[C++]:12:模拟实现list
[C++]:12:模拟实现list
一.看一看SGI的stl_list的源码:
1.基础结构+构造函数
1.节点结构:
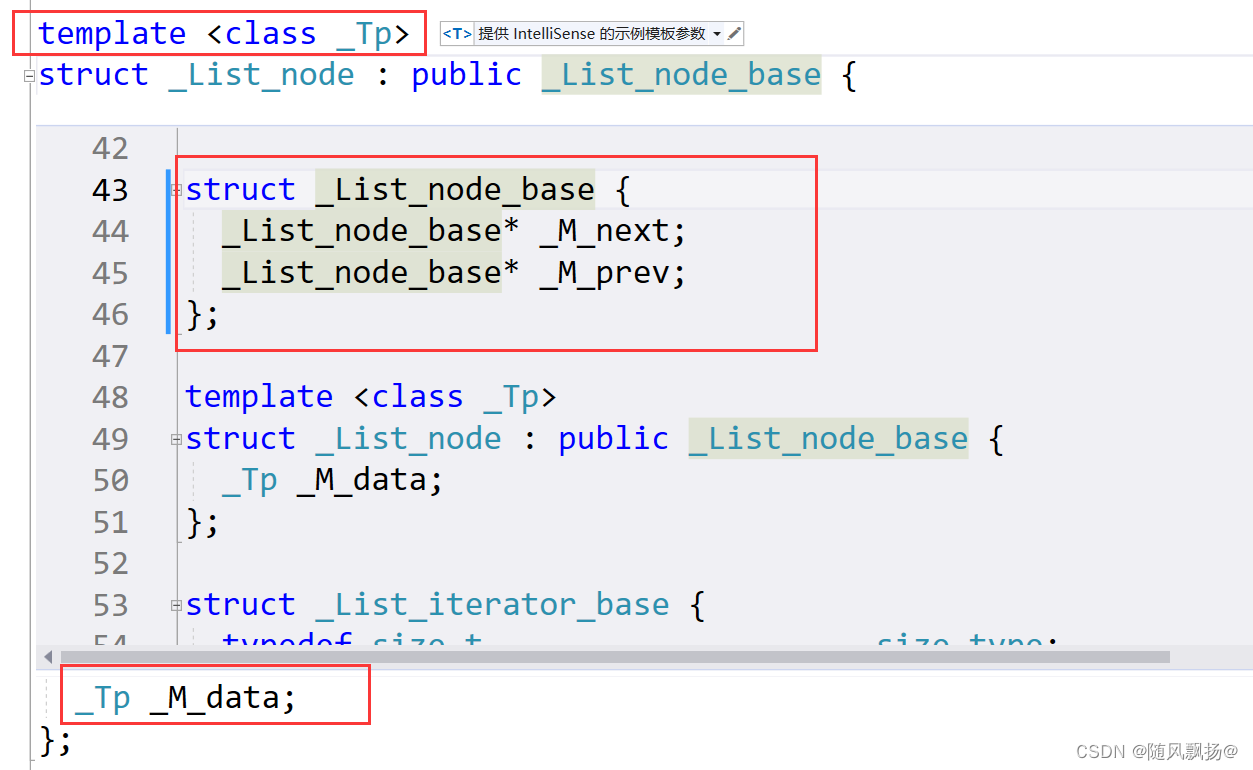
1.SGI下的节点通过两个结构体实现。
2.基础的链表节点只包括前驱指针和后继指针。
3.链表节点去继承基础链表节点,新增节点数据。
4.优化掉指针类型带模板参数。
2.节点构造函数:
1.节点本身在这个地方是没有构造函数的。
2.观察下面的链表的结构和链表的构造函数可以观察出一点细节。
