基于表达式引擎SPEL的数据权限控制
发布时间:2023年12月29日
本文介绍抽奖系统将菜单权限改造为数据权限时使用的技术方案 - 基于表达式引擎SPEL的数据权限控制方案
什么是表达式引擎,为什么使用表达式引擎,表达式引擎选型调研分析
- 可参考:Java 表达式引擎选型调研分析
抽奖系统改造过程
-
现状: 抽奖系统在改造之前,是基于菜单的权限控制,有菜单权限即可操作所有的抽奖活动,可能导致抽奖用户的信息泄露。
-
需求: 在创建抽奖活动时,允许添加活动负责人,只有活动负责人、创建人、超管有权限查看、操作该抽奖活动。即:放开菜单权限,所有人都允许创建抽奖活动,但是只允许访问自己有权限的活动
-
改造思路:
- 通过分析现有接口,除了分页查询接口,其他的例如修改,查看详情,删除,兑奖等相关接口,都是传了抽奖活动drawId的,我们很容易就想到可以通过切面的方式来实现。那么剩下的一个问题是,如何从各类接口参数中识别出drawId字段,这里提供2种思路:通过注解标记,通过Spel表达式引擎
- 注解标记: 在切面中获取到方法的args,遍历args,再遍历每个arg的field,判断field是否被特定的注解标记(eg:@DrawId),如果是的话则读取这个字段的值,这种方式对于简单的对象还比较好解析,但是对于嵌套比较深的对象,解析起来比较复杂。
- Spel表达式引擎(参考Spring Cache注解的使用方式): 直接通过编写spel表达式来解析


- 通过分析现有接口,除了分页查询接口,其他的例如修改,查看详情,删除,兑奖等相关接口,都是传了抽奖活动drawId的,我们很容易就想到可以通过切面的方式来实现。那么剩下的一个问题是,如何从各类接口参数中识别出drawId字段,这里提供2种思路:通过注解标记,通过Spel表达式引擎
-
改造方案:
- 梳理出所有需要改造的接口,顺着接口往下理,在访问数据库之前,进行权限判断、拼接sql等操作
- 这种方式对现有代码的改动很大,还有可能漏改,风险比较高
- 需要的开发时间和测试时间也较长
- 基于切面+SPEL的改造方式
- 几乎不改动现有代码,不影响之前的业务逻辑
- 统一处理,节省开发和测试回归的时间
- 数据解析很简单
- 缺点: 在修改了方法参数的排序、字段名之后如果没有及时调整spel表达式可能导致数据解析错误、失败
- 基于切面+字段注解的改造方式
- 也是一种比较好的方案,但是想尝试一下表达式引擎的用法
- 对于嵌套比较深的对象,解析起来比较复杂
- 梳理出所有需要改造的接口,顺着接口往下理,在访问数据库之前,进行权限判断、拼接sql等操作
-
着手开发:
- 定义注解,用于标记需要拦截的API以及相应的spel表达式,
@CheckDataRight
/** * @author idle fish * @since 2023/12/9 */ @Documented @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.METHOD) public @interface CheckDataRight { /** * 读取drawId的spel表达式 * * @return */ String value(); }- 数据权限拦截切面
- 定义注解,用于标记需要拦截的API以及相应的spel表达式,
/**
* drawId数据权限拦截器
*
* @author idle fish
* @since 2023/12/9
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
@Aspect
public class DataRightAop {
/**
* 如果访问的是页面,则返回这个没有权限的提示页面
*/
public static final String NO_RIGHTS = "/idle/fish/prize/nodatarights.ms";
@Resource
private DrawPrizeService drawPrizeService;
@Around("execution(* com.idle.fish.prize.web.controller.*.*(..)) && @annotation(checkDataRight)")
public Object checkDataRight(ProceedingJoinPoint point, CheckDataRight checkDataRight) {
// 初始化spel表达式解析器
SpelExpressionParser spelExpressionParser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// 读取当前方法的参数列表
Object[] args = point.getArgs();
// 初始化上下文
StandardEvaluationContext standardEvaluationContext = new StandardEvaluationContext(args);
// 读取spel表达式,并解析args,读取drawId并转为Long类型
Long drawId = spelExpressionParser.parseExpression(checkDataRight.value()).getValue(standardEvaluationContext, Long.class);
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
HttpServletResponse response = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getResponse();
// 读取当前登录的用户信息
AdminContext adminContext = (AdminContext) request.getSession().getAttribute(AdminAuthInterceptor.SESSION_CONTEXT_NAME);
// 校验权限
Boolean hasRight = adminContext == null || (adminContext.isAdministrator() || drawPrizeService.hasRight(drawId, adminContext.getAdminId()));
log.info("当前用户id:{}:name:{},超管:{},活动:{},权限:{}", adminContext == null ? "未登录" : adminContext.getAdminId(), adminContext == null ? "未登录" : adminContext.getName(), adminContext == null ? "未登录" : adminContext.isAdministrator(), drawId, hasRight);
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(hasRight)) {
// 有权限,放行
try {
return point.proceed();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("aop异常", e);
return null;
}
} else {
if (request.getRequestURI().endsWith(".ms")) {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) point.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (Objects.equals(ModelAndView.class, returnType)) {
// 如果返回的是页面,则转发到没有权限的提示页面
try {
request.getRequestDispatcher(NO_RIGHTS).forward(request, response);
return null;
} catch (ServletException | IOException e) {
log.error("转发失败", e);
return null;
}
} else {
// 如果返回的不是页面,则返回没权限的json数据
try (ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream()) {
outputStream.write(JSON.toJSONBytes(ResponseEntity.failed(null, "您没有当前活动的权限")));
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE);
