[反转链表] [合并两个有序链表][分割链表]
发布时间:2024年01月23日
反转链表
1、题目:
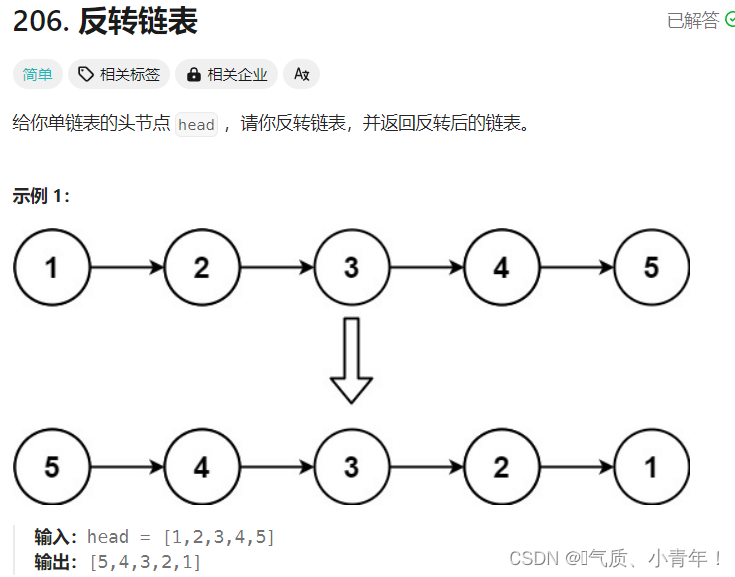
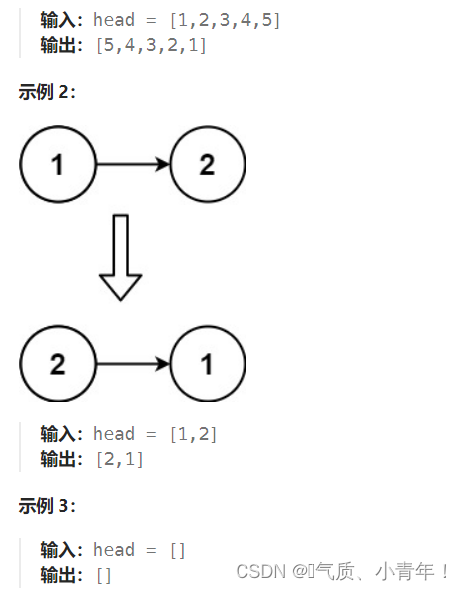
2.思路
?思路1:建立一个newHead,取一个节点进行头插。具体做法如下!
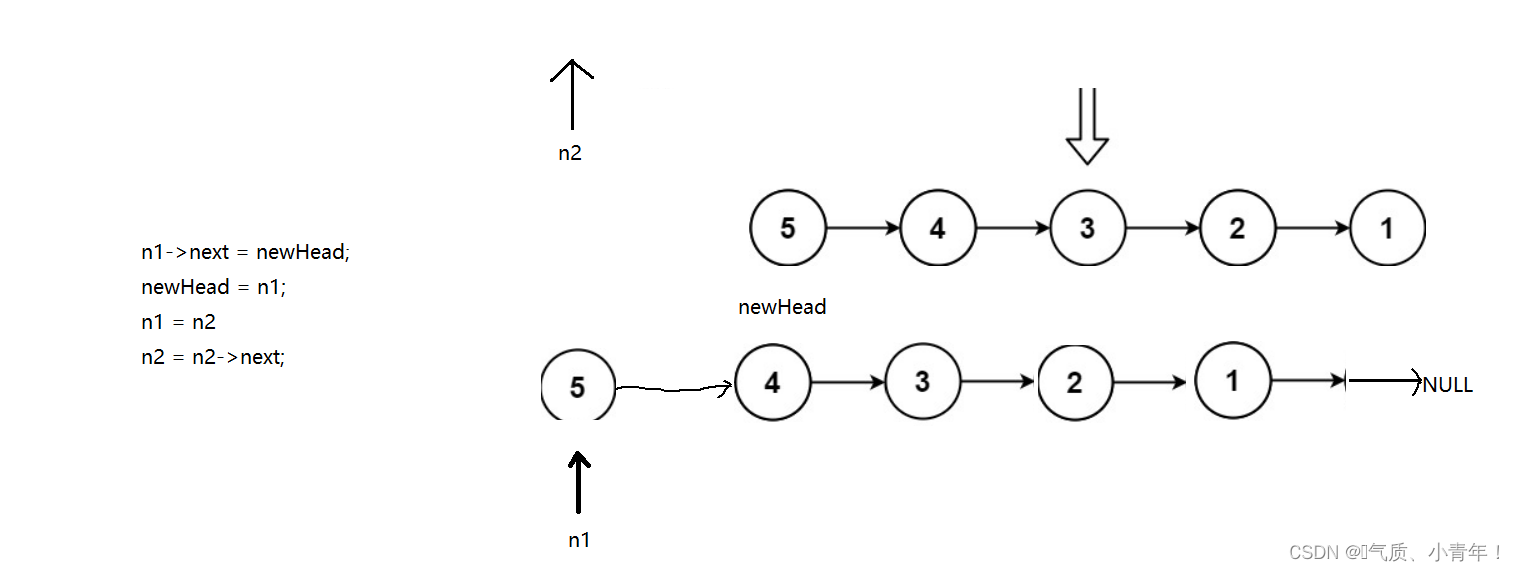
建立一个newHead(新头),由于一个节点里面存的是下一个节点的地址,如果取一个节点下来进行头插,那么,要取的下一个节点的地址找不到,因此定义n1,n2,n1用来往下拿结点进行头插,n2预备下一次要的节点 ,代码如下!!!
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* newHead = NULL;