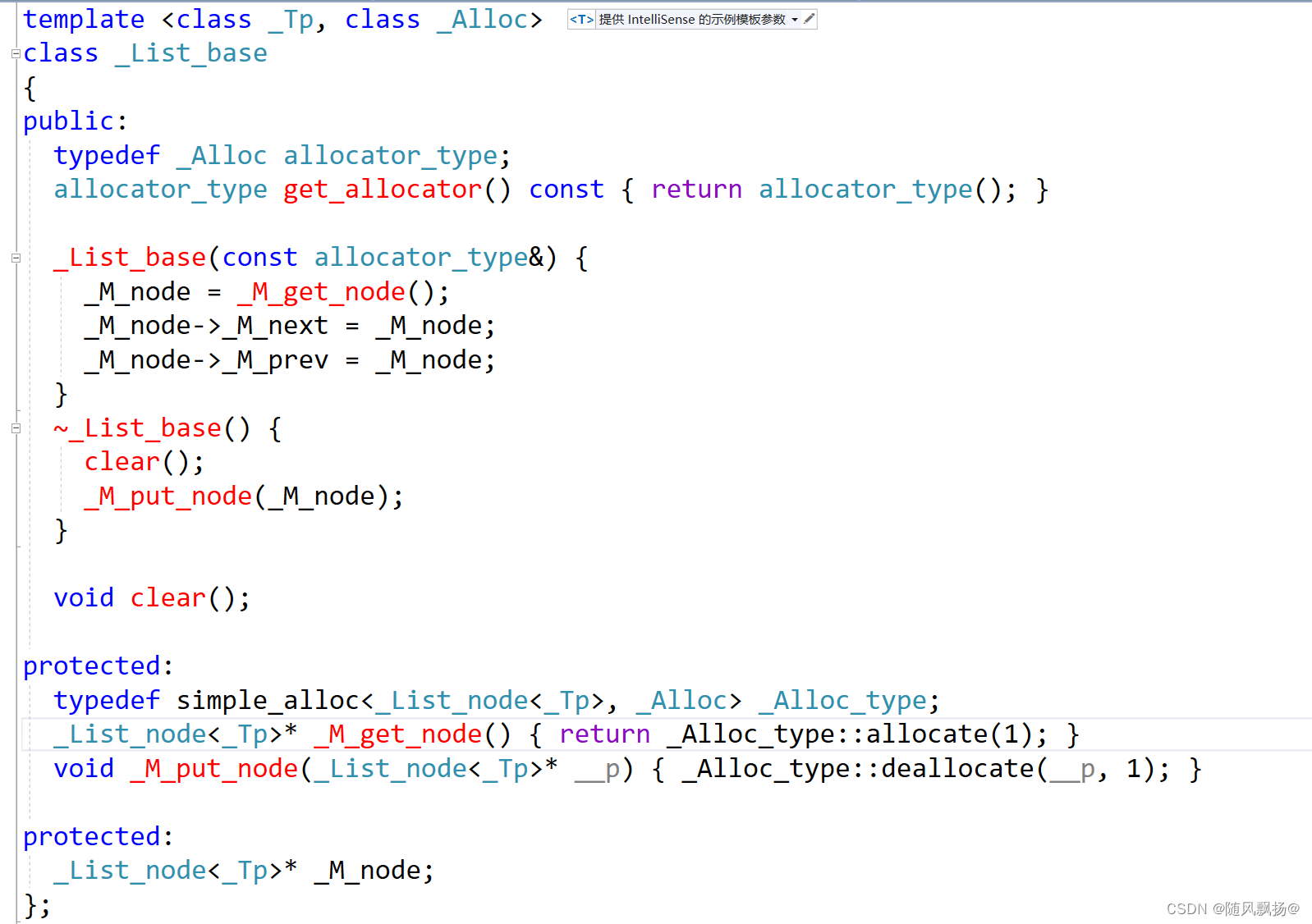
3.链表结构:
1._last_base类的构造通过_M_get_node方法进行节点的空间分配。
2.初始化一个基础的链表需要构造一个哨兵位的头节点。
3.开始的时候让哨兵位的头节点自己指向自己构造一个双向带头循环的一个结构。
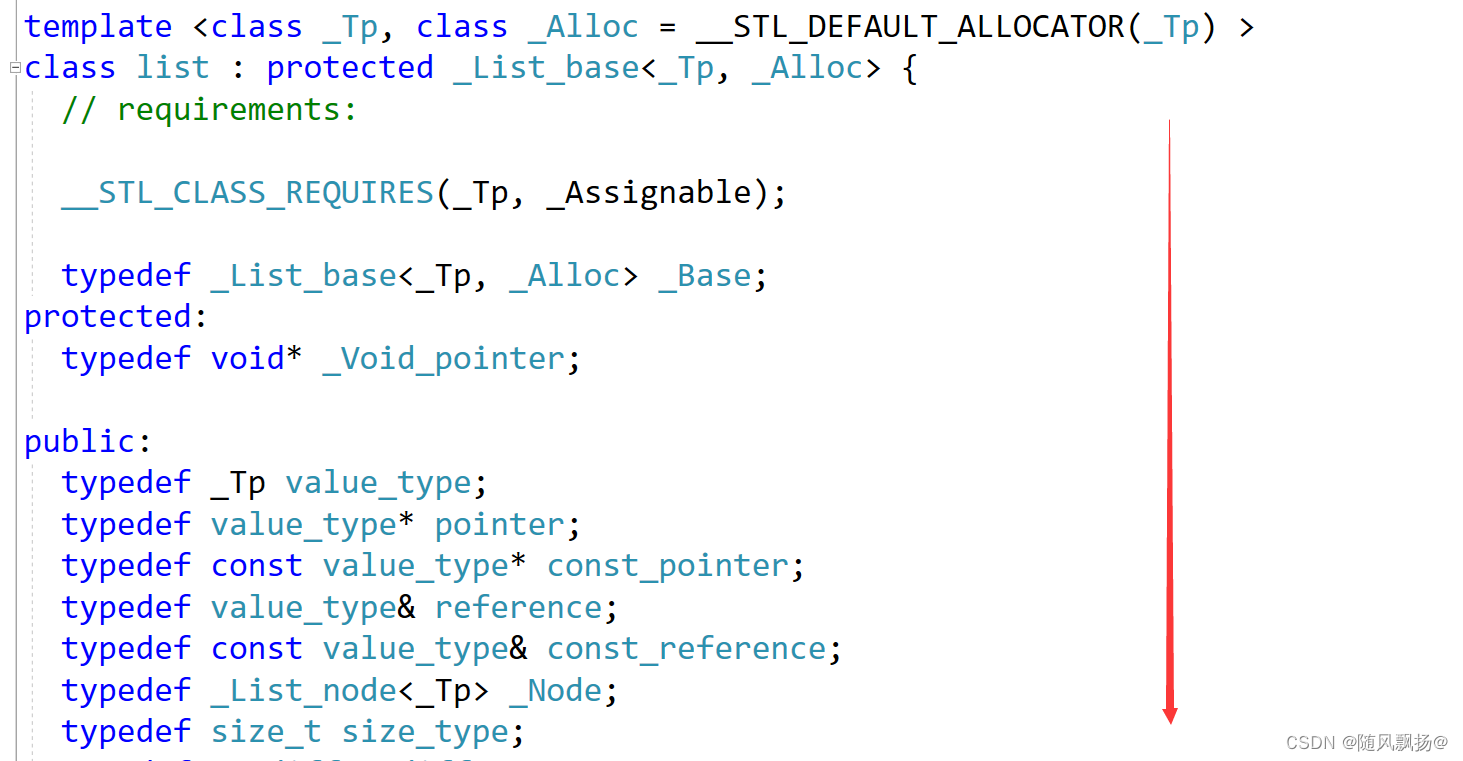
4.list类继承_list_base类的时候里面多了许多的typedef
4.链表的构造函数:
