数据分析-15-Bitcoin Historical Data比特币价格预测(包含代码数据)
发布时间:2023年12月19日
0. 代码数据下载
关注公众号:『AI学习星球』
回复:比特币价格预测 即可获取数据下载。
算法学习、4对1辅导、论文辅导或核心期刊可以通过公众号或CSDN滴滴我

1. 导入包和数据
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
from scipy import stats
import statsmodels.api as sm
import warnings
from itertools import product
from datetime import datetime
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
plt.style.use('seaborn-poster')
df = pd.read_csv('bitstampUSD_1-min_data_2012-01-01_to_2021-03-31 2.csv')
df.head()

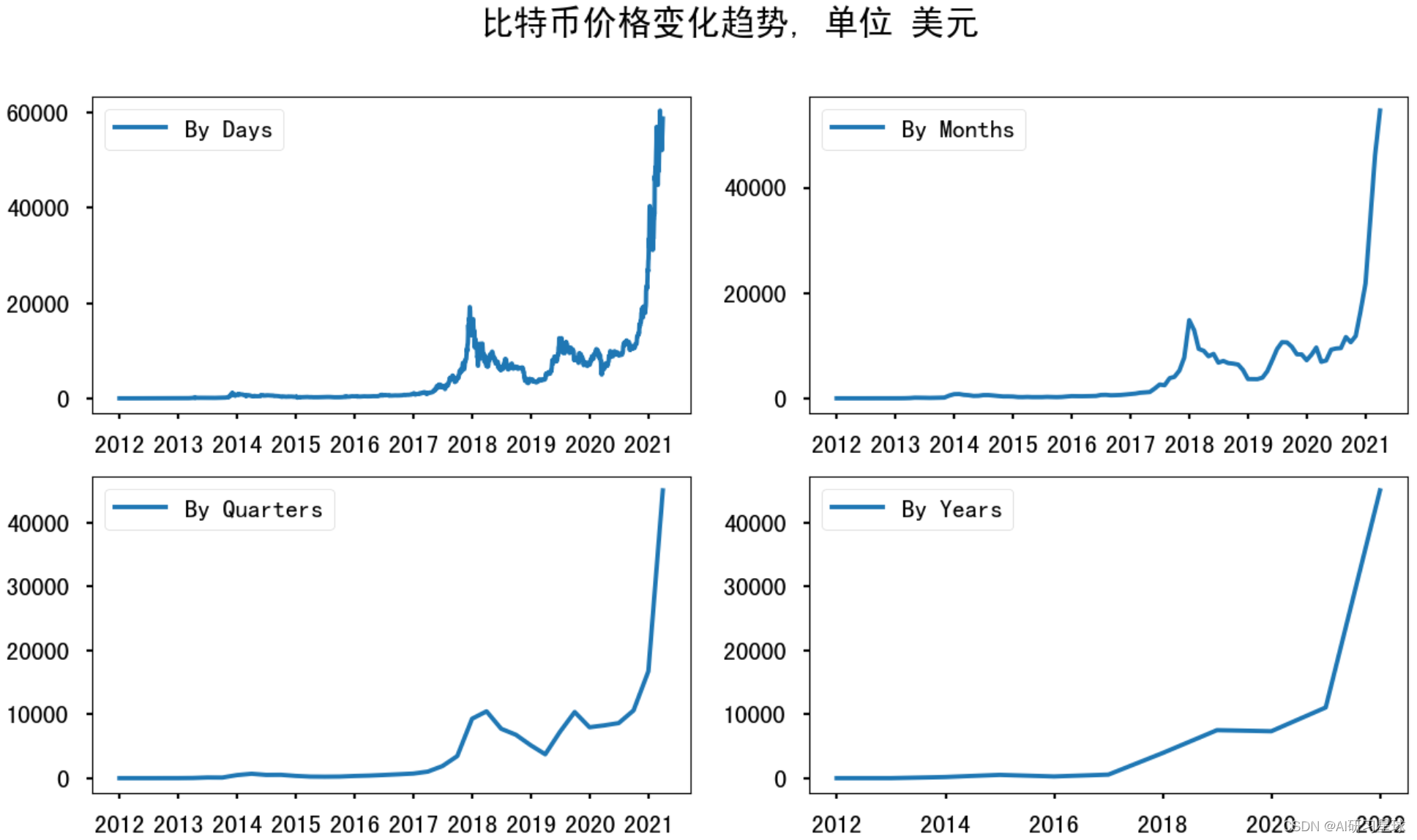
2.货币价格变化趋势分析
通过对数据库中四种因素来分别分析其对货币价格变化的影响并绘图
# 时间戳转化为日常时间格式
df.Timestamp = pd.to_datetime(df.Timestamp, unit='s')
# 对样本在不同时间频率上进行采样
df.index = df.Timestamp
df = df.resample('D').mean()
df_month = df.resample('M').mean()