//n1为向下取得插入的节点
struct ListNode* n1 = head;
//n2是给n1准备的节点
struct ListNode* n2 = head->next;
while(n1)
{
n1->next = newHead;
newHead = n1;
n1 = n2;
//当n2为NULL时,n2没有取得节点了
if(n2)
{
n2 = n2->next;
}
}
return newHead;
}
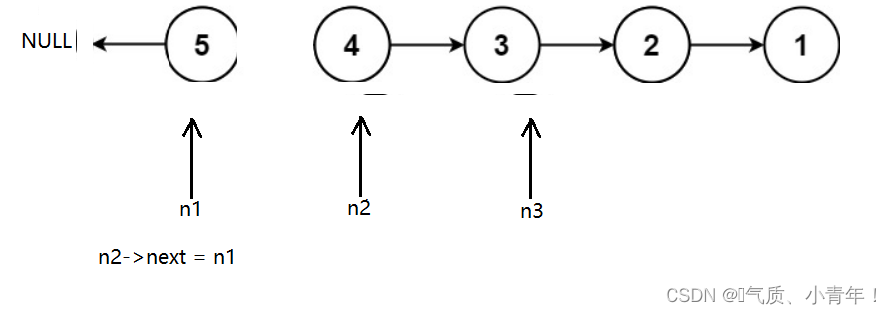
?思路2:把指针翻转,把指针反转的意思是,把存节点的地址交换,定义三个指针n1,n2,n3,n1 = NULL,n2 = head,n3 = head->next,n2为第一个节点翻转,n2->next = n1,n2里面原来存的地址找不到,因此要n3存下一个节点的地址,这样这个题就可以反转了!!!
