C++实现lower_bound、upper_bound函数
发布时间:2023年12月26日
目录
引言
关于这个lower_bound、upper_bound函数我是在学习算法的时候有一个find函数需要去写,然后这个老师就没用库函数,直接写了这个底层实现,然后说这个可以用lower_bound替代,我就想这不就是个简单的二分嘛,然后我就好奇这个函数的底层源码,为此写了这篇博客。
一、库函数介绍
#include <algorithm> //头文件
首先不论是lower_bound、upper_bound它们提供的数组必须是从小到大有序的,这是作为前提!
1.lower_bound
从左到右查找第一个大于等于val的元素,返回其对应的迭代器
//在 [first, last) 区域内查找不小于 val 的元素
ForwardIterator lower_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& val);
看一下示例
vector<int> nums{ 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
auto a = lower_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 3); //返回3所对应的迭代器
cout << *a << endl; //3
2.upper_bound
从左到右查找第一个大于val的元素,返回其对应的迭代器
//查找[first, last)区域中第一个大于 val 的元素。
ForwardIterator upper_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& val);
看一下示例
vector<int> nums{ 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
auto a = lower_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 3); //返回4所对应的迭代器
cout << *a << endl; //4
二、源码实现
1.lower_bound源码实现
就是一个简单的二分,我就不搞模板了,就能理解底层怎么实现的就行了
int my_lower_bound(const vector<int>& nums, const int& val)
{
int l = 0, r = nums.size() - 1;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (nums[mid] >= val) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r;
}
2.upper_bound源码实现
int my_upper_bound(const vector<int>& nums, const int& val)
{
int l = 0, r = nums.size() - 1;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (nums[mid] > val) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r;
}
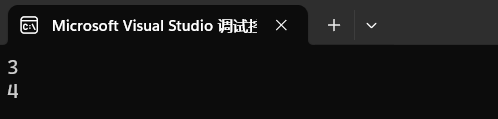
3.测试
可以看出结果是正确的
int main()
{
vector<int> nums{ 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
auto a = my_lower_bound(nums, 3);
cout << nums[a] << endl;
a = my_upper_bound(nums, 3);
cout << nums[a] << endl;
return 0;
}
三、全部代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int my_lower_bound(const vector<int>& nums, const int& val)
{
int l = 0, r = nums.size() - 1;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (nums[mid] >= val) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r;
}
int my_upper_bound(const vector<int>& nums, const int& val)
{
int l = 0, r = nums.size() - 1;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (nums[mid] > val) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> nums{ 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
auto a = my_lower_bound(nums, 3);
cout << nums[a] << endl;
a = my_upper_bound(nums, 3);
cout << nums[a] << endl;
return 0;
}
四、源码
1.lower_bound源码
template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
ForwardIterator lower_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& val)
{
ForwardIterator it;
iterator_traits<ForwardIterator>::difference_type count, step;
count = distance(first,last);
while (count>0)
{
it = first; step=count/2; advance (it,step);
if (*it<val) { //或者 if (comp(*it,val)),对应第 2 种语法格式
first=++it;
count-=step+1;
}
else count=step;
}
return first;
}
2.upper_bound源码
template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
ForwardIterator upper_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& val)
{
ForwardIterator it;
iterator_traits<ForwardIterator>::difference_type count, step;
count = std::distance(first,last);
while (count>0)
{
it = first; step=count/2; std::advance (it,step);
if (!(val<*it)) // 或者 if (!comp(val,*it)), 对应第二种语法格式
{ first=++it; count-=step+1; }
else count=step;
}
return first;
}
五、参考博客
C语言中文网:C++ lower_bound() 函数
C语言中文网:C++ upper_bound() 函数
C++参考手册:std::distance()
CSDN博客:实现lower_bound和upper_bound算法
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_60033897/article/details/135204120
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!