df_year = df.resample('A-DEC').mean()
df_Q = df.resample('Q-DEC').mean()
# 中文乱码处理
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 绘图
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[15, 8])
plt.suptitle("比特币价格变化趋势, 单位 美元", fontsize=22)
plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot(df.Weighted_Price, '-', label='By Days')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(222)
plt.plot(df_month.Weighted_Price, '-', label='By Months')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(223)
plt.plot(df_Q.Weighted_Price, '-', label='By Quarters')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(224)
plt.plot(df_year.Weighted_Price, '-', label='By Years')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
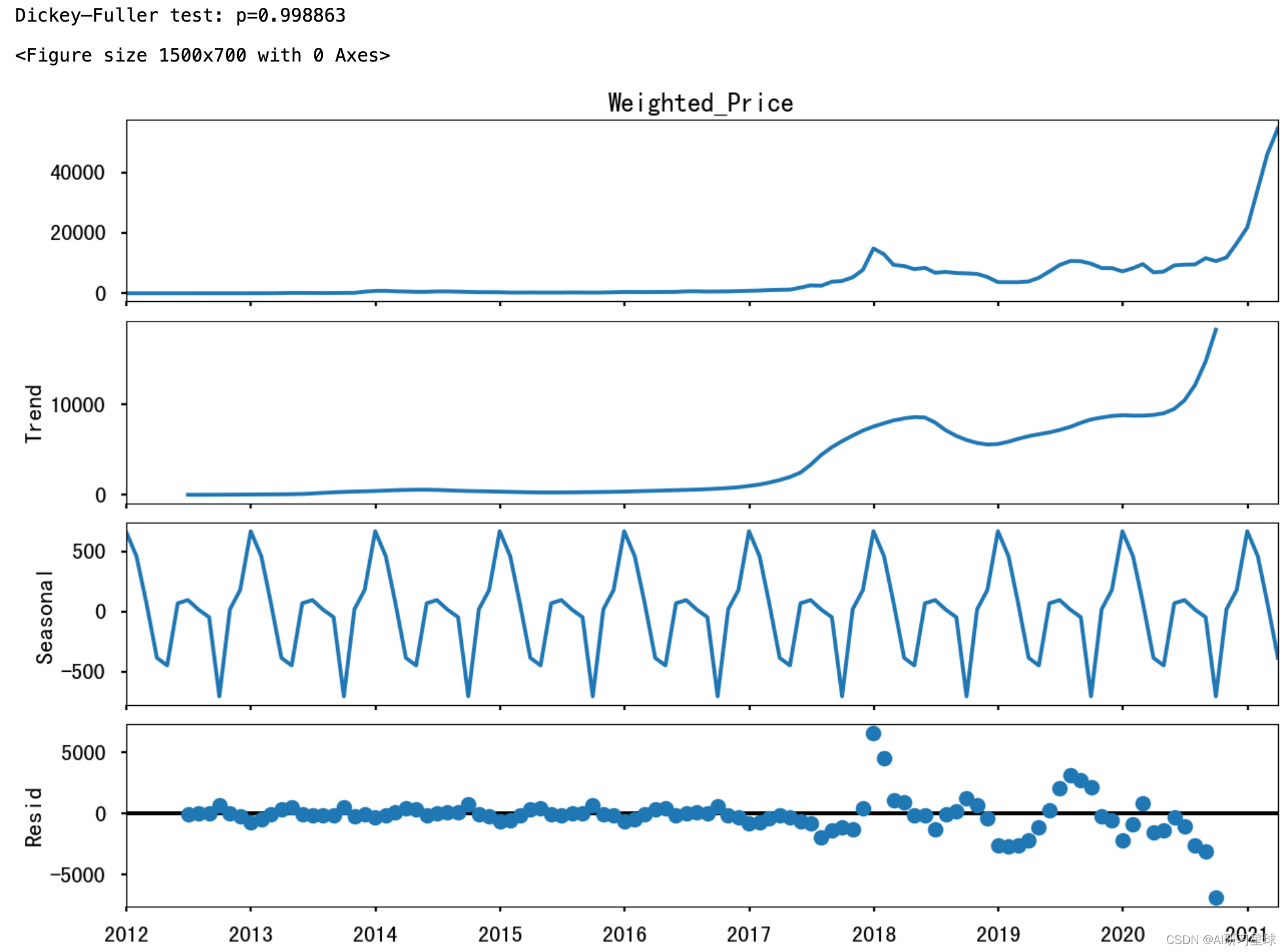
3. 稳定性检测与时间序列检测
对上述四种影响货币价格走向的四种因素分别进行稳定性与时间序列检测
plt.figure (figsize=[15, 7])
sm.tsa.seasonal_decompose(df_month.Weighted_Price).plot()
print("Dickey–Fuller test: p=%f" % sm.tsa.stattools.adfuller(df_month.Weighted_Price)[1])
plt.show()
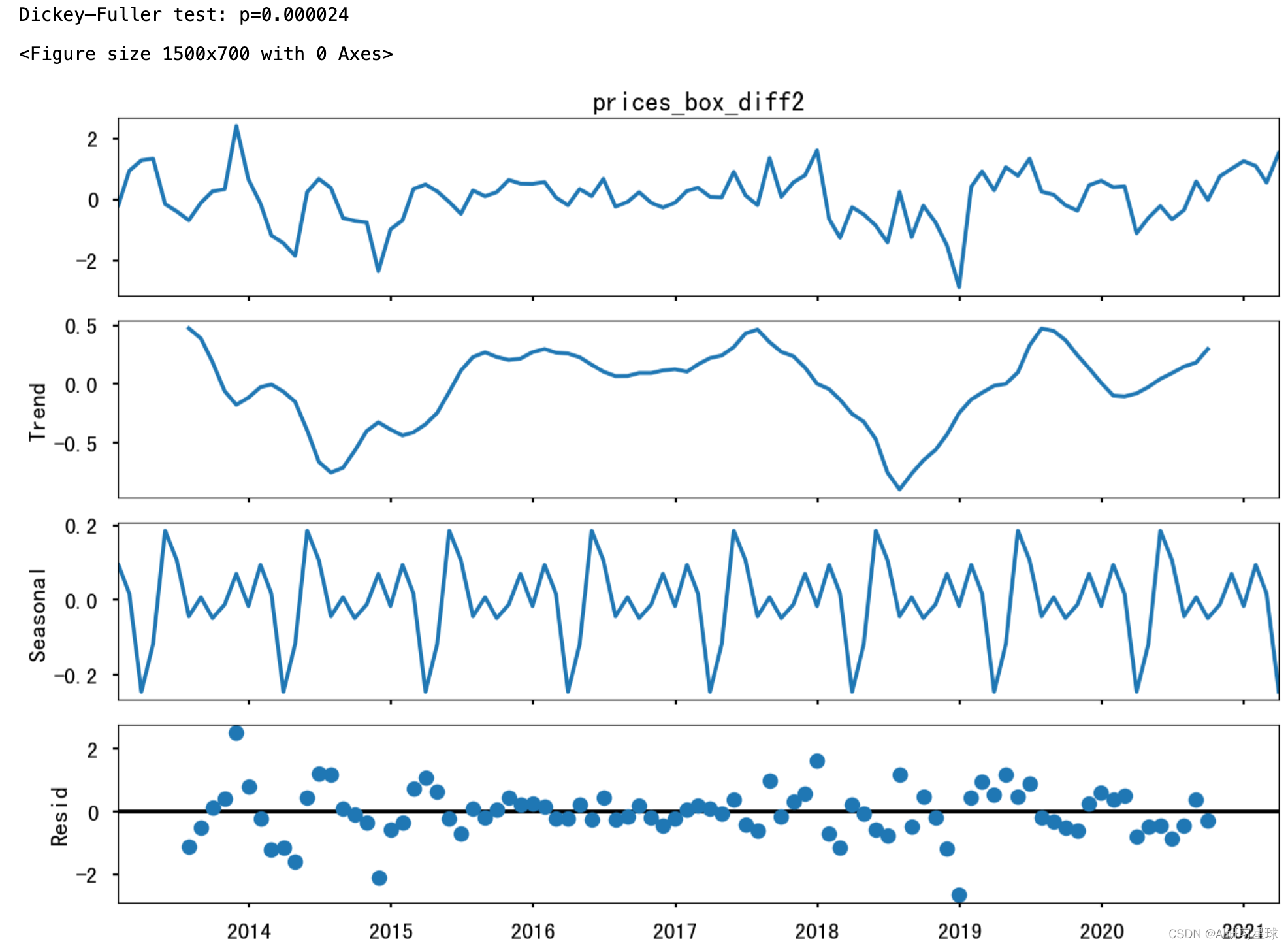
4. 数据变化
由于连续的响应变量不满足正态分布,所以数据需要进行Box-Cox变换
df_month['Weighted_Price_box'], lmbda = stats.boxcox(df_month.Weighted_Price)
print("Dickey–Fuller test: p=%f" % sm.tsa.stattools.adfuller(df_month.Weighted_Price)[1])
Dickey–Fuller test: p=0.998863
由于时间序列季节对数据的影响,所以季节差异化需要考虑,代码如下:
df_month['prices_box_diff'] = df_month.Weighted_Price_box - df_month.Weighted_Price_box.shift(12)
print("Dickey–Fuller test: p=%f" % sm.tsa.stattools.adfuller(df_month.prices_box_diff[12:])[1])