outputStream.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("无权限响应写入失败", e);
}
}
} else {
try {
request.getRequestDispatcher(NO_RIGHTS).forward(request, response);
} catch (ServletException | IOException e) {
log.error("转发失败", e);
}
}
return null;
}
}
}
-
标记需要拦截的接口,编写Spel表达式

-
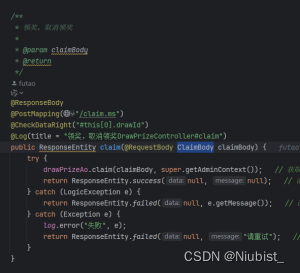
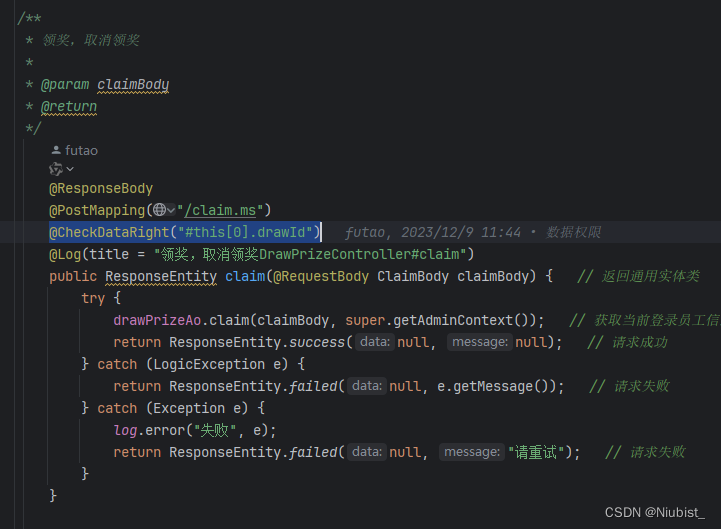
拿一个接口举例子:
/**
* 领奖,取消领奖
*
* @param claimBody
* @return
*/
public ResponseEntity claim(@RequestBody ClaimBody claimBody) {...}
/**
* @author idle fish
* @since 2023/12/8
*/
@Getter
@Setter
public class ClaimBody implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* 活动id
*/
private Long drawId;
/**
* 中奖人id
*/
private Long personId;
/**
* 奖项id
*/
private Long awardSettingId;
/**
* 领奖状态
* 0=取消领奖,1=领奖
*/
private Integer claimStatus;
}
-
当前接口的
drawId是在claim()方法的第一个参数ClaimBody中的drawId字段,那么对应的spel表达式为:#this[0].drawId- 表达式含义:结合切面的代码,我们传入的对象是
args,是个数组,这个数组的第一个参数即为ClaimBody,读取ClaimBody.drawId即可#this对应args[0]对应args数组第一个值ClaimBody.drawId对应ClaimBody.drawId
- 表达式含义:结合切面的代码,我们传入的对象是
-
验证:


扩展:SPEL表达式引擎使用案例
1. 创建对象,调用方法
SpelExpressionParser spelExpressionParser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression expression = spelExpressionParser.parseExpression("new String('good').toUpperCase()");
System.out.println("返回的是String:" + expression.getValue(String.class));
System.out.println("返回的是Object" + expression.getValue());
2. 读取传入的对象的属性进行计算
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
private static class Item {
private Integer price;
private Integer count;
}
// 计算规则
String rule = "price+count";
Item item = new Item(10, 20);
StandardEvaluationContext standardEvaluationContext = new StandardEvaluationContext(item);
Object objVal = new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression(rule).getValue(standardEvaluationContext);
Integer integerVal = new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression(rule).getValue(standardEvaluationContext, Integer.class);
System.out.println(objVal);
System.out.println(integerVal);
// 也可以直接通过这种方式来设置rootObject
Object value = new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("price*count").getValue(item);
System.out.println(value);
3. null引用与下标越界
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
private static class Item {
private Integer price;
private Integer count;
private List<String> productNameList;
}
Item item = new Item();
SpelExpressionParser spelExpressionParser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// 报错,因为productNameList是null
System.out.println(spelExpressionParser.parseExpression("productNameList.get(1)").getValue(item));
Item item = new Item();
// 如果list为null,不会自动初始化
item.setProductNameList(new ArrayList<>());
// 打开数组/集合自动增长
SpelExpressionParser spelExpressionParser = new SpelExpressionParser(new SpelParserConfiguration(true, true));
// 报错,因为productNameList是null
System.out.println(spelExpressionParser.parseExpression("productNameList.size()").getValue(item));
// 需要使用[n]这种方式访问,否则还是会报错
System.out.println(spelExpressionParser.parseExpression("productNameList[10]").getValue(item));
System.out.println(spelExpressionParser.parseExpression("productNameList.size()").getValue(item));
4. 读取属性、数组、集合、Map
Item item = new Item();
item.setPrice(999);
item.setProductNameList(Lists.newArrayList("抽烟", "喝酒", "烫头"));
List<Item> items = new ArrayList<>();
items.add(item);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("username", "idle fish");
// 通过方括号[n]读取数组,集合
// 通过.读取属性,属性可以直接写属性名,不需要写getter方法
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("[0].price").getValue(items, Integer.class));
// 通过方括号[key]读取map
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("[username]").getValue(map, String.class));
5. 构造集合、Map、数组
// 构造集合
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("{1,2,3}").getValue(List.class));
// 构造集合
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("{1,2,3,3}").getValue(Set.class));
// 构造map
