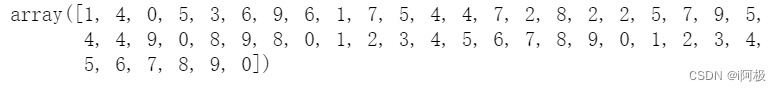
因此,通过使用预测标签和真实标签,我们可以找到模型的准确性。
# importing the accuracy_score from the sklearn
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# calculating the accuracy with y_test and predictions
accuracy_score(y_test, predictions)
输出:
0.9146800501882058
📢文章下方有交流学习区!一起学习进步!💪💪💪
📢首发CSDN博客,创作不易,如果觉得文章不错,可以点赞👍收藏📁评论📒
📢你的支持和鼓励是我创作的动力???
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!