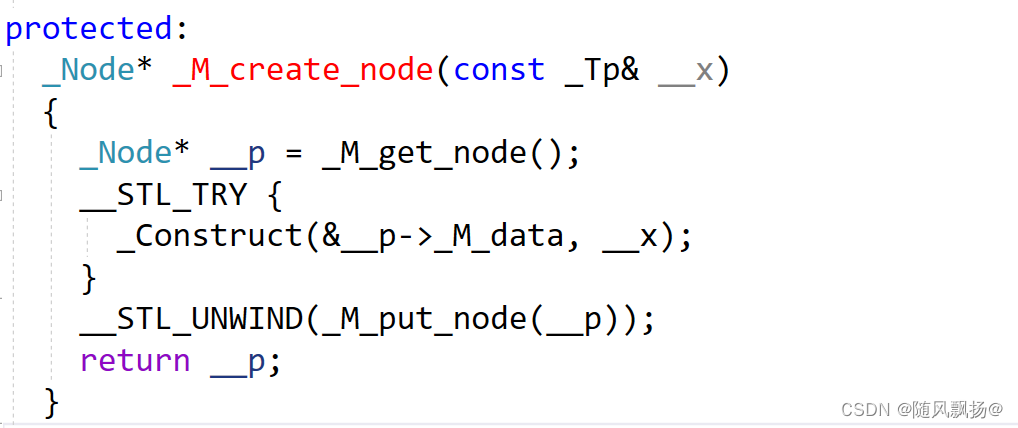
1.通过上面的代码我们发现我们构造一个节点并没有通过节点的构造函数进行构造。
2.在list类型中提供一个方法去在插入新的节点的时候去调用。


2.析构
1.节点析构:
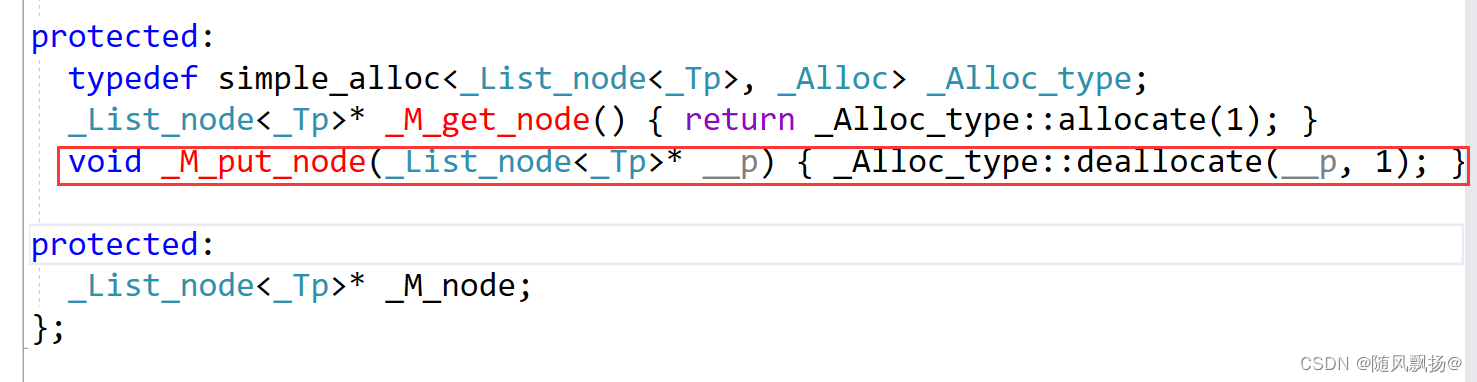
1.使用了内存池去回收节点的空间。
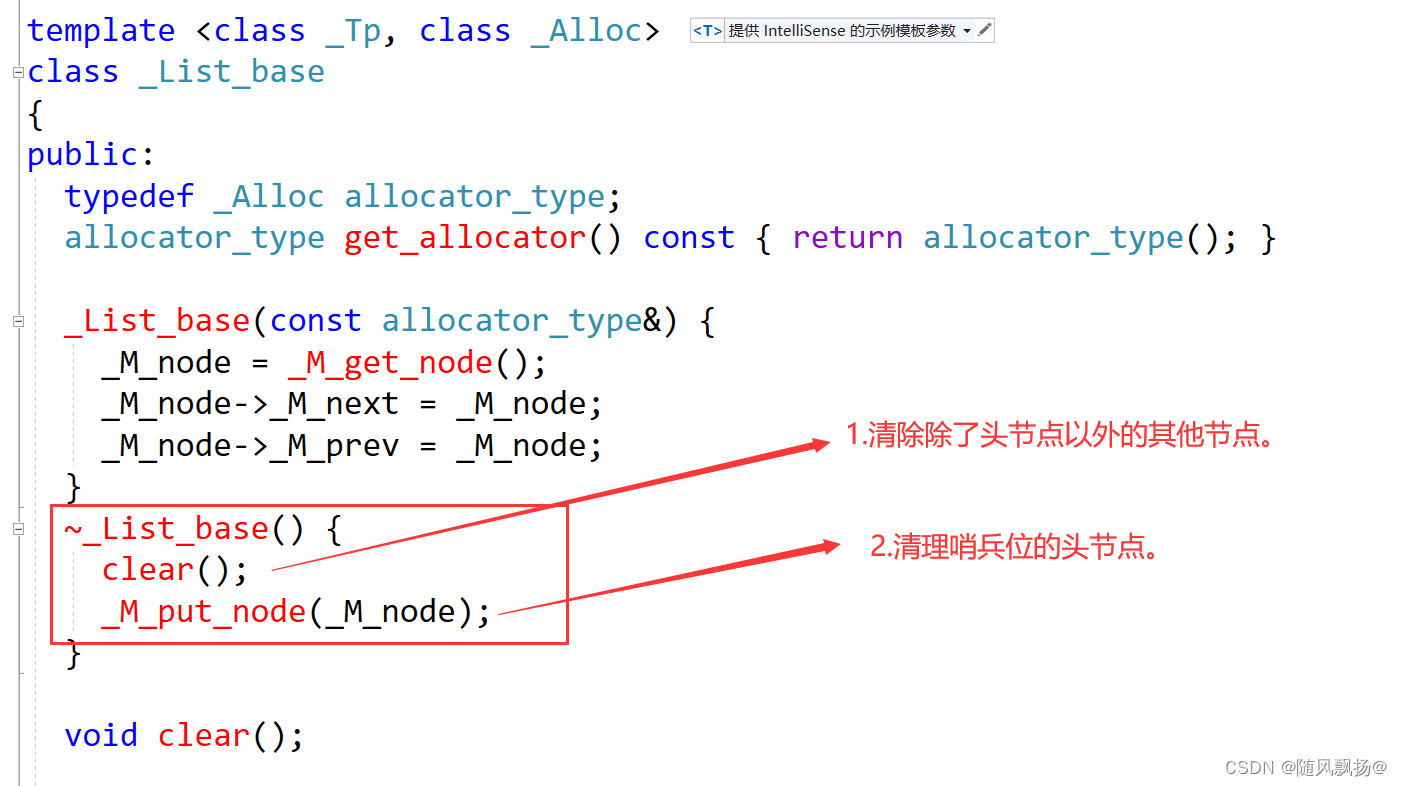
2.链表的析构:
3.迭代器
1.类比string或者vector他们的迭代器就是原生指针是比较方便的。
2.重写operator++ 和 operator*
3.对于节点来说结构不同于string和vector的。
4.参考SGI的源码发现对于内置类型是不可以实现运算符的重载。
5.实现一个迭代器的类型!


二.模拟实现list
1.基础结构+构造函数:
1.节点:
1.自己模拟实现就不这么复杂。
2.sgi通过内存池获取空间通过_creat_node get_node函数去对新增节点的创建。
3.节点自己把自己的数据在内部调整好的构造函数。
4.insert这样的函数去处理定义节点的问题。
//1.节点结构
template<class T>
struct ListNode {
//1.节点的构造函数:
ListNode(T x)
{
date = x;
}
//1.类+模板-->具体的类型。
ListNode<T>* prev=nullptr;
ListNode<T>* next=nullptr;
T date;
};
2.链表:
//3.链表结构
template<class T>
class list{
public:
//1.构造:双向带头循环链表的基本结构!
