图像检索(image retrieval)
发布时间:2024年01月16日
一、引言
1.1 问题背景
- 互联网用户数量的增加,加上存储容量的增加、更好的互联网连接和更高的带宽,导致了网络上多媒体内容的指数级增长,特别是图片内容已经变得无处不在,在吸引社交媒体用户和各种电子商务网站的客户方面发挥着重要作用
- 搜索图像(而不是文档)的方式:
- 提供图像的文本描述——text based image retrieval
- 提供一个与期望图像相似的图像——content based image retrieval : 这里的content 就为 visual description/query,既可以是目标的图像也可以是草图 (sketch)
1.2 基于草图的图像搜索(Sketchbased image retrieval ,SBIR)
-
**问题定义:**提供一个目标的草图而能够搜索到类似的图像
-
主要挑战:
- 挑战1——domain gap: 图像和草图之间的 domain gap,其中草图只包含对象的轮廓,因此与图像相比信息较少
- 挑战2——large intra-class variance present: 由于人类倾向于绘制具有不同抽象水平的草图,因此草图中存在很大的类内差异
-
关键问题: 为了泛化性,SBIR模型必须学会草图的组件与相应图像之间的对齐——学会将草图与图像中的潜在对齐联系起来——学会找的过程
图像搜索欺骗
- 现有评估方法的问题: 只关注基于类的检索,而不是基于形状或属性的检索,即在评估过程中,如果模型只是获取了与草图属于同一类的图像,则会给予信任,意味着图像中的物体不必与草图中的物体有相同的轮廓——准确率不高,无法应对未知类
- 现有解决想法: 采用 细粒度评估(fine-grained evaluation) 来组织这种特定于类的学习,例如 对于给定的草图,通过将数据库中图像的估计排名与人工注释的排名列表进行比较来评估检索结果—— 需要 extensive human labor 以及受到 human biases 的影响 —— 作者想法: 在零学习设置中采用粗粒度评估(coarse-grained evaluation) 来解决上述问题
1.3 Zero-Shot Sketch Based Image Retrieval (ZS-SBIR)
主要想法: ZS-SBIR可以被认为是生成草图中缺失的附加信息以检索相似图像的任务
具体想法: Deep Conditional Generative Models based on Adversarial Autoencoders and Variational Autoencoders for the ZS-SBIR task
2 Related Work
- SBIR的传统做法(Conventional pipeline in SBIR): 将图像和草图投影到公共特征空间中
3 Zero shot setting for SBIR
3.1 定义
-
S
S
S为草图的三元组:
S
=
{
(
x
i
s
k
e
t
c
h
,
x
i
i
m
g
,
y
i
)
∣
y
i
∈
Y
}
S = \{ (x^{sketch}_i,x^{img}_i,y_i)|y_i \in \mathcal{Y} \}
S={(xisketch?,xiimg?,yi?)∣yi?∈Y},将数据划分成训练集和测试集
- S t r = { ( x i s k e t c h , x i i m g ) ∣ y i ∈ Y t r a i n } S_{tr}=\{(x^{sketch}_i,x^{img}_i)|y_i \in Y_{train}\} Str?={(xisketch?,xiimg?)∣yi?∈Ytrain?}
- S t e = { ( x i s k e t c h , x i i m g ) ∣ y i ∈ Y t e s t } S_{te}=\{(x^{sketch}_i,x^{img}_i)|y_i \in Y_{test}\} Ste?={(xisketch?,xiimg?)∣yi?∈Ytest?}
-
D
D
D为所有图像的数据库,
g
I
g_I
gI?是从图像到类标签的映射,将数据库分为训练集和测试集
- D t r = { x i i m g ∈ D ∣ g I ( x i i m g ) ∈ Y t r a i n } D_{tr}=\{x^{img}_i \in D | g_I(x^{img}_i) \in Y_{train} \} Dtr?={xiimg?∈D∣gI?(xiimg?)∈Ytrain?}
- D t e = { x i i m g ∈ D ∣ g I ( x i i m g ) ∈ Y t e s t } D_{te}=\{x^{img}_i \in D | g_I(x^{img}_i) \in Y_{test} \} Dte?={xiimg?∈D∣gI?(xiimg?)∈Ytest?}
说明:
- 模型只在 S t r S_{tr} Str?上训练
- D t r D_{tr} Dtr?作为验证集来调整超参数
- 模型目标是:给定来自
S
t
e
S_{te}
Ste?上的一个草图
x
s
k
e
t
c
h
x^{sketch}
xsketch,能够从
D
t
e
D_{te}
Dte?上搜索到同一类的图像
模型必须学习草图和图像之间的显著共同特征
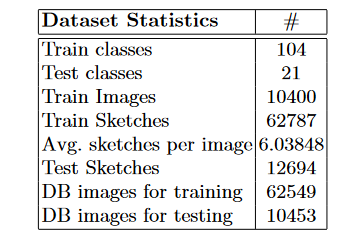
3.1 Benchmark
- 数据集: augmented Sketchy,包含73002个images,125个类
- 数据集划分: 104个训练类,21个测试类,特别地,21个测试类不包含在
I
m
a
g
e
n
e
t
Imagenet
Imagenet数据集的1000个类中——确保研究人员仍然可以在不违反零射击假设的情况下,在1000个Imagenet类上预训练他们的模型
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45022770/article/details/130630151
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Swig实现C++的VTK对象到Python的传递
- HTML--JavaScript--语法基础
- Linux修改文件名的常用方法
- C语言用函数指针实现计算器
- python编程从入门到实践(2)操作列表
- kubectl常用命令(主题篇)
- 驾驭Java控制流程:掌握程序执行的脉络
- Python文件命名规则:批量重命名与规则匹配的文件
- 浏览器渲染网页的过程
- Chapter 7 - 5. Congestion Management in Ethernet Storage Networks以太网存储网络的拥塞管理