Dickey–Fuller test: p=0.444282
为减少数据的随机性与波动性,需要进行数据规律化分布,代码如下:
# Regular differentiation
df_month['prices_box_diff2'] = df_month.prices_box_diff - df_month.prices_box_diff.shift(1)
plt.figure(figsize=(15,7))
# STL-decomposition
sm.tsa.seasonal_decompose(df_month.prices_box_diff2[13:]).plot()
print("Dickey–Fuller test: p=%f" % sm.tsa.stattools.adfuller(df_month.prices_box_diff2[13:])[1])
plt.show()
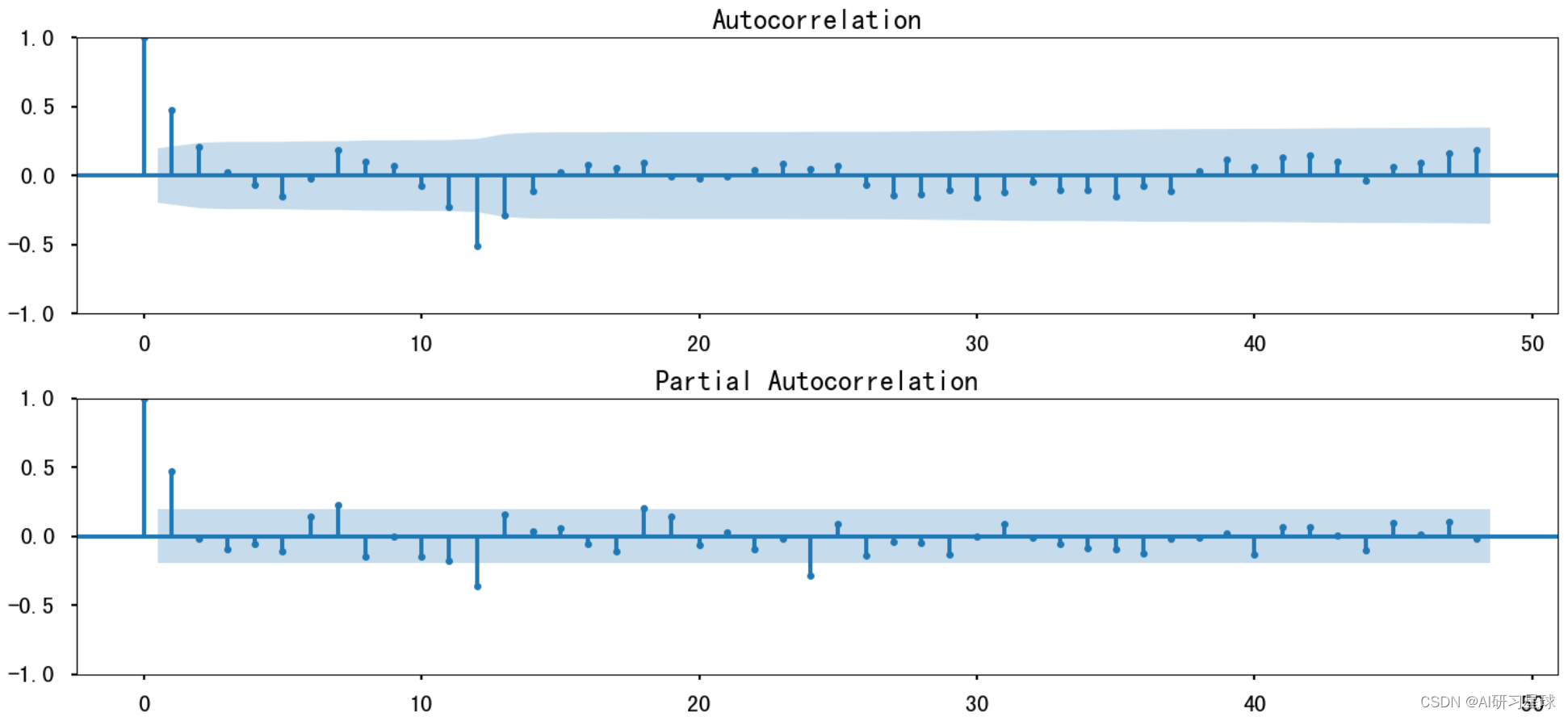
5. 模型分析
将处理完的数据导入对应的模型中,使用自相关和部分自相关图对参数进行初始近似处理
plt.figure(figsize=(15,7))
ax = plt.subplot(211)
sm.graphics.tsa.plot_acf(df_month.prices_box_diff2[13:].values.squeeze(), lags=48, ax=ax)
ax = plt.subplot(212)