list()
:head(new ListNode<T>(T()))
{
head->prev = head;
head->next = head;
}
private:
ListNode<T>* head;
};
}
3.实现迭代器+遍历数据:
1.内置类型没有办法进行运算符的重载。
2.迭代器本质就是节点的指针。
3.把一个节点指针类型包裹在一个自定义类型中。
4.在list和iterator_ListNode类中都对相应的类型进行了重定义。
1.迭代器实现:
template<class T>
struct itreator_ListNode {
//2.提供迭代器的方法:
typedef itreator_ListNode<T> self;
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
Node* _node;
itreator_ListNode(Node* x)
:_node(x)
{}
//1.运算符重载:
bool operator!=(self x)
{
return this->_node != x._node;
}
bool operator==(self x)
{
return this->_node == x._node;
}
//2.运算符重载++ --
self& operator++()
{
this->_node = this->_node->next;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self ret = *this;
this->_node = this->_node->next;
return ret;
}
self& operator--()
{
this->_node = this->_node->prev;
return *this;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self ret = *this;
this->_node = this->_node->prev;
return ret;
}
T operator*()
{
return this->_node->date;
}
};
template<class T>
class list{
public:
//1.构造:双向带头循环链表的基本结构!
list()
:head(new ListNode<T>(T()))
{
head->prev = head;
head->next = head;
}
//2.提供迭代器的方法:
typedef itreator_ListNode<T> iterator;
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
//2-1:迭代器应该满足左闭右开
//List_Node<T>* 类型到iterator类型是通过单参数的构造函数支持的!
iterator begin() { return head->next; }
iterator end() {return head;}
void push_back(T x)
{
//1.产生一个节点:
ListNode<T>* newnode = new ListNode<T>(x);
//2.进行节点的连接:
ListNode<T>* prev = head->prev;
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = prev;
