【Java基础概述-6】Collections集合工具类、可变参数、Map集合以及底层
目录
1.Collections工具类
? ? ? ? Collections是集合工具类:Java.utils.Collections。
? ? ? ? Collections并不属于集合,是用来操作集合的工具类。
? ? ? ? --public static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<? super T> C,T..elements):
? ? ? ? 批量添加集合中的数据,T..elements是可变参数,后面会阐述。
? ? ? ? <? super T>:泛型的上限,也就是?必须是T的父类。
? ? ? ? --public static void shuffle(List<?> list):打乱集合顺序。
? ? ? ? --public static <T> void sort(List<T> list):把集合按照默认规则排序。
? ? ? ? --public static<T> void sort(List<T> list,comparator<? super T>):将集合中的元素按照指定的规则排序。
????????
public class CollectionsDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(names,"张三","李四","王五");
System.out.println(names);
Collections.shuffle(names);
System.out.println(names);
ArrayList<Student> stu = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(stu,new Student("张三",18),new Student("李四",50),new Student("王五",30));
Collections.sort(stu, (o1, o2) -> o1.getAge()-o2.getAge());
//这里是lamda表达式简化匿名内部类的方法,可以参考我之前的文章。
System.out.println(stu);
}
}2.可变参数
? ? ? ? 可变参数用在形参中有多个数据。
? ? ? ? 可变参数的格式:数据类型..参数名称。
? ? ? ? 作用:可以传递一个或者多个参数,并且可以传递一个数组。
? ? ? ? 注意事项:
? ? ? ? 1.一个形参列表中可变参数只能有一个。
? ? ? ? 2.可变参数必须放在形参列表的最后面!!
? ? ? ? 3.传递进来的其实是一个数组。
????????
public static void main(String[] args) {
sum();
sum(1);
sum(1,2,3,4,5,6);
}
public static void sum(int...nums){
//可变参数方法内部本质是是一个数组
System.out.println("元素个数"+nums.length);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
}3.Map集合分析(面试重点)
? ? ? ? Map集合是一种双列集合,每个元素包含两个值。
? ? ? ? Map集合的每一个元素的格式:key=value。
? ? ? ? Map集合也被称为"键值对"。
? ? ? ? Map集合的完整格式:{key = value1,key2 = value2}。
? ? ? ?
3.1 Map集合的体系
? ? ? ?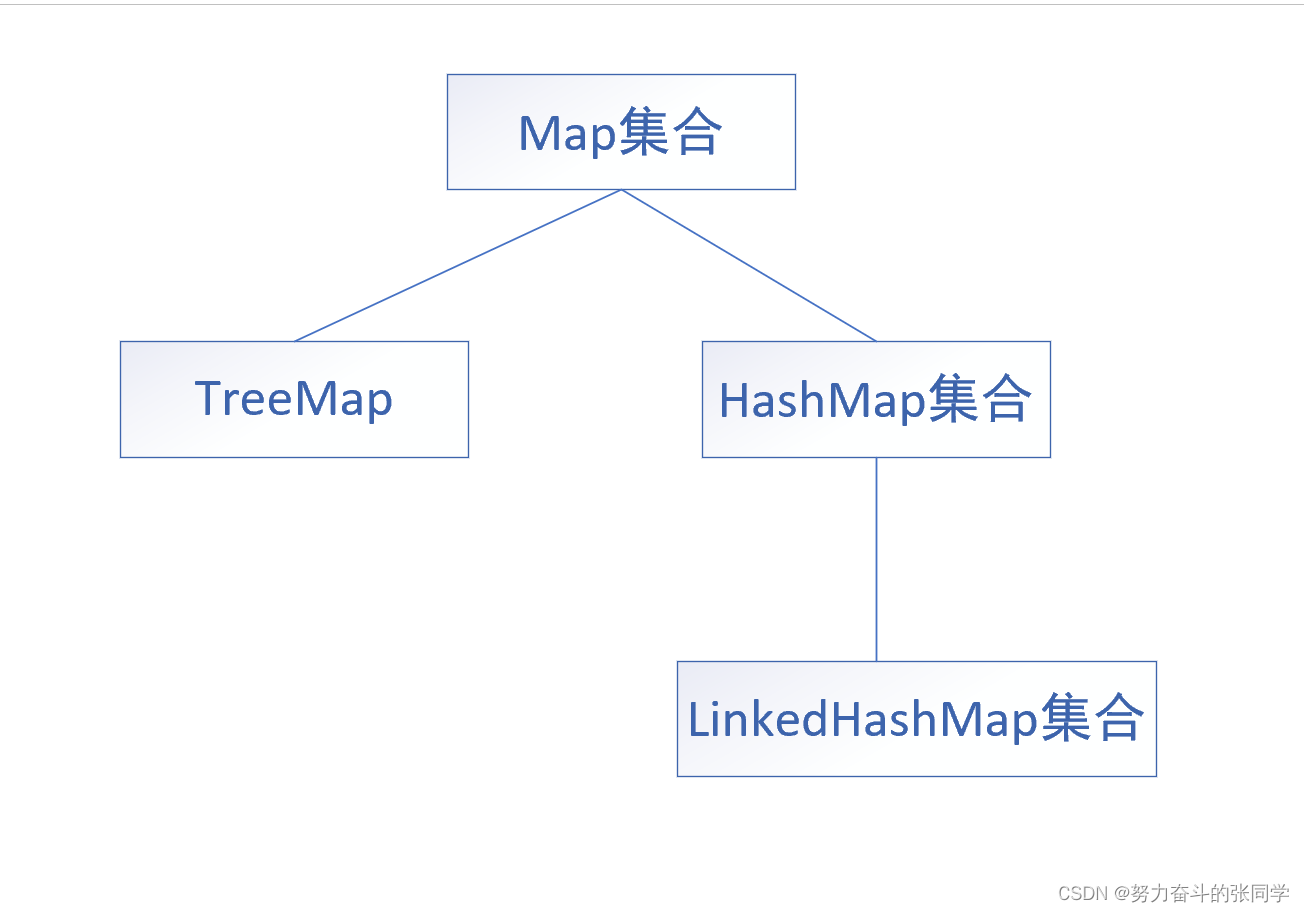
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Map集合的特点:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 1.Map集合的特点都是由键决定的。
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 2.Map集合的键是无序、不重复、无索引的。