sm.graphics.tsa.plot_pacf(df_month.prices_box_diff2[13:].values.squeeze(), lags=48, ax=ax)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
参数初始化与模型选择代码如下:
# Initial approximation of parameters
Qs = range(0, 2)
qs = range(0, 3)
Ps = range(0, 3)
ps = range(0, 3)
D=1
d=1
parameters = product(ps, qs, Ps, Qs)
parameters_list = list(parameters)
len(parameters_list)
# Model Selection
results = []
best_aic = float("inf")
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
for param in parameters_list:
try:
model=sm.tsa.statespace.SARIMAX(df_month.Weighted_Price_box, order=(param[0], d, param[1]),
seasonal_order=(param[2], D, param[3], 12)).fit(disp=-1)
except ValueError:
print('wrong parameters:', param)
continue
aic = model.aic
if aic < best_aic:
best_model = model
best_aic = aic
best_param = param
results.append([param, model.aic])
result_table = pd.DataFrame(results)
result_table.columns = ['parameters', 'aic']
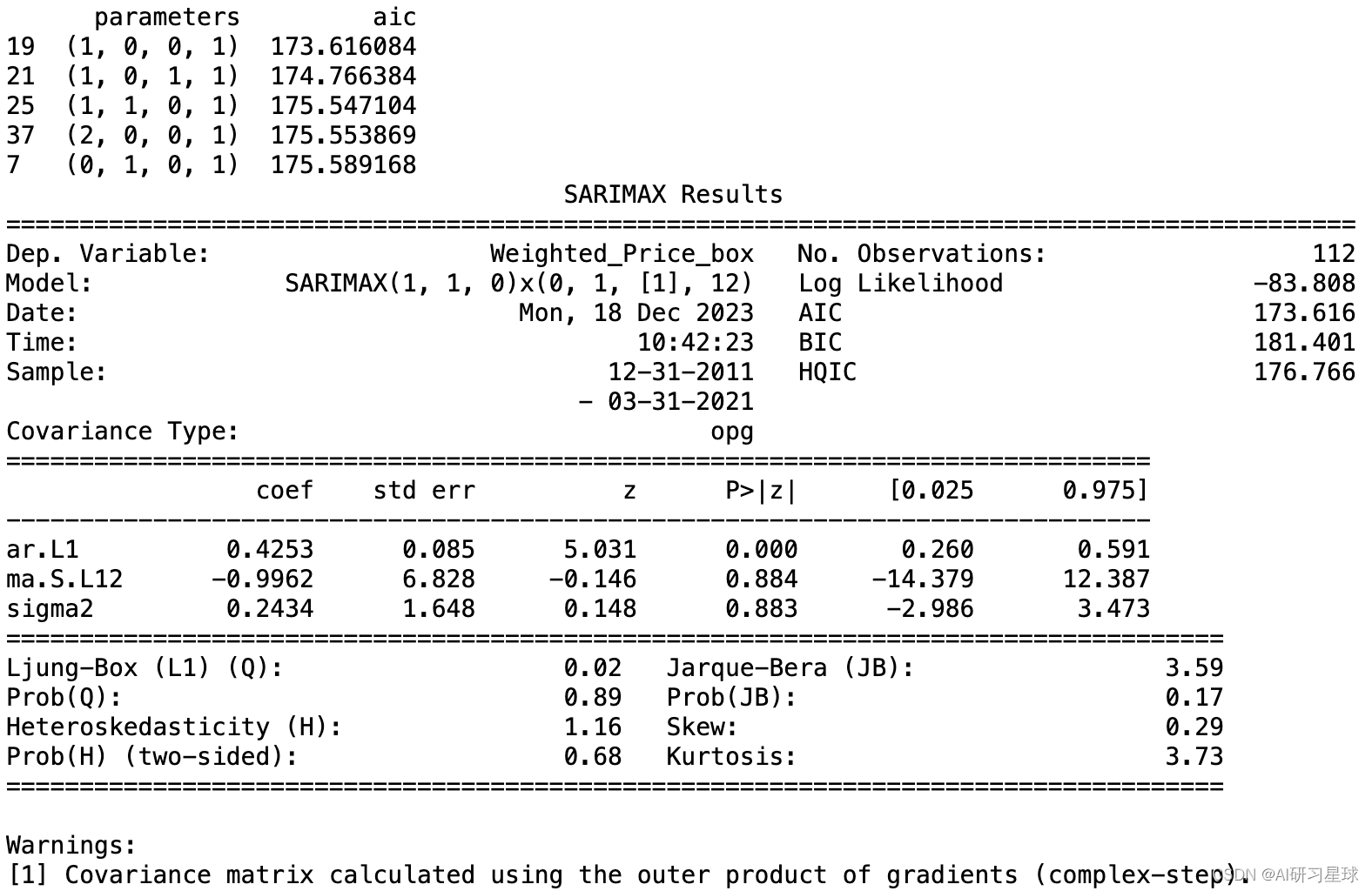
print(result_table.sort_values(by = 'aic', ascending=True).head())
print(best_model.summary())
参数与建模结果如所示:
6. 残留物分析
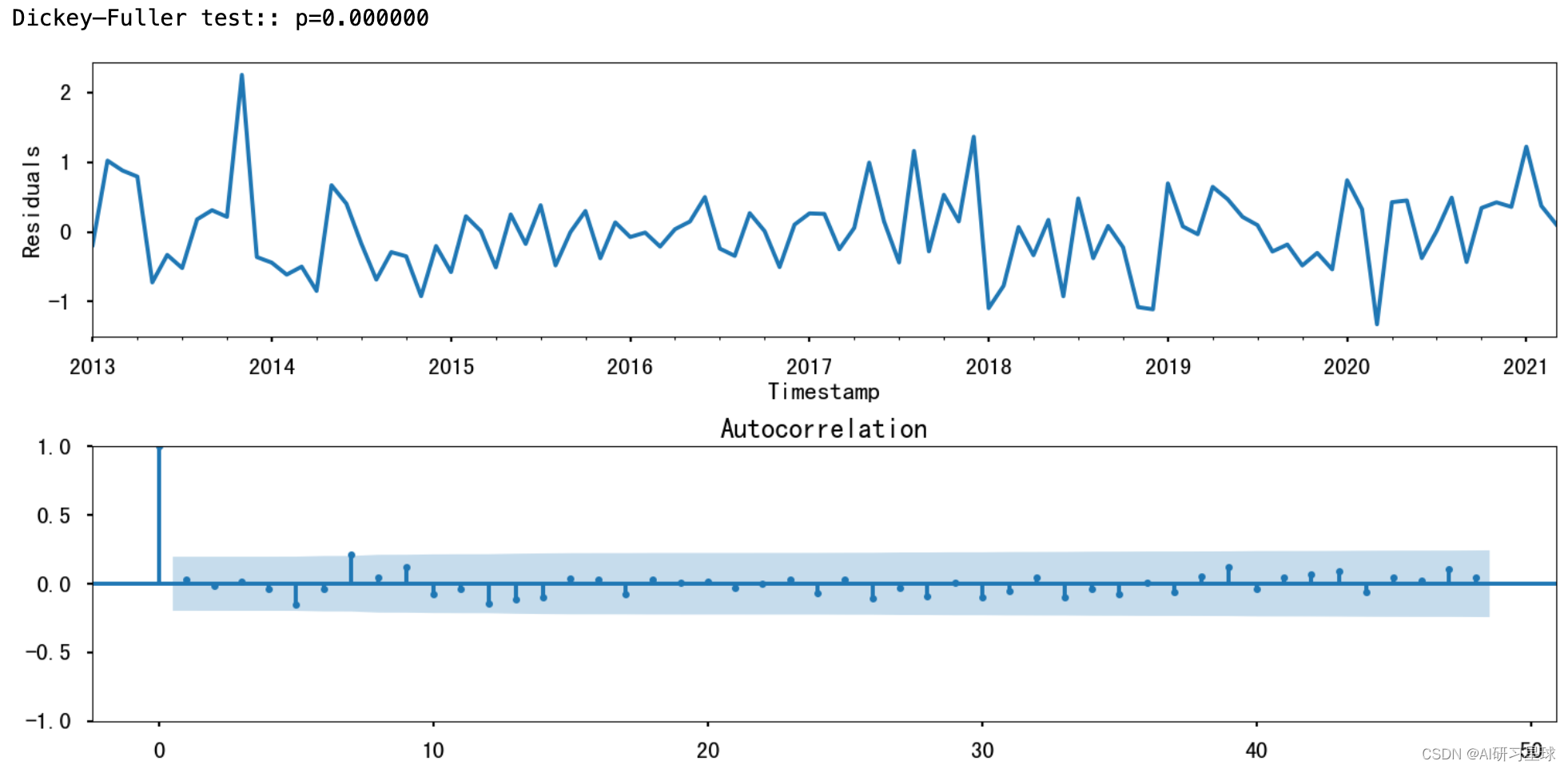
使用STL分解法对残留物进行分析
# STL-decomposition
plt.figure(figsize=(15,7))
plt.subplot(211)
best_model.resid[13:].plot()
plt.ylabel(u'Residuals')
ax = plt.subplot(212)
sm.graphics.tsa.plot_acf(best_model.resid[13:].values.squeeze(), lags=48, ax=ax)
print("Dickey–Fuller test:: p=%f" % sm.tsa.stattools.adfuller(best_model.resid[13:])[1])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
7. 预测
根据前六步得到的分析数据与模型结果,基于时间序列与四种因素对比特币价格进行预测,并与实际价格趋势曲线进行拟合对比
def invboxcox(y,lmbda):