head->prev = newnode;
newnode->next = head;
}
private:
Node* head;
};
2.数据遍历
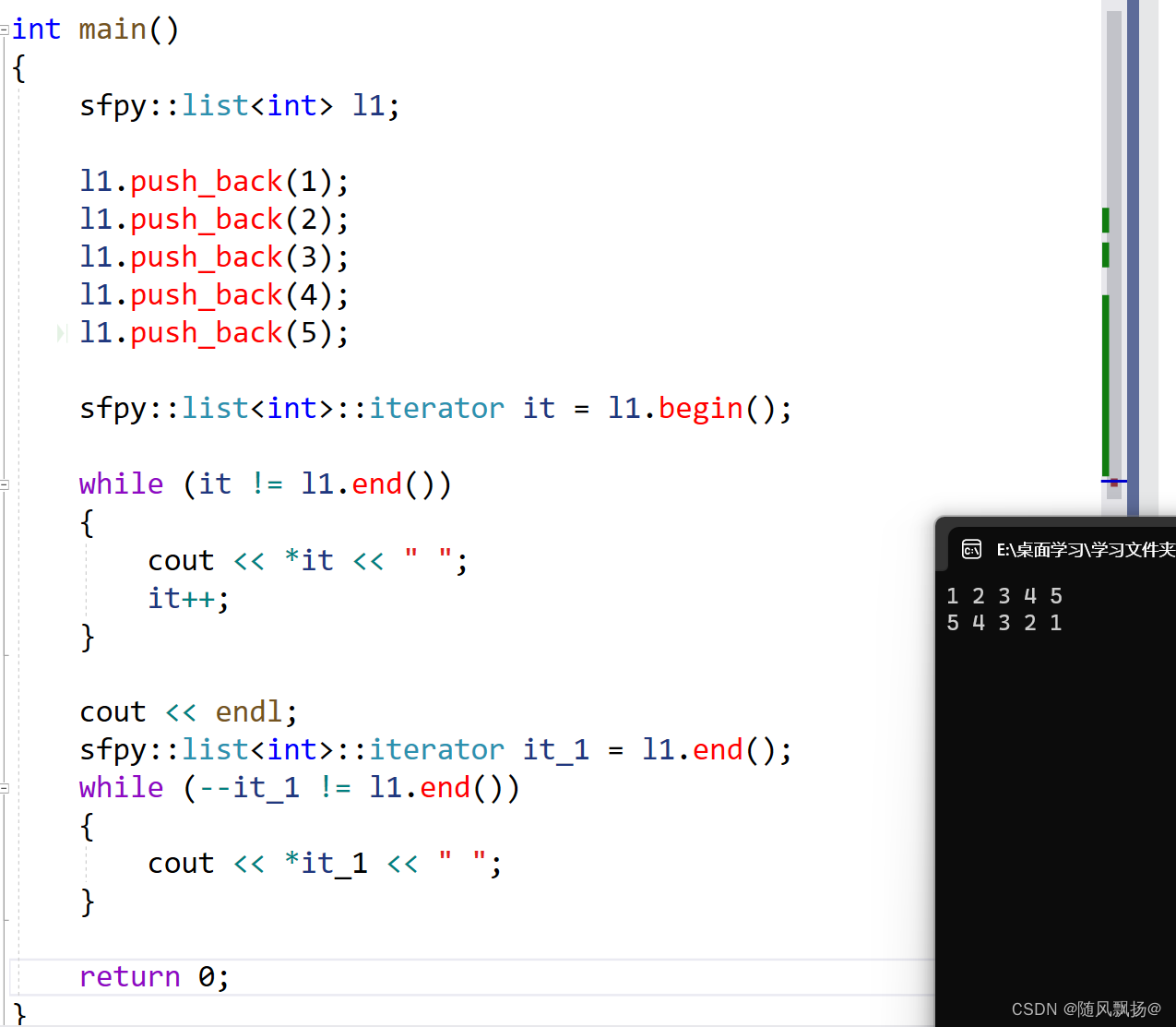
3.拷贝构造+赋值
//1.拷贝构造:
list(list& copy)
:head(new ListNode<T>(T()))
{
head->prev = head;
head->next = head;
//循环copy调用push_back
for (auto num : copy)
{
push_back(num);
}
}
//赋值相关+交换函数
void swap(list& tmp)
{
Node* head = this->head;
this->head = tmp.head;
tmp.head = head;
}
list operator=(list tmp)
{
swap(tmp);
return *this;
}
2.增
1.insert

1.模拟实现第一个insert函数提供迭代器和插入的节点数据:
//为什么不可以iterator&类型返回
//Node* 类型到iterator类型通过单参数的构造函数支持的:发生隐式类型转换!
//Node* 类型到iterator&类型没有被支持的!
iterator insert(iterator pos , T x = T())
{
//1.产生一个节点:
Node* newnode = new ListNode<T>(x);
//2.连接!
Node* next = pos._node->next;
pos._node->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = pos._node;
newnode->next = next;
next->prev = newnode;
return newnode;
}
2.push_front && push_back
void push_back(T x = T())
{
insert(head->prev, x);
}
void push_front(T x = T())
{
insert(head, x);
}
3.删
1.erase

//2.删除考虑返回一下下一个位置的迭代器:
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
Node* prev = pos._node->prev;
Node* next = pos._node->next;
prev->next = next;
next->prev = prev;
//1.使用默认生成的析构函数
delete pos._node;
return next;
}
2.pop_front && pop_back
void pop_back()
{
erase(head->prev);
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(head->next);
}
4.查
1.find
iterator find(T x)
{
iterator cur = begin();
while (cur != end())
{
if (cur._node->date == x)
return cur;
cur = cur._node->next;
//单参数构造函数支持的隐式类型转换!