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Map集合后面重复的键对应的元素会覆盖前面的元素。
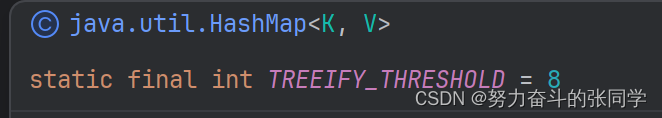
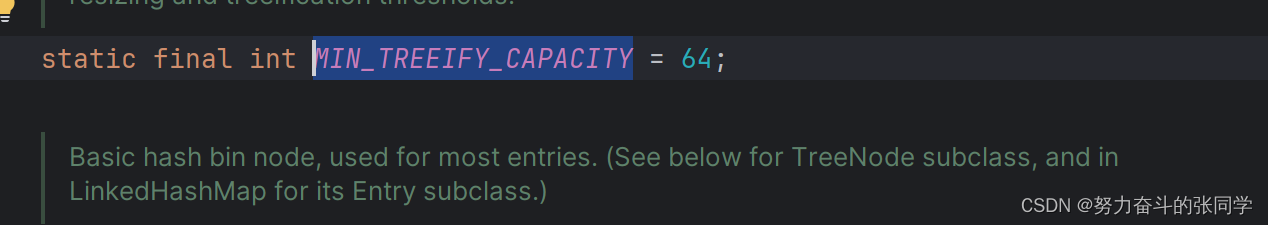
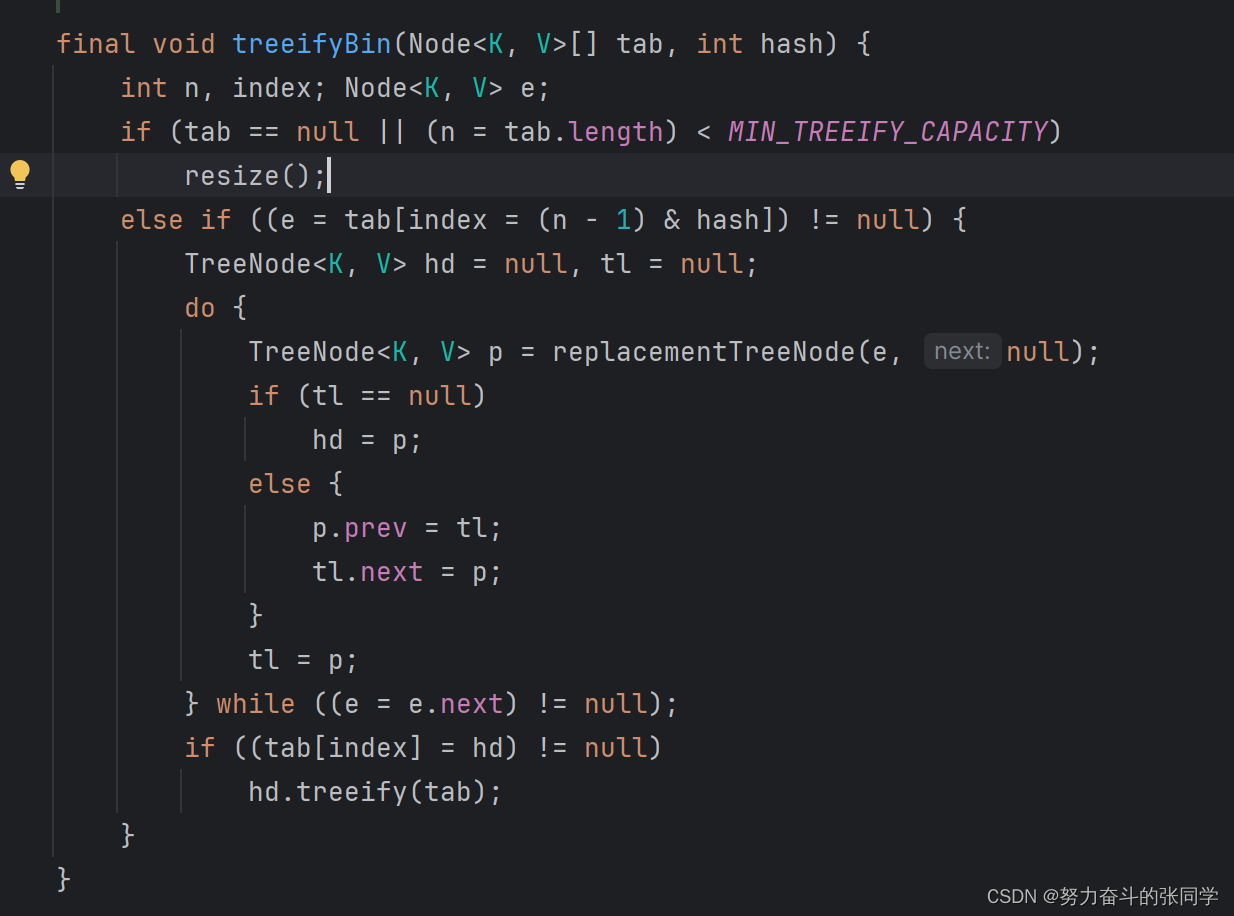
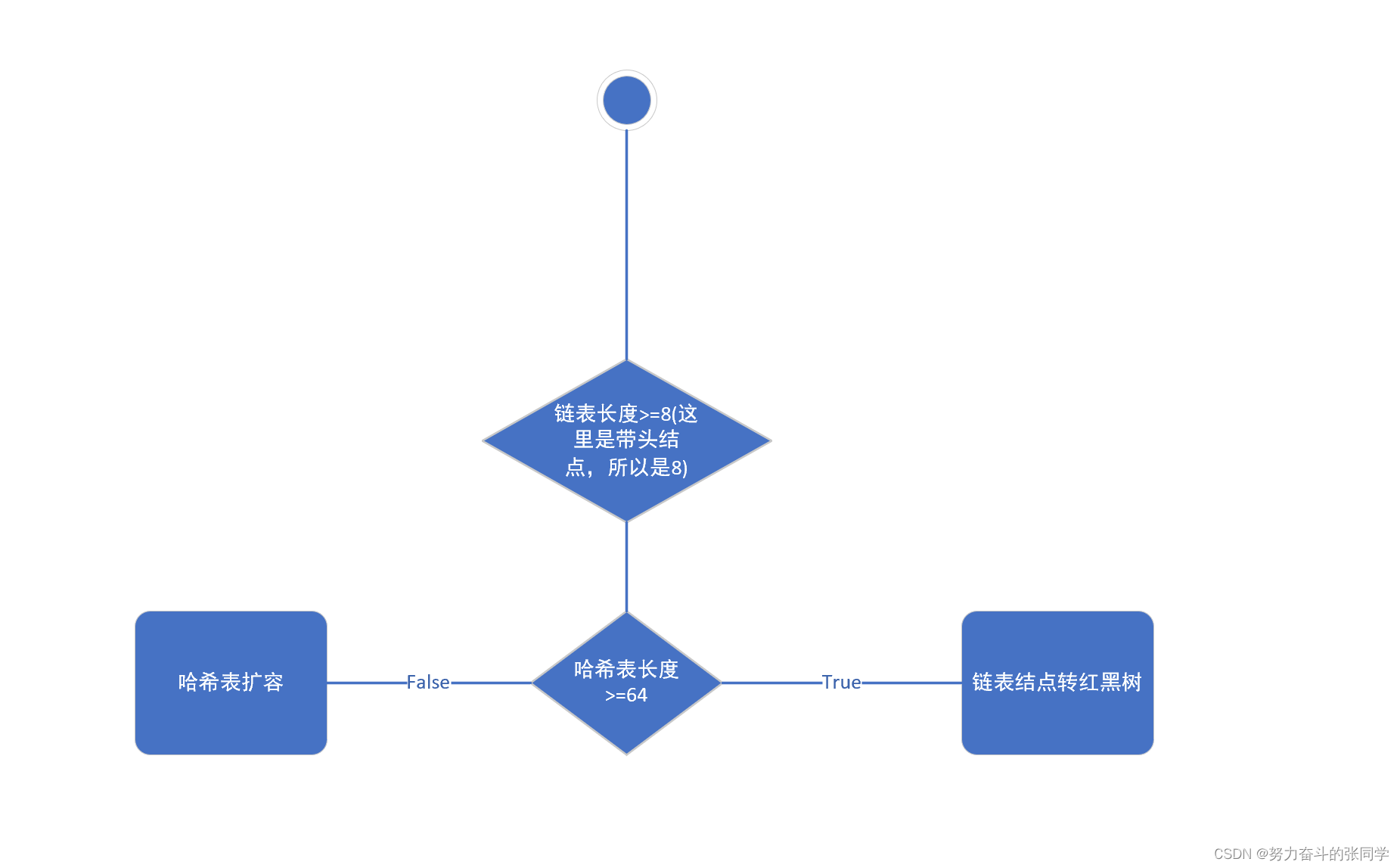
????????????????(联想):Set集合的底层是用Map集合的键做的,Set集合的元素也有这个特征,注意:HashMap底层中,这里解释下为什么JDK1.8之后有链表和红黑数:在哈希表数组长度>=64并且链表长度>=8(阈值)的适合呢,就会进行由链表节点转换成红黑树,这也是Set集合的特征)
????????????????当碰撞出现的概率增加时,hashmap 的查询速度会变慢。为了解决这个问题,我们可以将 hashmap 的容量扩大,这样就可以减少碰撞的概率,提高查询速度。
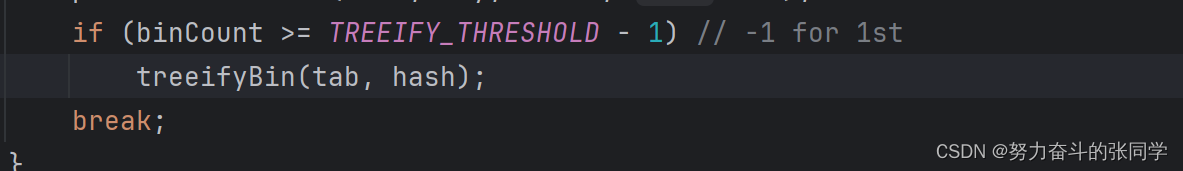
这里减掉1是为了减掉头节点。?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 3.Map集合的值是无要求的。
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 4.Map集合的键值对都可以是null。
????????
* HashMap:元素按照键是无序,不重复,无索引,值不做要求。
* LinkedHashMap:元素按照键是有序的,不重复,无索引,值不做要求。
? ? ? ? 3.2 Map集合常用API
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? --public V put(K key,V value):把指定的键与指定的值添加到Map集合中。
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? --public V remove(Object key):把指定的键值对元素在Map集合中删除,返回被删除元素。
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? --public V get(Object key):根据指定的键,在Map集合中获取对应的值。
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? --public Set<k> keySet():取Map集合中的键,存储在Set集合中。
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? --public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet():获取到Map集合中所有的键值对对象集合(Set集合)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? --public boolean containKey(Object key):判断该元素中是否有此键。
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? --clear()
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> maps = new HashMap<>();
//1.添加元素:无序、不重复,无索引
maps.put("iphoneX",10);
maps.put("娃娃",30);
maps.put("iphoneX",1000);
maps.put("手表",10);
System.out.println(maps);
//清空集合
// maps.clear();
System.out.println(maps);
//3.判断集合是否为空,为空则返回true,反之!!
