设计模式(三)-结构型模式(5)-外观模式
发布时间:2023年12月20日
一、为何需要外观模式(Facade)?
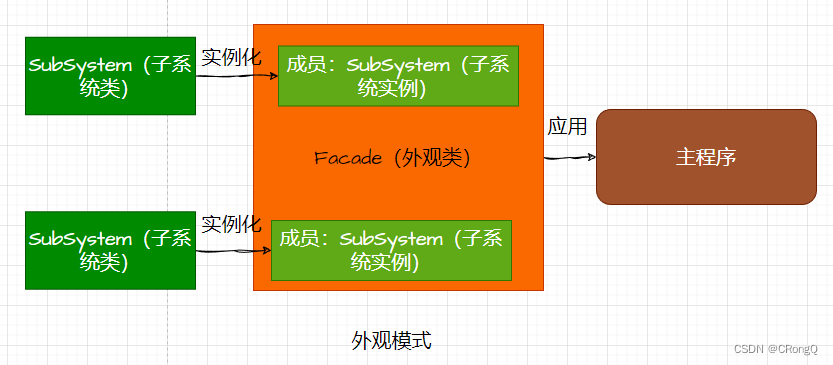
要实现一个大功能,我们需要将它拆分成多个子系统。然后每个子系统所实现的功能,就由一个称为外观的高层功能模块来调用。这种设计方式就称为外观模式。该模式在开发时常常被使用过,所以很容易理解,就不多说了。
特点:
某个功能模块存在多个子系统时,每个子系统实现各自的子任务,并且将它们组合在一起来完成一个完整的任务。
结构:
Facade(外观类):为子任务提供一个共同对外的高层接口。在客户端调用它的方法。
SubSystem(子系统类):实现子系统的功能。可以被外观类调用,也可以直接被客户端调用。
二、例子
需求:
实现一个登录帐户的功能,登录分为验证码验证、连接服务器、从数据库匹配帐户和密码的三个主要步骤。
//SubSystem:子系统(服务器)
public class Server
{
public void SocketToServer()
{
Console.WriteLine("连接服务器。");
}
}
//SubSystem:子系统(验证码)
public class VeriCode
{
public bool doVeriCode(string code)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}验证成功!", code);
return true;
}
}
//SubSystem:子系统(数据库)
public class Database
{
//假设这个字典所存的数据是来自数据库里的。
private Dictionary<int, string> UserInfos = new Dictionary<int, string>()
{
{123,"abc" },
{456,"xyz" },
{789,"abc123"},
};
//是否跟数据库里的信息匹配
public bool isExist(int userId, string pwd)
{
bool isExist = UserInfos.Contains(new KeyValuePair<int, string>(userId, pwd));
return isExist;
}
}
//Facade:外观(登录)
public class LogOnFacade
{
private Server server;
private VeriCode veriCode;
private Database database;
public LogOnFacade()
{
server = new Server();
veriCode = new VeriCode();
database = new Database();
}
public bool IsCode(string code)
{
return veriCode.doVeriCode(code);
}
public bool LogOnUser(int userId,string pwd)
{
server.SocketToServer();
return database.isExist(userId, pwd);
}
}
//主程序
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LogOnFacade logOn = new LogOnFacade();
logOn.IsCode("qwe1");
var isSuccess = logOn.LogOnUser(123, "abc");
var result = isSuccess ? "登录成功" : "登录失败";
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/chen1083376511/article/details/135095623
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!