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("{'username':'idle fish','age':188}").getValue(Map.class));
// 构造数组
int[] value = (int[]) new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("new int[]{1,2,3}").getValue();
System.out.println(value);
6. 运算
Item item = new Item();
item.setPrice(10);
item.setCount(3);
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("price + count").getValue(item, Integer.class));
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("price - count").getValue(item, Integer.class));
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("price * count").getValue(item, Integer.class));
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("price / count").getValue(item, Integer.class));
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("price % count").getValue(item, Integer.class));
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("price == count").getValue(item, Boolean.class));
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("price > count").getValue(item, Boolean.class));
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("price >= count").getValue(item, Boolean.class));
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("(price*count) >= 50").getValue(item, Boolean.class));
// 逻辑运算 and or not(!)
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("price >= 15 and count>=3").getValue(item));
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("price >= 15 or count>=3").getValue(item));
// 三元运算
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("price=(price>=10?15:price)").getValue(item));
7. 赋值
Item rootObject = new Item();
new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("price").setValue(rootObject, "99999999");
System.out.println(rootObject);
// 也可以通过get来赋值
Object value = new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("count=555").getValue(rootObject);
// 555
System.out.println(value);
System.out.println(rootObject);
8. 变量
Item item = new Item();
// 设置rootObject
StandardEvaluationContext standardEvaluationContext = new StandardEvaluationContext(item);
// 增加变量
standardEvaluationContext.setVariables(new JSONObject().fluentPut("username", "idle fish").fluentPut("age", 29));
SpelExpressionParser spelExpressionParser = new SpelExpressionParser(new SpelParserConfiguration(true, true));
spelExpressionParser.parseExpression("productNameList").setValue(standardEvaluationContext, new ArrayList<>());
System.out.println(item);
// 取值与赋值
spelExpressionParser.parseExpression("productNameList[0]=#username").getValue(standardEvaluationContext);
System.out.println(item);
// 赋值
spelExpressionParser.parseExpression("price=#age").getValue(standardEvaluationContext);
System.out.println(item);
9. #this与#root
// create an array of integers
List<Integer> primes = Lists.newArrayList(2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17);
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.setVariable("primes", primes);
List<Integer> primesGreaterThanTen = (List<Integer>) parser.parseExpression(
//.?[] 用来从集合中选择符合特定条件的元素。在这种情况下,它会遍历 #primes 集合中的每一个元素
"#primes.?[#this>10]").getValue(context);
System.out.println(primesGreaterThanTen);
10. 方法注册与引用
public void registerFunction(String name, Method m)
// 原始数据
String hello = "hello world";
// 标准评估上下文,并将rootObject传入
StandardEvaluationContext standardEvaluationContext = new StandardEvaluationContext(hello);
// 注册方法
standardEvaluationContext.registerFunction("revert", StringUtils.class.getDeclaredMethod("reverse", String.class));
// 调用注册的方法,并通过this将context中的rootObject传进去
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("#revert(#this)").getValue(standardEvaluationContext));
11. bean引用
- 在
StandardEvaluationContext中设置BeanResolver - 在
Expression中通过@beanName获取bean
StandardEvaluationContext standardEvaluationContext = new StandardEvaluationContext();
// bean解析
standardEvaluationContext.setBeanResolver(new BeanResolver() {
@Override