System.out.println(maps.isEmpty());//true
//4.根据键获取对应值。
Integer value = maps.get("娃娃");
System.out.println(value);
//5.根据键删除元素。
maps.remove("iphoneX");
System.out.println(maps);
//6.判断是否包含某个键,包含返回true,反之
System.out.println(maps.containsKey("手表"));
System.out.println(maps.containsKey("10"));
//7.判断是否包含某个值
System.out.println(maps.containsValue(100));
System.out.println(maps.containsValue(10));
//8获取全部键的集合:public Set<K> KeySet()
Set<String> strings = maps.keySet();
System.out.println(strings);
//9.获取全部值的集合:Collection<V> values();
Collection<Integer> values = maps.values();
System.out.println(value);
//10集合的大小
System.out.println(maps.size());
//11合并其他Map集合(拓展)
Map<String,Integer> maps2 = new HashMap<>();
maps.put("KK",100);
maps.put("ggbo",100);
maps.putAll(maps2);//把maps2倒入maps1中
System.out.println(maps);? ? ? ? 3.3 Map集合的遍历
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Map集合的遍历方式:3种。
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? (1)“键值对”的方式遍历:先获取Map集合全部的键,再根据键找值。
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?(2)"键值对"的方式遍历:难度较大。
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? (3)JDK1.8开始之后的新技术:Lamda表达式。
? ? ? ? a."键找值"的方式遍历:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 1.先获取Map集合的全部键,然后找值。
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> maps = new HashMap<>();
//1.添加元素:无序、不重复,无索引
maps.put("iphoneX",10);
maps.put("娃娃",30);
maps.put("iphoneX",1000);
maps.put("手表",10);
System.out.println(maps);
//键找值方式遍历
//a.获取当前Map集合的全部键集合。
Set<String> strings = maps.keySet();
//b.通过遍历键然后通过键取对应的值。
for (String key:strings){
Integer value = maps.get(key);
System.out.println(value);
}
}? ? ? ? b.键值对方式遍历
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> maps = new HashMap<>();
//1.添加元素:无序、不重复,无索引
maps.put("iphoneX",10);
maps.put("娃娃",30);
maps.put("iphoneX",1000);
maps.put("手表",10);
System.out.println(maps);
/*
* “键值对遍历”:更加面向对象的方式,代码复杂。
* “键值对”想把键值对当做一个整体遍历,也就是直接用foreach方式遍历:
* for(被遍历的数据类型 变量:集合名称)
*
* 但是我们发现Map集合的键值对数据直接是没有元素类型的,
*
*
* */
//把Map集合根据Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()转换成Set集合。
//Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entries = maps.entrySet();
//entries =[{手表=10},{iPhoneX}....]
//此时键值对元素作为一个整体就有了类型,类型是Map.Entry<String,Integer>
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entries = maps.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : entries) {
System.out.print(entry.getKey()+"->");
System.out.println(entry.getValue());
}
}? ? ? ? c.JDK1.8开始之后的新技术lamda(forEach)
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> maps = new HashMap<>();
//1.添加元素:无序、不重复,无索引
maps.put("iphoneX",10);
maps.put("娃娃",30);
maps.put("iphoneX",1000);
maps.put("手表",10);
System.out.println(maps);
/*
*
* Lambda方式遍历
*
* */
maps.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.println(k+"->"+v);
});
}? ? ? ? 3.4Map集合判重流程
????????Map集合认为键的元素内容一样重复了,可以重写hashCode()和equal方法!!,可以看把我之前Collection集合分析的文章
? ? ? ? 3.5 LinkedHashMap介绍?
? ? ? ? LinkedHashMap是HashMap的子类。
? ? ? ? --添加的元素是有序的,不重复的。
? ? ? ? HashSet集合相当于是HashMap集合的键不带值
? ? ? ? LinkedHashSet集合相当于是LinkedHashMap集合的键不带值。
? ? ? ? 都是基于哈希表存储,增删改查都快。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 基于springboot实现的饮食分享平台
- java中LinkedList和List继承有什么区别?
- 基于JavaWeb+BS架构+SpringBoot+Vue+Hadoop短视频流量数据分析与可视化系统的设计和实现
- 酷雷曼受邀出席2023东湖高新区科技成果转化专场活动
- 2024年Google Ads新手指南——广告运作与类型、工具
- linux服务器上安装oss对象存储(命令行工具使用oss)
- IDEA版SSM入门到实战(Maven+MyBatis+Spring+SpringMVC) -Spring中组件扫描
- 【德哥说库系列】-PostgreSQL跨版本升级
- vscode配置web开发环境(WampServer)
- API 安全设计的建议