if lmbda == 0:
return(np.exp(y))
else:
return(np.exp(np.log(lmbda*y+1)/lmbda))
# 预测
df_month2 = df_month[['Weighted_Price']]
date_list = [datetime(2017, 6, 30), datetime(2017, 7, 31), datetime(2017, 8, 31), datetime(2017, 9, 30),
datetime(2017, 10, 31), datetime(2017, 11, 30), datetime(2017, 12, 31), datetime(2018, 1, 31),
datetime(2018, 1, 28)]
future = pd.DataFrame(index=date_list, columns= df_month.columns)
df_month2 = pd.concat([df_month2, future])
df_month2['forecast'] = invboxcox(best_model.predict(start=0, end=75), lmbda)
plt.figure(figsize=(15,7))
df_month2.Weighted_Price.plot()
df_month2.forecast.plot(color='r', ls='--', label='Predicted Weighted_Price')
plt.legend()
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] =['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
plt.title('比特币涨势, 月份')
plt.ylabel('mean USD')
plt.show()
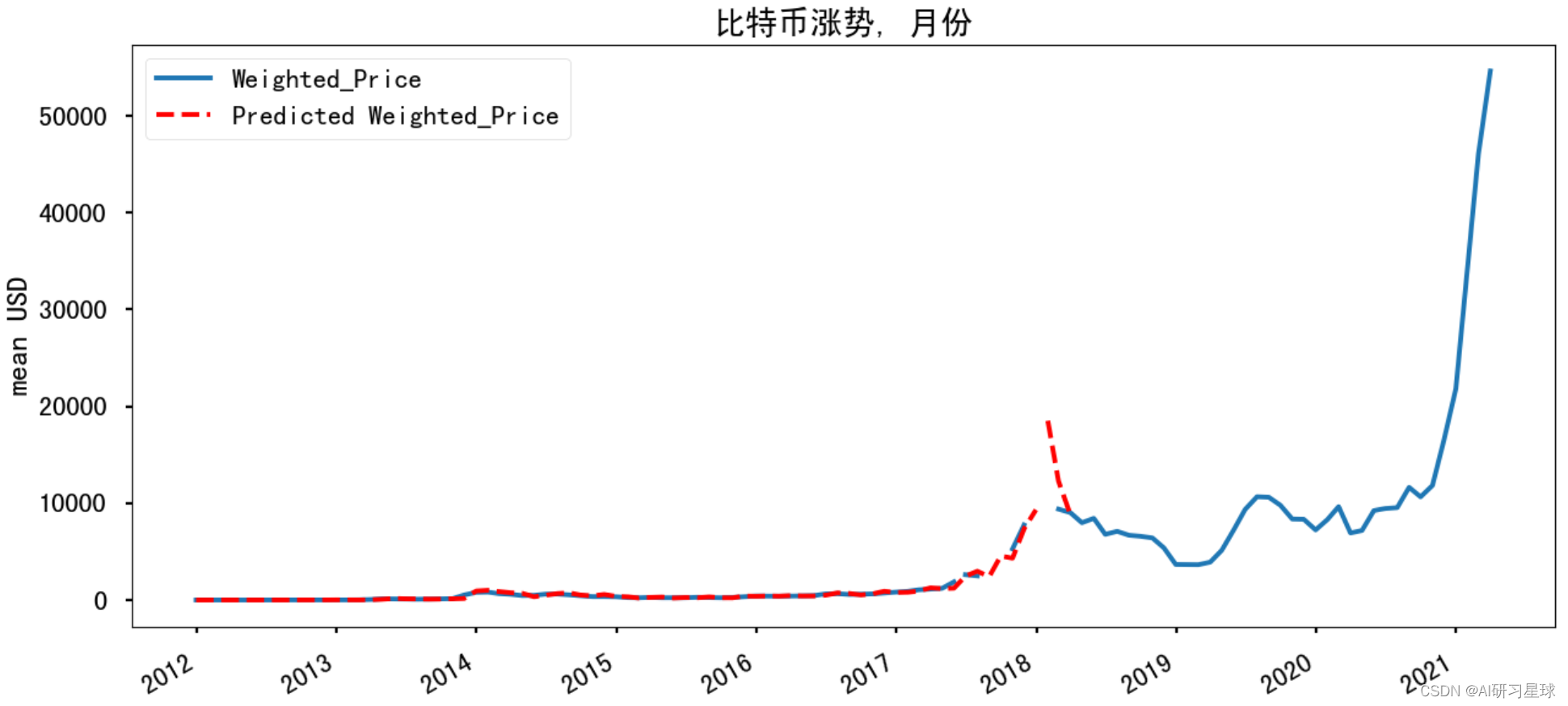
分析:由图可见,实际曲线与预测曲线拟合较好,说明模型的优越性,预测算法的准确性,有着较好的预测效果。
关注公众号:『AI学习星球』
回复:比特币价格预测 即可获取数据下载。
算法学习、4对1辅导、论文辅导或核心期刊可以通过公众号或CSDN滴滴我

文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42363541/article/details/135057262
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- ElasticSearch详细搭建以及常见错误high disk watermark [ES系列] - 第497篇
- JavaWeb—html, css, javascript, dom,xml, tomcat&servlet
- 【无标题】
- Linux 进程(十) 进程替换
- 在分类任务中准确率(accuracy)、精确率(precision)、召回率(recall)和 F1 分数是常用的性能指标,如何在python中使用呢?
- Java设计模式-建造者模式
- 【面向对象】C++/python/java的多态比较
- 企业网络订单软件定制开发的重要性|小程序网站搭建
- 【java】Optional操作
- 【Kafka每日一问】Kafka的高可用机制是什么?