public Object resolve(EvaluationContext context, String beanName) throws AccessException {
// 模拟bean解析
return new String("bean@" + beanName);
}
});
SpelExpressionParser spelExpressionParser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// 通过@拿到bean
Object value = spelExpressionParser.parseExpression("@userService").getValue(standardEvaluationContext);
System.out.println(value);
12. 避免空指针
- 在访问属性之前,通过
?判定,如果为空则直接返回null
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
private static class Item {
private Integer price;
private Integer count;
private List<String> productNameList;
private Item item;
}
Item item = new Item();
// 当前item的item字段为null,如果直接调用.priceInt会报错,但是在访问属性之前标记?,那么为空的话程序直接返回null,不会再往下执行
System.out.println(new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("item?.price").getValue(item));
13. 集合与map操作
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
private static class Item {
private Integer price;
private Integer count;
private List<String> productNameList;
private Map<String, Integer> studentScoreMap;
}
Item item = new Item();
// 这种方式会将整个花括号中的内容当成一个字符串,最终list中只有一个字符串
new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("productNameList").setValue(item, "{'抽烟','喝酒','烫头','',null}");
// 先通过表达式将字符串转为list,再setValue
new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("productNameList").setValue(item, new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("{'抽烟','喝酒','烫头','',null}").getValue(List.class));
// 将字符串转为map,并设值
new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("studentScoreMap").setValue(item, new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("{'Tim':59,'李四维':69,'青青':99,'juicy':89}").getValue(Map.class));
// 新建计算上下文,并设置rootObject
StandardEvaluationContext standardEvaluationContext = new StandardEvaluationContext(item);
// 注册方法
standardEvaluationContext.registerFunction("StringUtils_isNotBlank", StringUtils.class.getDeclaredMethod("isNotBlank", CharSequence.class));
// 通过.?[表达式]过滤集合,并产生一个新的集合
// 通过#methodName调用上面注册的方法
// 通过#this,引用list当前循环的元素
List filteredList = new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("productNameList.?[#StringUtils_isNotBlank(#this)]").getValue(standardEvaluationContext, List.class);
System.out.println(item.getProductNameList());
System.out.println(filteredList);
// 通过value过滤数据
Map value = new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("studentScoreMap.?[value<60]").getValue(standardEvaluationContext, Map.class);
// 通过key即可引用当前键值对的key
Map value2 = new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("studentScoreMap.?[key=='juicy']").getValue(standardEvaluationContext, Map.class);
// .^[表达式] 获取匹配的第一个元素
Map first = new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("studentScoreMap.^[value>60]").getValue(standardEvaluationContext, Map.class);
// .$[表达式] 获取匹配的最后一个元素
Map last = new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("studentScoreMap.$[value>60]").getValue(standardEvaluationContext, Map.class);
// .![表达式] 根据表达式生成一个新的集合
Set nameSet = new SpelExpressionParser().parseExpression("studentScoreMap.![key]").getValue(standardEvaluationContext, Set.class);
System.out.println(item.getStudentScoreMap());
System.out.println(value);
System.out.println(value2);
System.out.println(first);
System.out.println(last);
System.out.println(nameSet);
英文教程:https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/5.3.25/reference/html/core.html#expressions
中文教程:https://itmyhome.com/spring/expressions.html
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/futao__/article/details/135283352
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- MongoDB聚合:$currentOp
- 晋升1区131本,下跌1区202本!2023中科院分区期刊动态名单汇总
- 【昕宝爸爸小模块】深入浅出之为什么POI的SXSSFWorkbook占用内存更小
- 基于JavaWeb+BS架构+SpringBoot+Vue+Hadoop短视频流量数据分析与可视化系统的设计和实现
- 4D毫米波雷达——FFT-RadNet 目标检测与可行驶区域分割 CVPR2022
- 架构设计模式详解:夯实架构设计的基础
- Buildroot显示kernel logo
- 新火种AI|人形机器人敲响上市罗,首日市值高达390亿港元
- rpc和http的区别,使?场景
- 正反转控制电路图