}
return nullptr;
}
5.改:
2.amend
//修改数据:
void amend(iterator pos,T x)
{
pos._node->date = x;
}
6.析构函数:
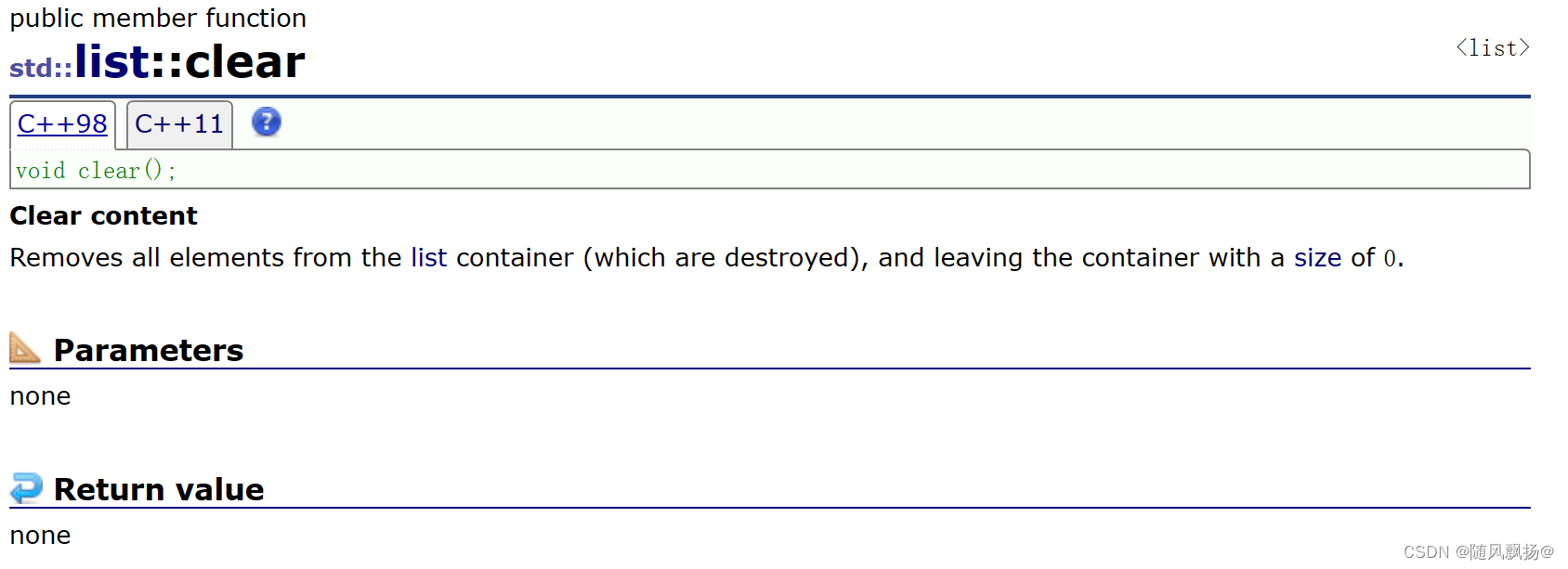
1.clear 和 ~list
1.清除所有的节点数据会保留头节点。
2.使用clear后的状态应该满足只有一个哨兵位的头节点并且前驱指向自己后继指向自己。
//4.遍历链表清理节点:
void clear()
{
Node* cur = head->next;
while (cur != head)
{
Node* next = cur->next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
head->next = head;
head->prev = head;
}
//析构:
~list()
{
clear();
delete head;
}
7.容量相关的函数:
1.size()
//容量相关:
size_t size()
{
assert(head != nullptr);
int count = 0;
if (empty())
return 0;
else
{
iterator cur = begin();
while (cur != end())
{
count++;
cur = cur._node->next;
//单参数构造函数支持的隐式类型转换!
}
return count;
}
}
2.empty()
bool empty()
{
assert(head != nullptr);
if (head->next == head)
return true;
return false;
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- uniapp rpx、px、em、rem、%、vh、vw的区别是什么?
- 腾讯云短信开发
- 如何使用凹凸贴图和位移贴图制作逼真的模型
- Python type函数:动态创建类
- 分享一个小妙招,把文档制作成可翻页的电子书
- K8S学习指南(38)-k8s权限管理对象 Group
- JSON初学习
- Hikvision综合安防管理平台files;.css接口存在任意文件读取漏洞 附POC软件
- SpringBoot 配置文件加载优先级
- Qt图像处理-基于OpenCv的图像二值化处理