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* n1 = NULL;
struct ListNode* n2 = head;
struct ListNode* n3 = head->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3)
{
n3 = n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
}
合并两个有序链表
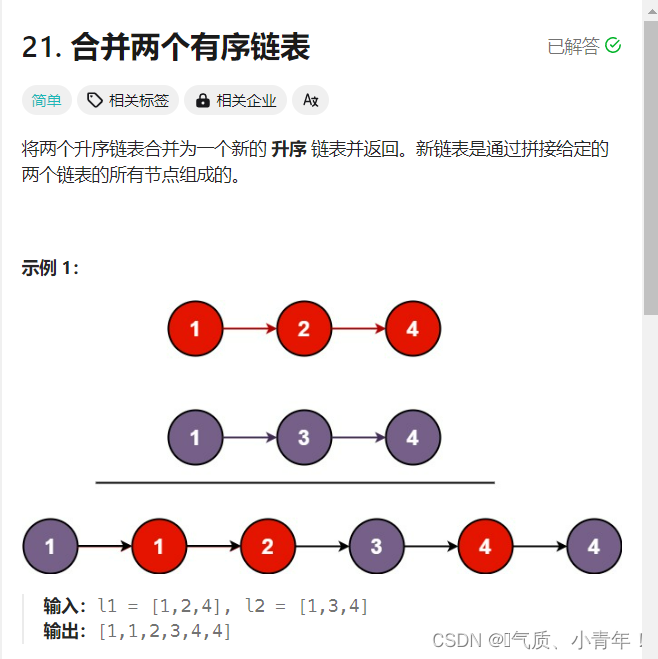
1、题目:
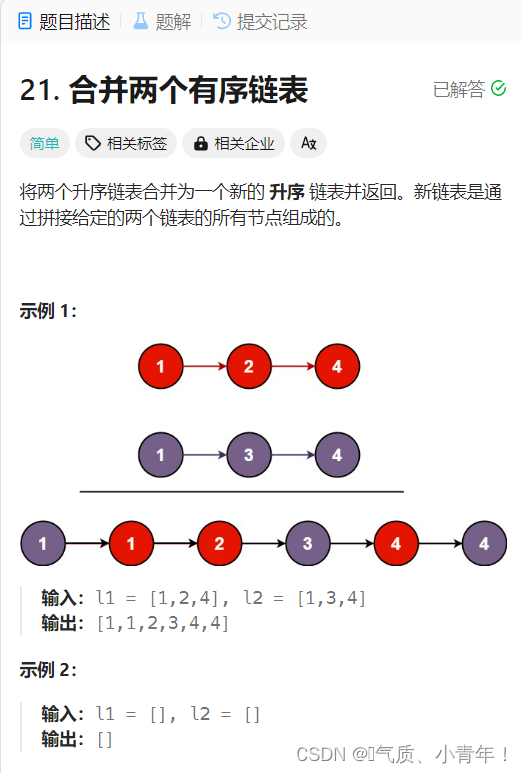
2、思路:
??这个题建立一个新链表,取小的数尾插即可,这儿有一些技巧,可以建立一个头结点,直接尾插,这样就省去了考虑newHead为NULL的情况,这个方法,在一些题中有妙用!!!``
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
if(l1==NULL)
{
return l2;
}
if(l2==NULL)
{
return l1;
}
//处理这个,建立一个头节点,把为NULL的一种可能性去掉
struct ListNode* tmp = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* tail= tmp;
while(l1&&l2)
{
if(l1->val<l2->val)
{
tail->next = l1;
tail = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
tail->next = l2;
tail = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
if(l1)
{
tail->next = l1;
}
if(l2)
{
tail->next = l2;
}
return tmp->next;
}
下面是一个正常的做法!!!
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
if(l1 ==NULL)
{
return l2;
}
if(l2 == NULL)
{
return l1;
}
struct ListNode* newHead,*tail;
newHead = NULL;
while(l1&&l2)
{
if(l1->val<l2->val)
{
if(newHead == NULL)
{
newHead = tail = l1;
}
else{
tail->next = l1;
tail = l1;
}
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
if(newHead == NULL)
{
newHead = tail = l2;
}
else{
tail->next = l2;
tail = l2;
}
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
if(l1)
{
tail->next = l1;
}
if(l2)
{
tail->next = l2;
}
return newHead;
}
分割链表
1、题目:
2、思路:
?建立两个链表,一个是<x的链表,一个是>=x的链表,最后把这两个链表组合起来,返回头即可
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
//建立两个链表
//一个小于x
//一个大于等于x
struct ListNode* partition(struct ListNode* head, int x){
/* if(head == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}*/
struct ListNode* litterHead = ( struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* litterTail = litterHead;
struct ListNode* biggerHead = ( struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* biggerTail = biggerHead;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val<x)
{
litterTail->next =cur;
litterTail = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
else
{
biggerTail->next = cur;
biggerTail = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
biggerTail->next = NULL;
litterTail->next = biggerHead->next;
return litterHead->next;
}
完结!!!
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_76821799/article/details/135781095
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章